Abstract.
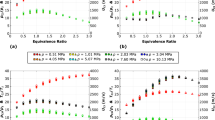
Ignition delays for low alkanes/oxygen mixtures highly diluted with argon were measured behind a reflected shock wave using ultraviolet emission spectrometry in wide ranges of temperature (1200–2700 K), pressure (0.1–1.8 MPa), equivalence ratio (0.5–2) and dilution (89–99%). For each alkane (methane, ethane and propane), a correlation between ignition delay time, temperature, pressure and concentration is proposed and compared with those obtained in previous studies. This correlation enables the estimation of the delay time with an accuracy better than 20% for all measurement ranges. Results are compared with those from a recent study of the detailed kinetic modelling of the alkane oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 12 March 2001 / Accepted 28 August 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamoureux, N., Paillard, CE. & Vaslier, V. Low hydrocarbon mixtures ignition delay times investigation behind reflected shock waves. Shock Waves 11, 309–322 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001930100108
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001930100108