Abstract
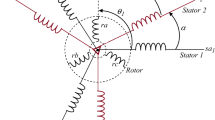
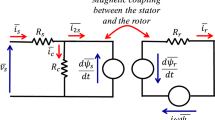
This paper presents an investigation of energy-efficiency improvement of an electrical drive system based on multi-winding machines. An improved power factor (PF) control scheme is proposed allowing energy-efficiency enhancement and optimization in high-power variable-speed drives based on multi-winding machines. Thus, the double-star induction machine is taken, as an example of multi-winding machines, to introduce the principle of the study presented in this paper. In fact, the purpose of this paper is to maintain the PF of the power winding, of the double-star induction machine, in vicinity of unity whatever the drive operating point, allowing discontinuous PWM (DPWM) techniques selection. Therefore, the switching losses can be reduced significantly using DPWM techniques at high PF values and this contributes strongly to energy-efficiency improvement. Moreover, in high-power applications, having low converter losses is essential to maintain thermal limits. In addition, this control scheme can be generalized for several kinds of multiphase machines.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levi E (2008) Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(5):1893–1909
Schofield N, Niu X, Beik O (2014) Multiphase machines for electric vehicle traction. In: IEEE conference and expo on transportation electrification (IEEE-ITEC)
Wang D, Wu X, Chen J, Guo Y (2014) A distributed magnetic circuit approach to analysis of multiphase induction machines with nonsinusoidal supply. IEEE Trans Ener Conv 99:1–11
Bu F, Hu Y, Huang W, Zhuang S, Shi K (2014) Control strategy and dynamic performance of dual stator-winding induction generator variable frequency AC generating system with inductive and capacitive loads. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(4):1681–1692
Feifei B, Wenxin H, Yuwen H, Kai S (2012) An integrated AC and DC hybrid generation system using dual-stator-winding induction generator with static excitation controller. IEEE Trans Ener Conv 27(3):810–812
Che HS, Duran MJ, Levi E, Jones M, Hew W-P, Rahim NA (2014) Postfault operation of an asymmetrical six-phase induction machine with single and two isolated neutral points. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(10):5406–5416
Karttunen J, Kallio S, Peltoniemi P, Silventoinen P, Pyrhonen O (2014) Decoupled vector control scheme for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(5):2185–2196
Tir Z, Soufi Y, Hashemnia MN, Malik Om P, Marouani K (2016) Fuzzy logic field oriented control of double star induction motor drive. Electr Eng. doi:10.1007/s00202-016-0377-2
Zarri L, Mengoni M, Gritli Y, Tani A, Filippetti F, Serra G, Casadei D (2013) Detection and localization of stator resistance dissymmetry based on multiple reference frame controllers in multiphase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(8):3506–3518
Mohammadpour, Mishra S, Parsa L (2014) Fault-tolerant operation of multiphase permanent-magnet machines using iterative learning control. IEEE J Emer Selec Top Power Electr 2(2):201–211
Hu Y, Kallio S, Zhu ZQ, Liu K (2014) Current control for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors accounting for current unbalance and harmonics. IEEE J Emer Selec Top Power Electr 2(2):272–284
Mengoni M, Zarri L, Tani A, Serra G (2011) Sensorless multiphase induction motor drive based on a speed observer operating with third-order field harmonics. IEEE Ener Conv Congr Expos (ECCE)
Jones M, Vukosavic SN, Dujic D, Levi E (2009) A synchronous current control scheme for multiphase induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ener Conv 24(4):860–868
Aguirre M, Madina P, Poza J, Aranburu A, Nieva T (2012) Analysis and comparison of PWM modulation methods in VSI-Fed PMSM drive systems. In: IEEE XX\({\rm th}\) international conference on electrical machines (IEEE-ICEM)
Jiao Y, Lee FC, Lu S (2014) Space vector modulation for three-level NPC converter with neutral point voltage balance and switching loss reduction. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(10):5406–5416
Ke M, Blaabjerg F (2014) Modulation methods for neutral-point-clamped wind power converter achieving loss and thermal redistribution under low-voltage ride-through. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(2):835–845
Prieto J, Barrero F, Duran MJ, Marin ST, Perales MA (2014) SVM procedure for -phase VSI with low harmonic distortion in the overmodulation region. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(1):92–97
Bierhoff M, Brandenburg H, Fuchs FW (2007) An analysis on switching loss optimized PWM strategies for three phase PWM voltage source converters. In: The 33rd annual conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Taipei
Rieto J, Jones M, Barrero F, Levi E, Toral S (2011) Comparative analysis of discontinuous and continuous PWM techniques in VSI-fed five-phase induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(12):5324–5335
Wu Y, Shafi MA, Knight AM, Mcmahon RA (2011) Comparison of the effects of continuous and discontinuous PWM schemes on power losses of voltage-sourced inverters for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26(1):182–191
Nguyen NV, Nguyen BX, Lee HH (2011) An optimized discontinuous PWM method to minimize switching loss for multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(9):3958–3966
Muljadi E, Lipo TA, Novotny DW (1989) Power factor enhancement of induction machines by means of solid-state excitation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 4(4):409–418
Morel L, Godfroid H, Mirzaian A, Kauffmann JM (1998) Double-fed induction machine: converter optimisation and field oriented control without position sensor. IEE Proc-Electr Power Appl 145(4):360–368
Tamrakar Malik OP (1999) Power factor correction of induction motors using PWM inverter fed auxiliary stator winding. IEEE Trans Ener Conv 14(3):426–432
Deng ZL, Pengsheng Y (2003) Power factor correction of a 400 kW winding rotor induction motor. In: The fifth international conference on power electronics and drive systems (IEEE-PEDS)
Marouani K, Nounou K, Benbouzid M, Tabbache B (2014) Power factor correction of an electrical drive system based on multiphase machines. In: IEEE international conference on green energy (IEEE-ICGE), Sfax, Tunisia
Kolar JW, Ertl H, Zach FC (1991) Influence of the modulation method on the conduction and switching losses of a PWM converter system. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 27(6):1063–1075
Ojo O (2004) The generalized discontinuous PWM scheme for three-phase voltage source inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(6):1280–1289
Marouani K, Baghli Lotfi, Hadiouche D, Kheloui A, Rezzoug A (2008) A new PWM strategy based on a 24-sector vector space decomposition for a six-phase VSI-fed dual stator induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(5):1910–1920
Hava M, Kerkman RJ, Lipo TA (1998) Carrier-based PWM-VSI overmodulation strategies: analysis, comparison, and design. IEEE Trans Power Elec 13(4):674–689
Kolar JW, Zach FC (1995) Losses in PWM converters using IGBTs. IEE Proc Electr Power Appl 142(4):285–288
Hava M, Kerkman RJ, Lipo TA (1999) Simple analytical and graphical methods for carrier-based PWM-VSI drives. IEEE Trans Power Elec 14(1):49–61
Narayanan G, Krishnamurthy HK, Zhao D, Ayyanar R (2006) Advanced bus-clamping PWM techniques based on space vector approach. IEEE Trans Power Electron 21(4):974–984
Vas P (1998) Sensorless vector and direct torque control. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marouani, K., Nounou, K., Benbouzid, M. et al. Investigation of energy-efficiency improvement in an electrical drive system based on multi-winding machines. Electr Eng 100, 205–216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0493-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0493-z