Abstract
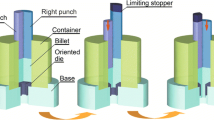
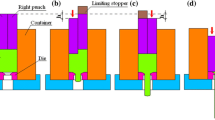
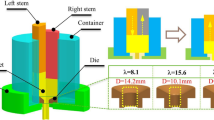
One of the goals in the field of extrusion technology is to simplify the process and increase shear deformation in order to improve the grain refining capacity. This article innovatively tries to design a split punch structure and makes them alternate downward loading, so alternate extrusion (AE) method is proposed. Optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are employed to characterize the microstructure of AZ31 magnesium alloy during AE. Compared with the conventional extrusion (CE) under the same conditions, the microscopic experiment results show that the grain is more refined and the microstructure is more homogeneous. AE produces a large number of different direction dislocations and entangle with each other. The reasons for the above phenomenon are the plastic zone’s range of AE significantly increased. And between interface of double punch and die form a range of shear zone, which provides fully refined grain source power in the extrusion process. The tensile test results show that the mechanical properties of AE were better than CE, which is consistent with the results of our microscopic experiment results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang CS, Zhao GQ, Chen H, Guan YJ, Kou FJ (2012) Numerical simulation and metal flow analysis of hot extrusion process for a complex hollow aluminum profile. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60:101–110
Chen Q, Zhao ZD, Zhao ZX, Hu CK, Shu DY (2011) Microstructure development and thixoextrusion of magnesium alloy prepared by repetitive upsetting-extrusion. J Alloy Compd 509:7303–7315
Zhao GQ, Chen H, Zhang CS, Guan YJ, Gao AJ, Li P (2014) Die optimization design and experimental study of a large wallboard aluminum alloy profile used for high-speed train. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74:539–549
Li F, Bian N, Xu YC (2014) An analytical model on twisting deformation of rod extrusion through conical die with rotating container. Mech Res Commun 61:27–35
Barnett MR, Sullivan A, Stanford N, Ross N, Beer A (2010) Texture selection mechanisms in uniaxially extruded magnesium alloys. Scripta Mater 63:721–724
Zhang Z (2013) Twinning and its related work hardening during the ambient extrusion of a magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 577:125–137
Li F, Shi W, Hu ZL, Zeng X (2015) Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZM6 magnesium alloy after continuous variable cross-section direct extrusion. Kovove Mater 53:1–7
Orlov D, Raab G, Lamark TT, Popov M, Estrin Y (2011) Improvement of mechanical properties of magnesium alloy ZK60 by integrated extrusion and equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 59:375–385
Orlov D, Ralston KD, Birbilis N, Estrin Y (2011) Enhanced corrosion resistance of Mg alloy ZK60 after processing by integrated extrusion and equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 59:6176–6186
Lu LW, Liu CM, Zhao J, Zeng WB, Wang ZC (2015) Modification of grain refinement and texture in AZ31 Mg alloy by a new plastic deformation method. J Alloy Compd 628:130–134
Khoddam S, Farhoumand A, Hodgson PD (2011) Axi-symmetric forward spiral extrusion, a kinematic and experimental study. Mat Sci Eng A 528:1023–1029
Shahbaz M, Pardis N, Ebrahimi R, Talebanpour B (2011) A novel single pass severe plastic deformation technique: vortex extrusion. Mat Sci Eng A 530:469–472
Yang XY, Miura H, Sakai T (2003) Dynamic evolution of new grains in magnesium alloy AZ31 during hot deformation. Mater Trans 44:197–203
Yang QS, Jiang B, Tian Y, Liu WJ, Pan FS (2013) A tilted weak texture processed by an asymmetric extrusion for magnesium alloy sheets. Mater Lett 100:29–31
Yang QS, Jiang B, He JJ, Song B, Liu WJ, Dong HW, Pan FS (2014) Tailoring texture and refining grain of magnesium alloy by differential speed extrusion process. Mat Sci Eng A 612:187–191
Fatemi-Varzaneh SM, Zarei-Hanzaki A (2009) Accumulative back extrusion (ABE) processing as a novel bulk deformation method [J]. Mat Sci Eng A 504:104–106
Faraji G, Jafarzadeh H, Jeong HJ, Mashhadi MM, Kim HS (2012) Numerical and experimental investigation of the deformation behavior during the accumulative back extrusion of an AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater Des 35:251–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is completed under my independent research, and without the phenomenon that quotes largely or plagiarizes other articles and so on. Therefore, I will be corresponding responsible for the thing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, F. & Jiang, H.W. Microstructural analysis and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy prepared by alternate extrusion (AE). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 4293–4301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0447-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0447-2