Abstract
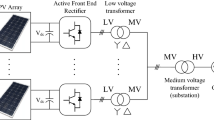
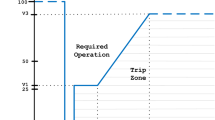
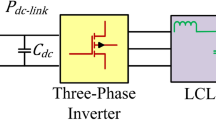
This paper proposes a flexible power control of a three-phase grid-connected PV system which fulfills the PV converter operations under normal conditions and symmetrical grid voltage sags. This control approach can be configured in the PV converters and flexibly change from one to another mode during operation. In normal operation mode, a Maximal Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm and PQ-control loop have been designed around the converters. Their aim is to maximize the PV power and to inject into the grid a current with low harmonic distortion, as well as energy at unity power factor. Under grid voltage dips, the PQ-control strategy has been changed within the grid voltage sag levels and the inverter rating currents. The MPPT control is deactivated, and the PV power has been reduced to the target value delivered by the inverter at the Point of Common Coupling. Case studies with simulations and experimental results have verified the effectiveness and flexibilities of the proposed power control strategy to release the advanced features.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milanovic JV, Djokic SZ (2003) Equipment sensitivity to disturbances in voltage supply. In: JIEEC, Bilbao
Teodorescu R, Liserre M, Rodriguez P (2011) Grid converters for photovoltaic and wind power systems. Wiley, London
Yang Y, Wang H, Blaabjerg F (2014) Reactive power injection strategies for single phase photovoltaic systems considering grid requirements. In: 29 Annual IEEE-APECE, pp 371–378
Yang Y, Blaabjerg F, Zou Z (2013) Benchmarking of grid fault modes in single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 49(5):2167–2176
Cadaval ER, Spagnuolo G, Franquelo LG, Paja CAR, Suntio T, Xiao WM (2013) Grid-connected photovoltaic generation plants: components and operation. IEEE Ind Electron Mag 7(3):6–20
Yang Y, Enjeti P, Blaabjerg F, Wang H (2013) Suggested grid code modifications to ensure wide-scale adoption of photovoltaic energy in distributed power generation systems. In: IEEE-IAS annual meeting, pp 1–8
Carnieletto R, Brandao DI, Farret FA, Simoes MG (2011) Smart grid initiative: a multifunctional single-phase voltage source inverter. IEEE Ind Appl Mag 17(5):27–35
Yeh HG, Gayme DF, Low SH (2012) Adaptive VAR control for distribution circuits with photovoltaic generators. IEEE Trans Power Syst 27(3):1656–1663
SMA Profitable Night Shift, Technical Information (2013). www.sma.de
Iov F, Hansen AD, Sorensen PE, Cutululis NA (2007) Mapping of grid faults and grid codes. Riso National Laboratory, Technical University of Denmark, Roskilde
Comitato Elettrotecnico Italiano (2011) Reference technical rules for connecting users to the active and passive LV distribution companies of electricity. In: CEI 0–21
Rodriguez P, Luna A, Munoz-Aguilar R, Corcoles F, Teodorescu R, Blaabjerg F (2011) Control of power converters in distributed generation applications under grid fault conditions. In: ECCE, pp 2649–2656
Azevedo MGS, Rodriguez P, Cavalcanti MC, Vázquez G, Neves FAS (2009) New control strategy to allow the photovoltaic systems operation under grid faults. In: COBEP, Brazilian, pp 196–201
Yang Y, Baabjerg F (2013) Low voltage ride through capability of a single phase photovoltaic system connected to the low voltage grid. Int J Photo Energy 2013:9
Kai D, Cheng KWE, Xue XD (2006) A novel detection method for voltage sags. In: ICPESA, pp 250–255
Lee DM, Habetler TG, Harley RG, Keister TL, Rostron JR (2007) A voltage sag supporter utilizing a PWM-switched auto transformer. IEEE Trans Power Electron 2(22):626–635
Bae B, Lee J, Jeong J, Han B (2010) Line-interactive single phase dynamic voltage restorer with novel sag detection algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 4(25):2702–2709
Fitzer C, Barnes M, Green P (2004) Voltage sag detection technique for a dynamic voltage restorer. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 1(40):203–212
Casaro M, Martins DC (2008) Grid-connected PV system: introduction to behavior matching. In: PESC-IEEE, pp 951–956
Kjaer SB, Pedersen JK, Blaabjerg F (2002) Power inverter topologies for photovoltaic modules-a review. In: 37th IAS annual meeting conference, vol 2, pp 782–788
Azevedo GMS, Cavalcanti MC, Neves FAS, Rodriguez P (2007) Implementation of a grid connected photovoltaic system controlled by digital signal processor. In: COBEP, Blumenau
Kerekes T, Teodorescu R, Klumpner C, Sumner M, Floricau D, Rodriguez P (2009) Evaluation of three phase transformerless photovoltaic inverter topologies. Power Electron 24(9):2202–2211
Hernandez OCM, Enjeti PN (2005) A fast detection algorithm suitable for mitigation of numerous power quality disturbances. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 6(41):1684–1690
Bae Y, Vu TK, Kim RY (2013) Implemental control strategy for grid stabilization of grid-connected PV system based on German grid code in symmetrical low-to-medium voltage network. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 3(28):619–631
Arnold G (2011) Challenges of integrating multi-GW solar power into the German distribution grids. http://www.iwes.fraunhofer.de/
Chou SF, Lee CT, Cheng PT, Blaabjerg F (2011) A reactive current injection technique for renewable energy converters in low voltage ride-through operations. In: IEEE-PES general meeting, pp 1–7
Lee CT, Hsu CW, Cheng PT (2011) A low-voltage ride through technique for grid-connected converters of distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 4(47):1821–1832
Mogos EF (2004) Production dans les réseaux de distribution, étude pluridisciplinaire de la modélisation pour le contrôle des sources. PHD Thesis, ENSAM, Lille
Hamrouni N (2009) Modélisation et commande des systèmes photovoltaïques connectés au réseau électrique basse tension. PHD Thesis, ENIT, Tunisie
Mahmoud AMA, Mashaly HM, Kandil SA, El Khaseb H, Nashed MNF (2000) Fuzzy logic implementation for photovoltaic maximum power tracking. In: IEEE international workshop on robot and human interactive communication, pp 155–60
Hamrouni N, Jraidi M, Chérif A (2008) New control strategy for 2-stage grid-connected photovoltaic system. Renew Energy 33:2212–2222
Kobayashi H (2012) Fault ride through requirements and measures of distributed PV systems in Japan. In: IEEE-PES general meeting, pp 1–6
Akagi H, Nabae A (1986) Control strategy of active power filters using multiple voltage source PWM converters. IEEE Trans Indus Electr 22(3):460–465
Pankow Y (2005) Etude de l’intégration de la production décentralisée dans un réseau basse tension, application au générateur photovoltaïque. PHD Thesis, ENSAM, France
Alali MAE (2002) Contribution à l’étude des compensateurs actifs des réseaux électriques basse tension. PHD Thesis, University Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France
Bojrup M (1999) Advanced control of active filters in a battery charger application. PHD Thesis, Lund Institute of Technology
Jamali S, Talavat V (2010) Dynamic fault location method for distribution networks with distributed generation. Electr Eng J 92:119–127
Yang Y, Blaabjerg F, Huai W, Marcelo GS (2016) Power control flexibilities for grid-connected multi-functional photovoltaic inverters. IET Renew Power Gener 99:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamrouni, N., Jraidi, M., Ghobber, A. et al. Control approach of a connected PV system under grid faults. Electr Eng 100, 1205–1217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0560-0