Abstract.
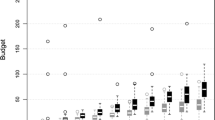
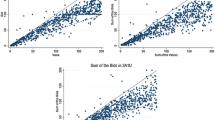
The behavioral properties of several auctions designed to elicit individual valuations for an object are studied using controlled laboratory experiments. Our experiments lead us to conclude that there are some behavioral differences between alternative incentive-compatible institutions for eliciting home-grown values, contrary to the theoretical expectation that these institutions are isomorphic. These results are consistent with earlier experimental results using induced values. The most important finding is that English auctions appear to elicit lower bids than Vickrey auctions, after controlling for observable socio-economic characteristics. Moreover, English auction bids also exhibit significantly less residual variance and may be sensitive to the number of rival bidders. It appears that the real-time learning allowed in the English auction significantly affects subject behavior. We also find that values elicited with the Becker, DeGroot and Marshak institution differ from those in both English and Vickrey auctions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received November 1993/Final version May 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutström, E. Home-grown values and incentive compatible auction design. Game Theory 27, 427–441 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001820050082
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001820050082