Abstract.
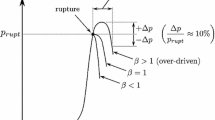
In order to improve the operation of a high-enthalpy free piston shock tunnel its tuned operation was studied analytically and experimentally. First, the piston motion in the free piston driver tube was analytically solved by proposing a simple piston/gasdynamic model, and the tuned operation condition was formulated as an eigenvalue with which the piston has sufficiently high speed at the moment of diaphragm rupture, so as to maintain a constant driver gas pressure, and reduces its speed to come to rest when very closely approaching the end of the driver tube. Second, the result of this analysis was validated by its comparison with experiments which were conducted in the medium-sized free piston shock tunnel HEK installed at the NAL Kakuda Research Center. By observing the detail of piston landing at the end of the driver tube the present tuned operation was found to be successfully achieved with the operating condition given here. Its advantages in improving the pressure recovery factor and in enhancing the stagnation enthalpy were successfully demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 8 June 1997 / Accepted 1 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itoh, K., Ueda, S., Komuro, T. et al. Improvement of a free piston driver for a high-enthalpy shock tunnel. Shock Waves 8, 215–233 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001930050115
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001930050115