Abstract
Summary
The study estimated the cost-effectiveness of risedronate compared to no treatment in UK women using the FRAX algorithm for fracture risk assessment. A Markov cohort model was used to estimate the cost-effectiveness. Risedronate was found cost-effective from the age of 65 years, assuming a willingness to pay for a QALY of £30,000.
Introduction
The aim of this study was to assess the cost-effectiveness of risedronate for the prevention and treatment in a UK setting using the FRAX® algorithm for fracture risk assessment. A further aim was to establish intervention thresholds with risedronate treatment.
Methods
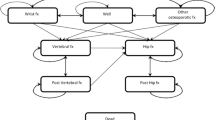
The cost-effectiveness of risedronate was compared to no treatment in post-menopausal women with clinical risk factors for fracture using a Markov cohort model populated with data relevant for the UK. The model incorporated the features of FRAX® (the WHO risk assessment tool). The analysis had a health care perspective and quality adjusted life years was used as the main outcome measure.
Results
Treatment was cost-effective from the age of 65 years, assuming a willingness to pay for a QALY of £30,000. Treatment was also cost-effective at all ages in women who had previously sustained a fragility fracture or in women with a parental history of hip fracture with a bone mineral density set at the threshold of osteoporosis. At the £30,000 threshold value for a QALY, risedronate was on average found to cost-effective below the 10-year probability of a major osteoporotic fractures of 13.0%.
Conclusions
Risedronate is a cost-effective agent for the treatment of established osteoporosis (osteoporosis and a prior fragility fracture) in women from the age of 50 years and older and above 65 years in women with osteoporosis alone. The results support the treatment recommendations in recent UK guidelines for osteoporosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Strom O, Borgstrom F, Oden A (2008) Case finding for the management of osteoporosis with FRAX((R))-assessment and intervention thresholds for the UK. Osteoporos Int 19:1395–1408
Fujiwara S, Nakamura T, Orimo H, Hosoi T, Gorai I, Oden A, Johansson H, Kanis JA (2008) Development and application of a Japanese model of the WHO fracture risk assessment tool (FRAX). Osteoporos Int 19:429–435
Tosteson AN, Melton LJ 3rd, Dawson-Hughes B, Baim S, Favus MJ, Khosla S, Lindsay RL (2008) Cost-effective osteoporosis treatment thresholds: the United States perspective. Osteoporos Int 19:437–447
Dawson-Hughes B, Tosteson AN, Melton LJ 3rd, Baim S, Favus MJ, Khosla S, Lindsay RL (2008) Implications of absolute fracture risk assessment for osteoporosis practice guidelines in the USA. Osteoporos Int 19:449–458
Siminoski K, Leslie WD, Frame H, Hodsman A, Josse RG, Khan A, Lentle BC, Levesque J, Lyons DJ, Tarulli G, Brown JP (2007) Recommendations for bone mineral density reporting in Canada: a shift to absolute fracture risk assessment. J Clin Densitom 10:120–123
Kurth AA, Pfeilschifter J (2007) Diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and osteoporosis in men. German Guidelines Update 2006. Orthopade 36:683–690 quiz 691
National Osteoporosis Guideline Group on behalf of the Bone Research Society, British Geriatrics Society, British Society of Rheumatology, Society of Endocrinology, British Orthopaedic Association, Primary Care Rheumatology Society, Osteoporosis 2000 and Osteoporosis Dorset (2008) Osteoporosis: clinical guideline for prevention and treatment
Kanis JA, Burlet N, Cooper C, Delmas PD, Reginster JY, Borgstrom F, Rizzoli R (2008) European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 19:399–428
Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A, Johansson H, McCloskey E (2008) FRAX and the assessment of fracture probability in men and women from the UK. Osteoporos Int 19:385–397
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) (2005) Bisphosphonates (alendronate, etidronate, risedronate), selective oestrogen receptor modulators (raloxifene) and parathyroid hormone (teriparatide) for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. London. www.nice.org.uk
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) (2007) Final appraisal determination. Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene, strontium ranelate and teriparatide for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. London. www.nice.org.uk
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) (2007). Final appraisal determination. Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and strontium ranelate for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. London. www.nice.org.uk
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) (2008). Final appraisal determination. Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene, strontium ranelate and teriparatide for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. London. www.nice.org.uk
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) (2008) Final appraisal determination. Alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and strontium ranelate for the primary prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures in postmenopausal women. London. www.nice.org.uk
Kanis JA, Oden A, Johnell O, Johansson H, De Laet C, Brown J, Burckhardt P, Cooper C, Christiansen C, Cummings S, Eisman JA, Fujiwara S, Gluer C, Goltzman D, Hans D, Krieg MA, La Croix A, McCloskey E, Mellstrom D, Melton LJ 3rd, Pols H, Reeve J, Sanders K, Schott AM, Silman A, Torgerson D, van Staa T, Watts NB, Yoshimura N (2007) The use of clinical risk factors enhances the performance of BMD in the prediction of hip and osteoporotic fractures in men and women. Osteoporos Int 18:1033–1046
Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. http://www.nice.org.uk/page.aspx?o=201974. 2008-05-03
Borgstrom F, Carlsson A, Sintonen H, Boonen S, Haentjens P, Burge R, Johnell O, Jonsson B, Kanis JA (2006) The cost-effectiveness of risedronate in the treatment of osteoporosis: an international perspective. Osteoporos Int 17:996–1007
Borgstrom F, Jonsson B, Strom O, Kanis JA (2006) An economic evaluation of strontium ranelate in the treatment of osteoporosis in a Swedish setting: based on the results of the SOTI and TROPOS trials. Osteoporos Int 17:1781–1793
Kanis JA, Borgstrom F, Johnell O, Jonsson B (2004) Cost-effectiveness of risedronate for the treatment of osteoporosis and prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 15:862–871
Kanis JA, Borgstrom F, Johnell O, Oden A, Sykes D, Jonsson B (2005) Cost-effectiveness of raloxifene in the UK: an economic evaluation based on the MORE study. Osteoporos Int 16:15–25
Jonsson B, Christiansen C, Johnell O, Hedbrandt J (1995) Cost-effectiveness of fracture prevention in established osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 5:136–142
Jonsson B, Kanis J, Dawson A, Oden A, Johnell O (1999) Effect and offset of effect of treatments for hip fracture on health outcomes. Osteoporos Int 10:193–199
Johnell O, Jonsson B, Jonsson L, Black D (2003) Cost effectiveness of alendronate (fosamax) for the treatment of osteoporosis and prevention of fractures. Pharmacoeconomics 21:305–314
Zethraeus N, Johannesson M, Jonsson B (1999) A computer model to analyze the cost-effectiveness of hormone replacement therapy. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 15:352–365
Kanis JA, Adams J, Borgstrom F, Cooper C, Jonsson B, Preedy D, Selby P, Compston J (2008) The cost-effectiveness of alendronate in the management of osteoporosis. Bone 42:4–15
Zethraeus N, Borgstrom F, Strom O, Kanis JA, Jonsson B (2007) Cost-effectiveness of the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis–a review of the literature and a reference model. Osteoporos Int 18:9–23
Borgstrom F, Johnell O, Kanis JA, Jonsson B, Rehnberg C (2006) At what hip fracture risk is it cost-effective to treat? International intervention thresholds for the treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 17:1459–1471
Kanis JA, Borgstrom F, Zethraeus N, Johnell O, Oden A, Jonsson B (2005) Intervention thresholds for osteoporosis in the UK. Bone 36:22–32
Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A, Borgstrom F, Johansson H, De Laet C, Jonsson B (2005) Intervention thresholds for osteoporosis in men and women: a study based on data from Sweden. Osteoporos Int 16:6–14
Kanis JA, Oden A, Johnell O, Jonsson B, de Laet C, Dawson A (2001) The burden of osteoporotic fractures: a method for setting intervention thresholds. Osteoporos Int 12:417–427
Seeley DG, Browner WS, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Scott JC, Cummings SR (1991) Which fractures are associated with low appendicular bone mass in elderly women? The study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Ann Intern Med 115:837–842
Singer BR, McLauchlan GJ, Robinson CM, Christie J (1998) Epidemiology of fractures in 15, 000 adults: the influence of age and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:243–248
de Lusignan S, Valentin T, Chan T, Hague N, Wood O, van Vlymen J, Dhoul N (2004) Problems with primary care data quality: osteoporosis as an exemplar. Inform Prim Care 12:147–156
Stevenson M, Jones ML, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J (2005) A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Health Technol Assess 9:1–160
Kanis JA, Brazier JE, Stevenson M, Calvert NW, Lloyd Jones M (2002) Treatment of established osteoporosis: a systematic review and cost-utility analysis. Health Technol Assess 6:1–146
National Statistics Online. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/StatBase/Product.asp?vlnk=14459&Pos=&ColRank=1&Rank=422
Oden A, Dawson A, Dere W, Johnell O, Jonsson B, Kanis JA (1998) Lifetime risk of hip fractures is underestimated. Osteoporos Int 8:599–603
Johnell O, Kanis JA, Oden A, Sernbo I, Redlund-Johnell I, Petterson C, De Laet C, Jonsson B (2004) Mortality after osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 15:38–42
Reginster J, Minne HW, Sorensen OH, Hooper M, Roux C, Brandi ML, Lund B, Ethgen D, Pack S, Roumagnac I, Eastell R (2000) Randomized trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established postmenopausal osteoporosis. Vertebral Efficacy with Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. Osteoporos Int 11:83–91
Harris ST, Watts NB, Genant HK, McKeever CD, Hangartner T, Keller M, Chesnut CH 3rd, Brown J, Eriksen EF, Hoseyni MS, Axelrod DW, Miller PD (1999) Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Vertebral Efficacy With Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. Jama 282:1344–1352
McClung MR, Geusens P, Miller PD, Zippel H, Bensen WG, Roux C, Adami S, Fogelman I, Diamond T, Eastell R, Meunier PJ, Reginster JY (2001) Effect of risedronate on the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. Hip Intervention Program Study Group. N Engl J Med 344:333–340
Siris ES, Simon JA, Barton IP, McClung MR, Grauer A (2008) Effects of risedronate on fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. Osteoporos Int 19:681–686
Watts NB, Chines A, Olszynski WP, McKeever CD, McClung MR, Zhou X, Grauer A (2008) Fracture risk remains reduced one year after discontinuation of risedronate. Osteoporos Int 19:365–372
Bagger YZ, Tanko LB, Alexandersen P, Ravn P, Christiansen C (2003) Alendronate has a residual effect on bone mass in postmenopausal Danish women up to 7 years after treatment withdrawal. Bone 33:301–307
Black DM, Schwartz AV, Ensrud KE, Cauley JA, Levis S, Quandt SA, Satterfield S, Wallace RB, Bauer DC, Palermo L, Wehren LE, Lombardi A, Santora AC, Cummings SR (2006) Effects of continuing or stopping alendronate after 5 years of treatment: the Fracture Intervention Trial Long-term Extension (FLEX): a randomized trial. Jama 296:2927–2938
Lloyd-Jones M, Wilkinson A (2006) Adverse effects and persistence with therapy in patients taking oral alendronate, etidronate or risedronate: a systematic review. NHS R & D HTA ScHARR, Sheffield
Huybrechts KF, Ishak KJ, Caro JJ (2006) Assessment of compliance with osteoporosis treatment and its consequences in a managed care population. Bone 38:922–928
Seeman E, Compston J, Adachi J, Brandi ML, Cooper C, Dawson-Hughes B, Jonsson B, Pols H, Cramer JA (2007) Non-compliance: the Achilles' heel of anti-fracture efficacy. Osteoporos Int 18:711–719
Stevenson M, Davis S, Kanis J (2006) The hospitalization costs and outpatient costs of fragility fractures. Women's Health Medicine 4:149–151
Borgstrom F, Zethraeus N, Johnell O, Lidgren L, Ponzer S, Svensson O, Abdon P, Ornstein E, Lunsjo K, Thorngren KG, Sernbo I, Rehnberg C, Jonsson B (2006) Costs and quality of life associated with osteoporosis-related fractures in Sweden. Osteoporos Int 17:637–650
Strom O, Borgstrom F, Zethraeus N, Johnell O, Lidgren L, Ponzer S, Svensson O, Abdon P, Ornstein E, Ceder L, Thorngren KG, Sernbo I, Jonsson B (2008) Long-term cost and effect on quality of life of osteoporosis-related fractures in Sweden. Acta Orthop 79:269–280
Zethraeus N, Borgström F, Ström O, Kanis J, Jönsson B (2006) What is the risk of institutionalization after hip fracture? Osteoporos Int 17(Suppl 2):60
McLellan A, Reid D, Forbes K, Reid R, Campbell C, Gregori A (1999) Effectiveness of strategies for the secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in Scotland. www.nhshealthquality.org/nhsqis/controller?p_service=Content.show&p_applic=CCC&pContentID=2755. 6th May 2007
Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A, Borgstrom F, Zethraeus N, De Laet C, Jonsson B (2004) The risk and burden of vertebral fractures in Sweden. Osteoporos Int 15:20–26
Oleksik A, Lips P, Dawson A, Minshall ME, Shen W, Cooper C, Kanis J (2000) Health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women with low BMD with or without prevalent vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res 15:1384–1392
Kind P, Dolan P, Gudex C, Williams A (1998) Variations in population health status: results from a United Kingdom national questionnaire survey. BMJ 316:736–741
World Health Organization Assessment of osteoporosis at the primary health care level (2008). www.who.int/chp/topics/rheumatic/en/index.html
Kanis J, behalf of the World Health Organization Scientific Group (2008) Assessment of osteoporosis at the primary health-care level. Technical Report. WHO Collaborating Centre, University of Sheffield, UK
Strom O, Borgstrom F, Sen SS, Boonen S, Haentjens P, Johnell O, Kanis JA (2007) Cost-effectiveness of alendronate in the treatment of postmenopausal women in 9 European countries–an economic evaluation based on the fracture intervention trial. Osteoporos Int 18:1047–1061
Royal College of Physicians (1999) Osteoporosis: clinical guidelines for the prevention and treatment. Royal College of Physicians, London
Royal College of Physicians and Bone and Tooth Society of Great Britain (2000) Update on pharmacological interventions and an algorithm for management. Royal College of Physicians and Bone and Tooth Society of Great Britain, London
Royal College of Physicians, Bone and Tooth Society of Great Britain and National Osteoporosis Society Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis (2002) Guidelines on prevention and treatment. Royal College of Physicians, Bone and Tooth Society of Great Britain and National Osteoporosis Society Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, London
European Community (1998) Report on osteoporosis in the European Community. EC, Strasbourg
Kanis JA, Delmas P, Burckhardt P, Cooper C, Torgerson D (1997) Guidelines for diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. The European Foundation for Osteoporosis and Bone Disease. Osteoporos Int 7:390–406
Iglesias CP, Torgerson DJ, Bearne A, Bose U (2002) The cost utility of bisphosphonate treatment in established osteoporosis. QJM 95:305–311
Brown JP, Josse RG (2002) 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada. CMAJ 167:S1–S34
Kanis JA, Black D, Cooper C, Dargent P, Dawson-Hughes B, De Laet C, Delmas P, Eisman J, Johnell O, Jonsson B, Melton L, Oden A, Papapoulos S, Pols H, Rizzoli R, Silman A, Tenenhouse A (2002) A new approach to the development of assessment guidelines for osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 13:527–536
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to Alliance for Better Bone Health for their financial support of this study.
Conflicts of interest
JAK, FB, OS, EMcC, HJ and AO act as advisors to and have received funding from many pharmaceutical companies involved in marketing products for treatment of osteoporosis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borgström, F., Ström, O., Coelho, J. et al. The cost-effectiveness of risedronate in the UK for the management of osteoporosis using the FRAX®. Osteoporos Int 21, 495–505 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-009-0989-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-009-0989-8