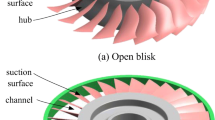
Abstract
In the robotic polishing process, the tool and the blisk interfere easily because of the narrow operation space and seriously twisted curved surfaces. Algorithms are proposed to detect and avoid collisions with high efficiency and accuracy. First, the curved surface of the blade is discretized into a set of points, and the collision detection between the tool and the blisk is converted into the calculation of distances between the tool and points on blade surface. Then, the tool axial vector is adjusted with the minimum rotation angle to avoid collision, which reduces the impact on surface profile accuracy after changing the tool postures. The machining quality is finally guaranteed by controlling the material removal depth of the polishing process. The proposed method realizes the collision detection and interference avoidance of the blisk polishing effectively, while it also ensures the surface quality of workpiece when adjusting the tool posture. Simulation and experiments are carried out to verify the feasibility and advantages of the proposed method.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji W, Wang L (2019) Industrial robotic machining: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(1):1239–1255
Yang J, Li D, Ye C, Ding H (2020) An analytical C3 continuous tool path corner smoothing algorithm for 6R robot manipulator. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 64:101947
Xiao GJ, Huang Y (2016) Equivalent self-adaptive belt grinding for the real-R edge of an aero-engine precision-forged blade. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(9/12):1697–1706
Duan J, Shi Y, Lin X, Dong T (2011) Flexible polishing machine with dual grinding heads for aeroengine blade and blisk. Adv Mater Res 317-319:2454–2460
Xiao G, Huang Y, Wang J (2018) Path planning method for longitudinal micromarks on blisk root-fillet with belt grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(1):797–810
Zhang T, Su J (2018) Collision-free planning algorithm of motion path for the robot belt grinding system. Int J Adv Robot Syst 15(4):1729881418793778
Ahmet C, Ali N (2010) A novel iso-scallop tool-path generation for efficient five-axis machining of free-form surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51(9/12):1083–1098
Lin T, Lee J, Bohez E (2009) A new accurate curvature matching and optimal tool based five-axis machining algorithm. J Mech Sci Technol 23(10):2624–2634
Fard M, Feng H (2009) Effect of tool tilt angle on machining strip width in five-axis flat-end milling of free-form surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(3/4):211–222
Du J, Liu PC, Zhi HY, Ding P (2019) Global interference detection technology for five-axis machining of complex surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102(9/12):4273–4287
Wang Z, Lin X, Shi Y (2020) Efficiently constructing collision-free regions of tool orientations for holder in five-axis machining of blisk. Chin J Aeronaut 33(10):2743–2756
Llushin O, Elber G, Halperin D, Weir R, Kim SM (2005) Precise global collision detection in multi-axis NC-machining. Comput Aided Des 37(9):909–920
Huang Z, Wei P (2020) Collision detection method of blisk grinding and polishing. Comput Integr Manuf Syst 26(12):3350–3358 (In Chinese)
Hwang J (1992) Interference-free tool-path generation in the NC machining of parametric compound surfaces. Comput Aided Des 24(12):667–676
Ding S, Mannan MA, Poo AN, Yang D, Han Z (2003) Adaptive iso-planar tool path generation for machining of free-form surfaces. Comput Aided Des 35(2):141–153
Li H, Feng H (2004) Efficient five-axis machining of free-form surfaces with constant scallop height tool paths. Int J Prod Res 42(12):2403–2417
Tournier C, Duc E (2005) Iso-scallop tool path generation in 5-axis milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(9/10):867–875
Takeuchi Y, Morishige K, Kase K (1999) Tool path generation using C-space for 5-axis control machining. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans 121(1):144–149
Chen S, Cheung C, Zhang F (2019) Optimization of tool path for uniform scallop-height in ultra-precision grinding of free-form surfaces. Nanomanuf Metrol 2:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41871-019-00048-0
Gao Z (2015) Application on programming and simulation of the fan blade NC machining based on UG. Appl Mech Mater 740:87–90
Cai Y, Xi G (2002) Global tool interference detection in five-axis machining of sculptured surfaces. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 216(10):1345–1353
Chen F, Chen F, Zhao H, Li D, Chen L, Tan C, Ding H (2019) Contact force control and vibration suppression in robotic polishing with a smart end effector. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 57:391–403
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Key Research and Development Plan under Grant No. 2020YFB1710400, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 52090054, the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China, under Grant No. 2020CFA077, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. 2020kfyXJJS064.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuanming Wang: conceptualization, writing—original draft, validation; Jixiang Yang: resources, instructing, review; Dingwei Li: experiments; Han Ding: instructing, review
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
The authors agree to publication in The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yang, J., Li, D. et al. Tool path generation with global interference avoidance for the robotic polishing of blisks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117, 1223–1232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07698-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07698-9