Abstract
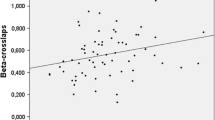
This study aimed to assess the clinical, biochemical and hormonal factors contributing to low bone density in a large ambulatory group of patients with cirrhosis of diverse aetiology. Bone density of the lumbar spine, neck of femur, total hip, total body, as well as total body fat, was measured by dual X-ray (DEXA) absorptiometry in 81 men and 32 women (average age 50.3 years). Morning blood and urine samples were taken for hormonal and biochemical analysis. Viral hepatitis was the most common cause of cirrhosis (54%) and the severity of cirrhosis ranged from Child-Pugh A5–C14. Osteoporosis was most common in the lumbar spine but was present at any site in 31% of women and 22% of men, with osteopenia present in another 40% of both genders. Urinary deoxypyridinoline, a marker of bone resorption, was elevated in 56% of patients and was associated with increasing severity of cirrhosis and a higher prevalence of osteoporosis, particularly of the lumbar spine. Hip-bone density was primarily affected by low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and was associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism in one third of these patients. Additional important predictors for low bone density at all sites were age in women and testosterone in men. These findings indicate that, although the pathophysiology of osteoporosis in chronic liver disease is heterogeneous, high bone turnover may be the underlying pathophysiological mechanism in a significant subgroup of cirrhotic patients and may reflect metabolic effects of hypogonadism or secondary hyperparathyroidism on bone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collier J, Ninkovic M, Compston J (2002) Guidelines on the management of osteoporosis associated with chronic liver disease. Gut 50 [Suppl 1]:1–-9
Stellon A, Webb A, Compston J, Williams R (1987) Low bone turnover state in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 7:137–142
Diamond T, Stiel D, Lunzer M, Eckstein R, Posen S (1989) Hepatic osteodystrophy: static and dynamic bone histomorphometry and serum bone Gla-protein in 80 patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 96:213–221
Guanabens N, Pares A, Brancos A, et al (1990) Factors influencing the development of metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 85:1356–262
McDonald J, Dunstan C, Dilworth P, et al (1991) Bone loss after liver transplantation. Hepatology 14:613–619
McCaughan G, Feller R (1994) Osteoporosis in chronic liver disease: pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Dig Dis 12:223–231
Hodgson S, Dickson E, Eastell R, Erikson E, Bryant S, Riggs B (1993) Rates of cancellous bone remodelling and turnover in osteopenia associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Bone 14:819–827
Hammond G, Nisker J, Jones L, Siiteri P (1980) Estimation of the percentage of free steroid in undiluted serum by centrifugal ultrafiltration dialysis. J Biol Chem 255:5023–5026
Hodgson S, Dickson E, Wahner H, Johnson K, Mann K, Riggs B (1985) Bone loss and reduced osteoblast function in primary biliary cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med 103:855–860
Monegal A, Navasa M, Guanabens N, et al (1997) Osteoporosis and bone mineral metabolism disorders in cirrhotic patients referred for orthotopic liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int 60:148–154
Gallego-Rojo F, Gonzalez-Calvin J, Munoz-Torres M, Mundi J, Fernandez-Perez R, Rodrigo-Moreno D (1998) Bone mineral density, serum insulin-like growth factor and bone turnover markers in viral cirrhosis. Hepatology 28:695–699
Herlong H, Recker R, Maddrey W (1982) Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: histological features and response to 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Gastroenterology 83:103–108
Cuthbert J, Pak C, Zerwekh J, Glass K, Combes B (1984) Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: increased bone resorption and turnover in the absence of osteoporosis or osteomalacia. Hepatology 4:1–8
Coates P (1999) Clinical use of bone resorption markers. Clin Biochemist Rev 20:39–49
Ricard-Blum S, Bresson-Hadni S, Vuitton D, Ville G, Grimaud J (1992) Hydroxypyridinium collagen cross-links in human liver fibrosis: study of alveolar echinococcosis. Hepatology 15:599–602
Conigrave A, Quinn S, Brown E (2000) L-amino acid sensing by the extracellular Ca2+ sensing receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4814–4819
Silverberg S, Fitzpatrick L, Bilezikian J. Primary hyperparathyroidism. In: Becker K (ed) Principles and practice of endocrinology and metabolism. Lipincott, Philadelphia, pp. 512–514
Arnaud S (1981) 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment of bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 83:137–149
Rouillard S, Lane N (2001) Hepatic osteodystrophy. Hepatology 33:301–307
Diamond T, D S, Mason R, et al (1989) Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 69:1234–1239
Stellon A, Webb A, Compston J, Williams R (1986) Lack of osteomalacia in chronic cholestatic liver disease. Bone 7:181–185
Lips P, Obrant, KJ (1991) The pathogenesis and treatment of hip fractures. Osteoporosis Int 1:218–231
Lips P, Netelenbos J, Jongen M, van Giekel F, Althuis L, van Schaik C (1982) Histomorphometric profile and vitamin D status in patients with femoral neck fracture. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res 4:85–93
Diamond T, Smerdly S, Kormas N, Sekel R, Vu T, Day P (1998) Hip fracture in elderly men: the importance of subclinical vitamin D deficiency and hypogonadism. Med J Aust 169:138–141
Chapuy M-C, Preziosi P, Maamer M, et al (1997) Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in an adult normal population. Osteoporosis Int 7:439–443
Tangpricha V, Pearce E, Chen T, Holick M (2002) Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults. Am J Med 112:659–662
Gannage-Yared M, Chemali R, Yaacoub N, Halaby G (2000) Hypovitaminosis D in a sunny country: relation to lifestyle and bone markers. J Bone Miner Res 15:1856–1862
Vasikaran S, Sturdy G, Musk A, Flicker L (2000) Vitamin D insufficiency and hyperparathyroidism in Perth blood donors. Med J Aust 172:X06–-X7
McGrath J, Kimlin M, Saha S, Eyles D, Paris A (2001) Vitamin D insufficiency in south-east Queensland. Med J Aust 174:150–151
Heaf J. Hepatic osteodystrophy (1985) Scand J Gastroenterol 20:1035–1040
Compston J (1986) Hepatic osteodystrophy: vitamin D metabolism in patients with liver disease. Gut 27:1073–1090
Hay J (1995) Bone disease in cholestatic liver disease. Gastroenterology 108:276–283
Diamond T, Stiel D, Lunzer M, Wilkinson M, Roche J, Posen S (1990) Osteoporosis and skeletal fractures in chronic liver disease. Gut 31:82–87
Baker H (1995) Testicular dysfunction in systemic disease. In: Becker K (ed) Principles and practice of endocrinology and metabolism. Lippincott, Philadelphia, p. 1085
Burke C, Anderson D (1972) Sex hormone binding globulin is an estrogen amplifier. Nature 240:38
Dawson-Hughes B, Shipp C, Sadowski L, Dallal G (1987) Bone density of the radius, spine and hip in relation to percent ideal body weight in postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int 40:310–314
Pocock N, Eisman J, Gwinn T, et al (1989) Muscle strength, physical fitness and weight but not age predict femoral neck bone mass. J Bone Miner Res 4:441–447
Baker D, Roberts R, Towell T (2000) Factors predictive of bone mineral density in eating-disordered women: a longitudinal study. Int J Eat Disord 27:29–35
Selby P, Peacock M (1986) The effect of transdermal oestrogen on bone calcium-regulating hormones and liver in postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol Oxf 25:543–547
O'Donohue J, Williams J (1997) Hormone replacement therapy in women with liver disease. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104:1–3
Arver S, Dobs A, Meikle A, et al (1997) Long-term efficacy and safety of a permeation-enhanced testosterone transdermal system in hypogonadal men. Clin Endocrinol 47:727–737
Matloff D, Kaplan M, Neer R, Goldberg M, Bitman W, Wolfe H(1982) Osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment. Gastroenterology 83:97–102
Van Berkum F, Beukers R, Birkenhager J, Kooij P, Schalm S, Pols H (1990) Bone mass in women with primary biliary cirrhosis: the relation with histological stage and the use of steroids. Gastroenterology 99:1134–1139
Crippin J, Jorgensen R, Dickson E, Lindor K (1994) Hepatic osteodystrophy in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of medical treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 89:47–50
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Sing Kai Lo, Institute of National Health, University of Sydney, for his assistance with statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crawford, B.A.L., Kam, C., Donaghy, A.J. et al. The heterogeneity of bone disease in cirrhosis: a multivariate analysis. Osteoporos Int 14, 987–994 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-003-1495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-003-1495-z