Abstract
Summary
In a prospective community-based cohort study, we investigated the relationship between trabecular bone score (TBS) and regional fat depots in 1474 Korean postmenopausal women. TBS was positively related with subcutaneous fat and negatively related with visceral fat.
Introduction
The effect of fat distribution (visceral/subcutaneous) on bone quality or microarchitecture has rarely been investigated due to measurement difficulty. We aimed to investigate the relationship between TBS reflecting bone microarchitecture and regional fat depots in Korean women.
Methods
Cross-sectional data evaluation was made from subjects participating in an ongoing prospective community-based cohort study since 2001. A total of 1474 postmenopausal women in the Ansung cohort were analyzed. Regional body fat mass, bone mineral density (BMD) at the lumbar spine, and total hip and lumbar spine TBS were measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Results
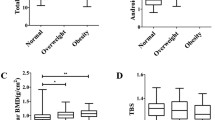
In an age-adjusted partial correlation analysis, TBS was not associated with total fat mass, but negatively associated with trunk fat mass. However, TBS was positively related with leg (r = 0.102, P < 0.05) and gynoid fat mass (r = 0.086, P < 0.05) and negatively related with android fat mass (r = −0.106; P < 0.05). In linear regression models controlling age, BMI, and physical activity, android fat was inversely associated with TBS (β = −0.595, P < 0.001), whereas gynoid fat was positively associated with TBS (β = 0.216, P < 0.001). Lumbar spine and total hip BMDs revealed positive associations with total and all regional fat depots regardless of fat distribution.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that relatively large visceral fat and small subcutaneous fat may have a detrimental effect on TBS, a bone microarchitecture index.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reid IR, Evans MC, Cooper GJ, Ames RW, Stapleton J (1993) Circulating insulin levels are related to bone density in normal postmenopausal women. Am J Physiol 265:E655–E659
Takeda S, Elefteriou F, Levasseur R, Liu X, Zhao L, Parker KL, Armstrong D, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2002) Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell 111:305–317
Gnudi S, Sitta E, Fiumi N (2007) Relationship between body composition and bone mineral density in women with and without osteoporosis: relative contribution of lean and fat mass. J Bone Miner Metab 25:326–332
Kim JH, Choi HJ, Kim MJ, Shin CS, Cho NH (2012) Fat mass is negatively associated with bone mineral content in Koreans. Osteoporos Int 23:2009–2016
Kim CJ, Oh KW, Rhee EJ et al (2009) Relationship between body composition and bone mineral density (BMD) in perimenopausal Korean women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71:18–26
Zhao LJ, Liu YJ, Liu PY, Hamilton J, Recker RR, Deng HW (2007) Relationship of obesity with osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1640–1646
Hsu YH, Venners SA, Terwedow HA et al (2006) Relation of body composition, fat mass, and serum lipids to osteoporotic fractures and bone mineral density in Chinese men and women. Am J Clin Nutr 83:146–154
Kotani K, Tokunaga K, Fujioka S, Kobatake T, Keno Y, Yoshida S, Shimomura I, Tarui S, Matsuzawa Y (1994) Sexual dimorphism of age-related changes in whole-body fat distribution in the obese. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 18:207–202
Gilsanz V, Chalfant J, Mo AO, Lee DC, Dorey FJ, Mittelman SD (2009) Reciprocal relations of subcutaneous and visceral fat to bone structure and strength. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3387–3393
Heiss CJ, Sanborn CF, Nichols DL, Bonnick SL, Alford BB (1995) Associations of body fat distribution, circulating sex hormones, and bone density in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:1591–1596
Choi HS, Kim KJ, Kim KM, Hur NW, Rhee Y, Han DS, Lee EJ, Lim SK (2010) Relationship between visceral adiposity and bone mineral density in Korean adults. Calcif Tissue Int 87:218–225
Zillikens MC, Uitterlinden AG, van Leeuwen JP, Berends AL, Henneman P, van Dijk KW, Oostra BA, van Duijn CM, Pols HA, Rivadeneira F (2010) The role of body mass index, insulin, and adiponectin in the relation between fat distribution and bone mineral density. Calcif Tissue Int 86:116–125
Kang SM, Yoon JW, Ahn HY, Kim SY, Lee KH, Shin H, Choi SH, Park KS, Jang HC, Lim S (2011) Android fat depot is more closely associated with metabolic syndrome than abdominal visceral fat in elderly people. PLoS One 6:e27694
Ng AC, Melton LJ 3rd, Atkinson EJ, Achenbach SJ, Holets MF, Peterson JM, Khosla S, Drake MT (2013) Relationship of adiposity to bone volumetric density and microstructure in men and women across the adult lifespan. Bone 55:119–125
Winzenrieth R, Michelet F, Hans D (2013) Three-dimensional (3D) microarchitecture correlations with 2D projection image gray-level variations assessed by trabecular bone score using high-resolution computed tomographic acquisitions: effects of resolution and noise. J Clin Densitom 16:287–296
Iki M, Tamaki J, Kadowaki E, Sato Y, Dongmei N, Winzenrieth R, Kagamimori S, Kagawa Y, Yoneshima H (2014) Trabecular bone score (TBS) predicts vertebral fractures in Japanese women over 10 years independently of bone density and prevalent vertebral deformity: the Japanese Population-Based Osteoporosis (JPOS) cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 29:399–407
Boutroy S, Hans D, Sornay-Rendu E, Vilayphiou N, Winzenrieth R, Chapurlat R (2013) Trabecular bone score improves fracture risk prediction in non-osteoporotic women: the OFELY study. Osteoporos Int 24:77–85
Silva BC, Boutroy S, Zhang C et al (2013) Trabecular bone score (TBS)-a novel method to evaluate bone microarchitectural texture in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1963–1970
Cho NH, Jang HC, Choi SH, Kim HR, Lee HK, Chan JC, Lim S (2007) Abnormal liver function test predicts type 2 diabetes: a community-based prospective study. Diabetes Care 30:2566–2568
Lewiecki EM, Gordon CM, Baim S et al (2008) International Society for Clinical Densitometry 2007 Adult and Pediatric Official Positions. Bone 43:1115–1121
Seeman E (2001) Clinical review 137: sexual dimorphism in skeletal size, density, and strength. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4576–4584
Ammann P, Rizzoli R (2003) Bone strength and its determinants. Osteoporos Int 14(Suppl 3):S13–S18
Reid IR (2010) Fat and bone. Arch Biochem Biophys 503:20–27
Silva BC, Leslie WD, Resch H, Lamy O, Lesnyak O, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Bilezikian JP (2014) Trabecular bone score: a noninvasive analytical method based upon the DXA image. J Bone Miner Res 29:518–530
Fu X, Ma X, Lu H, He W, Wang Z, Zhu S (2011) Associations of fat mass and fat distribution with bone mineral density in pre- and postmenopausal Chinese women. Osteoporos Int 22:113–119
Tchernof A, Desmeules A, Richard C, Laberge P, Daris M, Mailloux J, Rheaume C, Dupont P (2004) Ovarian hormone status and abdominal visceral adipose tissue metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3425–3430
MacKenzie SM, Huda SS, Sattar N, Fraser R, Connell JM, Davies E (2008) Depot-specific steroidogenic gene transcription in human adipose tissue. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 69:848–854
Rosen CJ, Bouxsein ML (2006) Mechanisms of disease: is osteoporosis the obesity of bone? Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2:35–43
Elefteriou F, Takeda S, Ebihara K et al (2004) Serum leptin level is a regulator of bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:3258–3263
Yamauchi M, Sugimoto T, Yamaguchi T, Nakaoka D, Kanzawa M, Yano S, Ozuru R, Sugishita T, Chihara K (2001) Plasma leptin concentrations are associated with bone mineral density and the presence of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 55:341–347
Klein KO, Larmore KA, de Lancey E, Brown JM, Considine RV, Hassink SG (1998) Effect of obesity on estradiol level, and its relationship to leptin, bone maturation, and bone mineral density in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:3469–3475
Simpson ER (2003) Sources of estrogen and their importance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86:225–230
Cartier A, Lemieux I, Almeras N, Tremblay A, Bergeron J, Despres JP (2008) Visceral obesity and plasma glucose-insulin homeostasis: contributions of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1931–1938
Pou KM, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U et al (2007) Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes are cross-sectionally related to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 116:1234–1241
Wood IS, Wang B, Jenkins JR, Trayhurn P (2005) The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-18 is expressed in human adipose tissue and strongly upregulated by TNFalpha in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:422–429
Morley JE, Baumgartner RN (2004) Cytokine-related aging process. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 59:M924–M929
Lesser IA, Gasevic D, Lear SA (2013) The effect of body fat distribution on ethnic differences in cardiometabolic risk factors of Chinese and Europeans. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 38:701–706
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Genome Research Institute, the Korean Center for Disease Control and Prevention (contract #2001∼2003-348-6111-221, 2004-347-6111-213 and 2005-347-2400-2440-215) and a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI12C1338). The funding source had no role in the collection of the data or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Choi, H.J., Ku, E.J. et al. Regional body fat depots differently affect bone microarchitecture in postmenopausal Korean women. Osteoporos Int 27, 1161–1168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3329-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3329-1