Abstract
Summary
Changes in organic matrix may contribute to the anti-fracture efficacy of anti-remodeling agents. Following one year of treatment in beagle dogs, bisphosphonates alter the organic matrix of vertebral trabecular bone, while raloxifene had no effect. These results show that pharmacological suppression of turnover alters the organic matrix component of bone.
Introduction
The collagen matrix contributes significantly to a bone’s fracture resistance yet the effects of anti-remodeling agents on collagen properties are unclear. The goal of this study was to assess changes in collagen cross-linking and isomerization following anti-remodeling treatment.
Methods
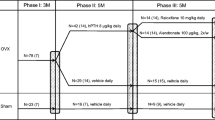
Skeletally mature female beagles were treated for one year with oral doses of vehicle (VEH), risedronate (RIS; 3 doses), alendronate (ALN; 3 doses), or raloxifene (RAL; 2 doses). The middle dose of RIS and ALN and the lower dose of RAL approximate doses used for treatment of post menopausal osteoporosis. Vertebral trabecular bone matrix was assessed for collagen isomerization (ratio of α/β C-telopeptide [CTX]), enzymatic (pyridinoline [PYD] and deoxypyridinoline [DPD]), and non-enzymatic (pentosidine [PEN]) cross-links.
Results
All doses of both RIS and ALN increased PEN (+34–58%) and the ratio of PYD/DPD (+14–26%), and decreased the ratio of α/β CTX (−29–56%) compared to VEH. RAL did not alter any collagen parameters. Bone turnover rate was significantly correlated to PEN (R = −0.664), α/β CTX (R = 0.586), and PYD/DPD (R = −0.470).
Conclusions
Bisphosphonate treatment significantly alters properties of bone collagen suggesting a contribution of the organic matrix to the anti-fracture efficacy of this drug class.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Nevitt MC, Bauer DC, Genant HK, Haskell WL, Marcus R, Ott SM, Torner JC, Quandt SA, Reiss TF, Ensrud KE (1996) Randomized trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 348:1535–1541
Harris ST, Watts NB, Genant HK, McKeever CD, Hangartner T, Keller M, Chesnut CH 3rd, Brown J, Eriksen EF, Hoseyni MS, Axelrod DW, Miller PD (1999) Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Vertebral Efficacy With Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. JAMA 282:1344–1352
Reginster J, Minne HW, Sorensen OH, Hooper M, Roux C, Brandi ML, Lund B, Ethgen D, Pack S, Roumagnac I, Eastell R (2000) Randomized trial of the effects of risedronate on vertebral fractures in women with established postmenopausal osteoporosis. Vertebral Efficacy with Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. Osteoporos Int 11:83–91
Ettinger B, Black DM, Mitlak BH, Knickerbocker RK, Nickelsen T, Genant HK, Christiansen C, Delmas PD, Zanchetta JR, Stakkestad J, Gluer CC, Krueger K, Cohen FJ, Eckert S, Ensrud KE, Avioli LV, Lips P, Cummings SR (1999) Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene: results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial. Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation (MORE) Investigators. Jama 282:637–645
Sambrook PN, Geusens P, Ribot C, Solimano JA, Ferrer-Barriendos J, Gaines K, Verbruggen N, Melton ME (2004) Alendronate produces greater effects than raloxifene on bone density and bone turnover in postmenopausal women with low bone density: results of EFFECT (Efficacy of FOSAMAX versus EVISTA Comparison Trial) International. J Intern Med 255:503–511
Siris ES, Harris ST, Eastell R, Zanchetta JR, Goemaere S, Diez-Perez A, Stock JL, Song J, Qu Y, Kulkarni PM, Siddhanti SR, Wong M, Cummings SR (2005) Skeletal effects of raloxifene after 8 years: results from the continuing outcomes relevant to Evista (CORE) study. J Bone Miner Res 20:1514–1524
Delmas PD (2000) How does antiresorptive therapy decrease the risk of fracture in women with osteoporosis? Bone 27:1–3
Delmas PD, Seeman E (2004) Changes in bone mineral density explain little of the reduction in vertebral or nonvertebral fracture risk with anti-resorptive therapy. Bone 34:599–604
Burr DB, Turner CH (2003) Biomechanics of bone. In: Favus M (ed) Primer on the metabolic bone diseases and disorders of mineral metabolism. American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, Washington DC, pp 58–64
Boivin GY, Chavassieux PM, Santora AC, Yates J, Meunier PJ (2000) Alendronate increases bone strength by increasing the mean degree of mineralization of bone tissue in osteoporotic women. Bone 27:687–694
Monier-Faugere MC, Geng Z, Paschalis EP, Qi Q, Arnala I, Bauss F, Boskey AL, Malluche HH (1999) Intermittent and continuous administration of the bisphosphonate ibandronate in ovariohysterectomized beagle dogs: effects on bone morphometry and mineral properties. J Bone Miner Res 14:1768–1778
Viguet-Carrin S, Garnero P, Delmas PD (2006) The role of collagen in bone strength. Osteoporos Int 17:319–336
Cloos PA, Fledelius C (2000) Collagen fragments in urine derived from bone resorption are highly racemized and isomerized: a biological clock of protein aging with clinical potential. Biochem J 345(Pt 3):473–480
Garnero P, Fledelius C, Gineyts E, Serre CM, Vignot E, Delmas PD (1997) Decreased beta-isomerization of the C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen alpha 1 chain in Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 12:1407–1415
Burr D (2002) The contribution of the organic matrix to bone’s material properties. Bone 31:8–11
Allen MR, Iwata K, Phipps R, Burr DB (2006) Alterations in canine vertebral bone turnover, microdamage accumulation, and biomechanical properties following 1-year treatment with clinical treatment doses of risedronate or alendronate. Bone 39:872–879
Allen MR, Iwata K, Sato M, Burr DB (2006) Raloxifene enhances vertebral mechanical properties independent of bone density. Bone 39:1130–1135
Komatsubara S, Mori S, Mashiba T, Ito M, Li J, Kaji Y, Akiyama T, Miyamoto K, Cao Y, Kawanishi J, Norimatsu H (2003) Long-term treatment of incadronate disodium accumulates microdamage but improves the trabecular bone microarchitecture in dog vertebra. J Bone Miner Res 18:512–520
Mashiba T, Hirano T, Turner CH, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB (2000) Suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates increases microdamage accumulation and reduces some biomechanical properties in dog rib. J Bone Miner Res 15:613–620
Mashiba T, Turner CH, Hirano T, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB (2001) Effects of suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates on microdamage accumulation and biomechanical properties in clinically relevant skeletal sites in beagles. Bone 28:524–531
Allen MR, Burr DB (2007) Mineralization, microdamage, and matrix: how bisphosphonates influence material properties of bone. BoneKEy 4:49–60; http://www.bonekey-ibms.org/cgi/content/abstract/ibmske;44/42/49
Parfitt A, Drezner M, Glorieux F, Kanis J, Malluche H, Meunier P, Ott S, Recker R (1987) Bone histomorphometry: Standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. J Bone Miner Res 2:595–610
Viguet-Carrin S, Roux JP, Arlot ME, Merabet Z, Leeming DJ, Byrjalsen I, Delmas PD, Bouxsein ML (2006) Contribution of the advanced glycation end product pentosidine and of maturation of type I collagen to compressive biomechanical properties of human lumbar vertebrae. Bone 39:1073–1079
Grandhee SK, Monnier VM (1991) Mechanism of formation of the Maillard protein cross-link pentosidine. Glucose, fructose, and ascorbate as pentosidine precursors. J Biol Chem 266:11649–11653
Cloos PA, Lyubimova N, Solberg H, Qvist P, Christiansen C, Byrjalsen I, Christgau S (2004) An immunoassay for measuring fragments of newly synthesized collagen type I produced during metastatic invasion of bone. Clin Lab 50:279–289
Rosen CJ, Hochberg MC, Bonnick SL, McClung M, Miller P, Broy S, Kagan R, Chen E, Petruschke RA, Thompson DE, de Papp AE (2005) Treatment with once-weekly alendronate 70 mg compared with once-weekly risedronate 35 mg in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized double-blind study. J Bone Miner Res 20:141–151
Guenther HL, Guenther HE, Fleisch H (1981) The influence of 1-hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonate and dichloromethanediphosphonate on lysine hydroxylation and cross-link formation in rat bone, cartilage and skin collagen. Biochem J 196:303–310
Hanson DA, Eyre DR (1996) Molecular site specificity of pyridinoline and pyrrole cross-links in type I collagen of human bone. J Biol Chem 271:26508–26516
Banse X, Sims TJ, Bailey AJ (2002) Mechanical properties of adult vertebral cancellous bone: correlation with collagen intermolecular cross-links. J Bone Miner Res 17:1621–1628
Bailey AJ, Sims TJ, Ebbesen EN, Mansell JP, Thomsen JS, Mosekilde L (1999) Age-related changes in the biochemical properties of human cancellous bone collagen: relationship to bone strength. Calcif Tissue Int 65:203–210
Oxlund H, Barckman M, Ortoft G, Andreassen TT (1995) Reduced concentrations of collagen cross-links are associated with reduced strength of bone. Bone 17:365S–371S
Oxlund H, Mosekilde L, Ortoft G (1996) Reduced concentration of collagen reducible cross links in human trabecular bone with respect to age and osteoporosis. Bone 19:479–484
Bailey AJ, Wotton SF, Sims TJ, Thompson PW (1992) Post-translational modifications in the collagen of human osteoporotic femoral head. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185:801–805
Lees S, Eyre DR, Barnard SM (1990) BAPN dose dependence of mature crosslinking in bone matrix collagen of rabbit compact bone: corresponding variation of sonic velocity and equatorial diffraction spacing. Connect Tissue Res 24:95–105
Monnier VM (1989) Toward a Maillard reaction theory of aging. Prog Clin Biol Res 304:1–22
Bailey AJ, Paul RG, Knott L (1998) Mechanisms of maturation and ageing of collagen. Mech Ageing Dev 106:1–56
Vashishth D, Wu P, Gibson G (2004) Age-related loss in bone toughness is explained by non-enzymatic glycation of collagen. Trans Orthop Res Soc 29
Wu P, Koharski C, Nonnenmann H, Vashishth D (2003) Loading on non-enzymatically glycated and damaged bone results in an instantaneous fracture. Trans Orthop Res Soc 28:404
Catanese J, Bank R, Tekoppele J, Keaveny T (1999) Increased cross-linking by non-enzymatic glycation reduces the ductility of bone and bone collagen. Proc ASME 1999 Bioengineering Conference 42:267–268
Hernandez CJ, Tang SY, Baumbach BM, Hwu PB, Sakkee AN, van der Ham F, Degroot J, Bank RA, Keaveny TM (2005) Trabecular microfracture and the influence of pyridinium and non-enzymatic glycation-mediated collagen cross-links. Bone 37:825–832
Boxberger J, Vashishth D (2004) Nonenzymatic glycation affects bone fracture by modifying creep and inelastic properties of collagen. Trans Orthop Res Soc 29
Tang S, Sharan A, Novak E, Ford T, Vashishth D (2005) Nonenzymatic glycation causes loss of toughening mechanisms in human cancellous bone. Trans Orthop Res Soc 30
Wang X, Shen X, Li X, Agrawal CM (2002) Age-related changes in the collagen network and toughness of bone. Bone 31:1–7
Vashishth D, Gibson GJ, Khoury JI, Schaffler MB, Kimura J, Fyhrie DP (2001) Influence of nonenzymatic glycation on biomechanical properties of cortical bone. Bone 28:195–201
Saito M, Fujii K, Marumo K (2006) Degree of mineralization-related collagen crosslinking in the femoral neck cancellous bone in cases of hip fracture and controls. Calcif Tissue Int 79:160–168
Siegmund T, Allen MR, Burr D (2007) A ductile-to-brittle transition in bone failure due to non-enzymatic collagen-crosslinks - A computational study. Trans Orthop Res Soc 32:1360
Paschalis EP, Boskey AL, Kassem M, Eriksen EF (2003) Effect of hormone replacement therapy on bone quality in early postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 18:955–959
Paschalis EP, Recker R, DiCarlo E, Doty SB, Atti E, Boskey AL (2003) Distribution of collagen cross-links in normal human trabecular bone. J Bone Miner Res 18:1942–1946
Paschalis EP, Betts F, DiCarlo E, Mendelsohn R, Boskey AL (1997) FTIR microspectroscopic analysis of human iliac crest biopsies from untreated osteoporotic bone. Calcif Tissue Int 61:487–492
Paschalis EP, Betts F, DiCarlo E, Mendelsohn R, Boskey AL (1997) FTIR microspectroscopic analysis of normal human cortical and trabecular bone. Calcif Tissue Int 61:480–486
Durchschlag E, Paschalis EP, Zoehrer R, Roschger P, Fratzl P, Recker R, Phipps R, Klaushofer K (2006) Bone material properties in trabecular bone from human iliac crest biopsies after 3- and 5-year treatment with risedronate. J Bone Miner Res 21:1581–1590
Sarkar S, Mitlak BH, Wong M, Stock JL, Black DM, Harper KD (2002) Relationships between bone mineral density and incident vertebral fracture risk with raloxifene therapy. J Bone Miner Res 17:1–10
Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Harris F, Genant HK, Ensrud K, LaCroix AZ, Black DM (2002) Improvement in spine bone density and reduction in risk of vertebral fractures during treatment with antiresorptive drugs. Am J Med 112:281–289
Li Z, Meredith MP, Hoseyni MS (2001) A method to assess the proportion of treatment effect explained by a surrogate endpoint. Stat Med 20:3175–3188
Watts NB, Cooper C, Lindsay R, Eastell R, Manhart MD, Barton IP, van Staa TP, Adachi JD (2004) Relationship between changes in bone mineral density and vertebral fracture risk associated with risedronate: greater increases in bone mineral density do not relate to greater decreases in fracture risk. J Clin Densitom 7:255–261
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Keith Condon, Diana Jacob, Mary Hooser, and Lauren Waugh for histological preparation. This work was supported by NIH Grants AR047838 and AR007581 and research grants from The Alliance for Better Bone Health (Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals and sanofi-aventis), and Lilly Research Laboratories, as well as an unrestricted grant from Eli Lilly to INSERM. Merck and Co. kindly provided the alendronate. This investigation utilized an animal facility constructed with support from Research Facilities Improvement Program Grant Number C06 RR10601-01 from the National Center for Research Resources, National Institutes of Health.
Conflict of interest statement
Matthew R. Allen has current research funding from Eli Lilly, Amgen, and the Alliance for Better Bone Health.
Diana Julie Leeming is a full-time employee of Nordic Bioscience.
David B. Burr has research funding from the Alliance for Better Bone Health, Eli Lilly and Co., and Amgen. He serves as a consultant and speaker for Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals and for Eli Lilly and Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, M.R., Gineyts, E., Leeming, D.J. et al. Bisphosphonates alter trabecular bone collagen cross-linking and isomerization in beagle dog vertebra. Osteoporos Int 19, 329–337 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-007-0533-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-007-0533-7