Abstract
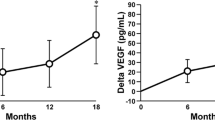
Since the ability of parathyroid hormone (PTH) to increase osteoblast maturation and activity is associated with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) we determined the changes in serum bFGF levels in patients treated with human parathyroid hormone (hPTH) (1–34) for 12 months and 12 months follow up. All studied subjects (n=51) had postmenopausal osteoporosis, had been receiving long-term treatment with glucocorticoid plus estrogen or estrogen/progesterone and were randomly allocated either to a group receiving hPTH, 400 U/day (n=28), or to a control group (n=23). Osteocalcin (OST), bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BSAP) and bFGF were monitored at the baseline, every 3 months for 18 months, and at 24 months. In the hPTH group, OST increased by more than 150% above baseline at 3 months and was maintained at this level throughout the treatment period. BSAP had increased more than 80% over the baseline level at 3 months and was maintained at 90% above baseline for the next 9 months. bFGF levels had increased by 45% at 3 months, 60% at 6 to 9 months (P<0.05) and had increased more than 90% from baseline by 12 months (P<0.05). We found that daily hPTH injections increased bFGF levels. These results support the hypothesis that up-regulation of bFGF could play a role in the osteoblastic response to PTH.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, Prince R, Gaich GA, Reginster JY, Hodsman AB, Eriksen EF, Ish-Shalom S, Genant HK, Wang O, Mitlak BH (2001) Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 344:1434–1441
Black DM, Greenspan SL, Ensrud KE, Palermo L, McGowan JA, Lane TL, Garnero P, Bouxsein ML, Biliezikian J, Rosen CJ (2003) The effects of parathyroid hormone and alendronate alone or in combination in postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 349:1207–1215
Finkelstein JS, Hayes A, Hunzelman JL, Wyland JJ, Lee H, Neer RM (2003) The effects of parathyroid hormone, alendronate, or both in men with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 349:1216–1226
Hurley MM, Marie P, Florkiewicz R (2002) Fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor families in bone. In: Bilezikian JP, Raisz LG, Rodan G (eds) Principles of bone biology. Academic, San Diego, pp 825–851
Mayahara H, Ito T, Nagai H, Miyajima H, Tsukuda R, Takatomi S, Mizoguchi J, Kato K (1993) In vivo stimulation of endosteal bone formation by basic fibroblast growth factor in rats. Growth Factors 9:73–80
Hurley MM, Tetradis S, Huang YF, Hock J, Kream BE, Raisz LG Sabbieti MG (1999) Parathyroid hormone regulates the expression of fibroblast growth factor 2 mRNA and fibroblast growth factor receptor mRNA in osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res 14:776–783
Okada Y, Montero A, Zhang X, Sobue T, Lorenzo J, Doetschman T, Coffin JD, Hurley MM (2003) Impaired osteoclast formation in bone marrow cultures of Fgf2 null mice in response to parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem 278:21258–21266
Lane NE, Sanchez S, Modin GW, Genant HK, Pierini E, Arnaud CD (1998) Parathyroid hormone treatment can reverse corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Invest 102:1627–1633
Lane NE, Sanchez S, Genant HK, Jenkins DK, Arnaud CD (2000) Short term increases in bone turnover markers predict parathyroid hormone-induced spinal bone mineral density gains in postmenopausal women with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 11:434–442
Buxton EC, Yao W, Lane NE (2004) Changes in serum receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, and interleukin 6 levels in patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis treated with human parathyroid hormone (1–34). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3332–3336
Canalis E, Hock JM, Raisz LG (1994) Anabolic and catabolic effects of parathyroid hormone on bone and interactions with growth factors. The parathyroids, Chap 4, pp 65–82
Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Linkart T, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (2001) Evidence that the anabolic effect of PTH on bone require IGF 1 in growing mice. Endocrinology 142:4349–4356
Zhang X, Sobue T, Hurley MM (2002) FGF-2 increases colony formation, PTH receptor, and IGF-1 mRNA in mouse marrow stromal cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:526–531
Power RA, Iwanec UT, Wronski TJ (2002) Changes in gene expression associated with the bone anabolic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor in aged ovariectomized rats. Bone 31:143–148
Dobnig H, Turner RT (1995) Evidence that intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone increases bone formation in adult rats by activation of bone lining cells. Endocrinology 136:3632–3638
Shizuya T, Yokose S, Hori M, Noda T, Suda T, Yoshiki S, Yamaguchi A (1997) Parathyroid hormone exerts disparate effects on osteoblast differentiation depending on exposure time in rat osteoblastic cells. J Clin Invest 99:2961–2970
Stanislaus D, Yang X, Liang JD, Wolfe J, Cain RL, Onyia JE, Falla N, Marder P, Bidwell JP, Queener W, Hock JM (2000) In vivo regulation of apoptosis in metaphyseal trabecular bone of young rats by synthetic human parathyroid hormone (1.34) fragment. Bone 27:209–218
Carroll LA, Hanasono MM, Mikullec AA, Kita M, Koch RJ (2002) Triamcinolone stimulates bFGF production and inhibits TGF beta 1 production by human derma fibroblast. Dermatol Surg 28:704–709
Ogata S, Yorioka N, Kohno N (2001) Glucose and prednisolone alter basic fibroblast growth factor expression in peritoneal mesothelial cells and fibroblasts. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2787–2796
Nagashima M, Wauke K, Hirano D, Ishigami S, Aono H, Takai M, Sasano M, Yoshino S (2000) Effect of combinations of anti-rheumatic drugs on the production of vascular endothelial cell growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in cultured synoviocytes and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 39:1255–1262
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr. L.G. Raisz for careful review of the manuscript and for his insightful comments. This work was supported by grants from the NIH AG021189; NIH AR048841-01, DK46661-07, and the Rosalind Russell Arthritis Research Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hurley, M., Yao, W. & Lane, N.E. Changes in serum fibroblast growth factor 2 in patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis treated with human parathyroid hormone (1–34). Osteoporos Int 16, 2080–2084 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-005-1998-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-005-1998-x