Abstract
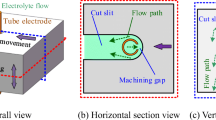
Deep narrow slits of titanium alloys are extensively used in the aerospace industry. Electrochemical machining (ECM) is suitable for fabricating deep narrow slits owing to its advantages such as no tool wear, no residual stress, and no thermal stress. However, the machining surface of titanium alloy is prone to passivation, and the pitting is prone to generating on the non-machined surface, which restricts forming precision enhancement. In this study, the electrochemical dissolution characteristics of TB6 titanium alloy were investigated using the method of electrolyte lateral flow, and the experiments of the deep narrow slit machining were also conducted on the basis of the self-developed vibration apparatus. The results reveal that the mixed electrolyte composed of NaCl and NaNO3 is capable of enhancing the current efficiency and surface quality of TB6 titanium alloy. Moreover, the average slit width at the entrance of the deep narrow slit is limited at 2.48 mm, and the average slit width in the depth direction is limited at 2.67 mm using the method of vibration superimposed on the high-speed linear feeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Özcan M, Hämmerle C (2012) Titanium as a reconstruction and implant material in dentistry: advantages and pitfalls. Materials 5(9):1528–1545
Niu Y, Hou HL, Li MQ, Li ZQ (2008) High temperature deformation behavior of a near alpha Ti600 titanium alloy. Mat Sci Eng A 492(1–2):24–28
Akram M, Bashir S, Rafique MS, Hayat A, Mahmood K, Dawood A, Bashir MF (2015) Morphological and spectroscopic characterization of laser-ablated tungsten at various laser irradiances. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 119(3):859–870
Xiong RB, Wu HB (2016) Study on cutting mechanism of Ti6Al4V in ultra-precision machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5):1311–1317
Pervaiz S, Rashid A, Deiab I, Nicolescu M (2014) Influence of tool materials on machinability of titanium- and nickel-based alloys: a review. Mater Manuf Process 29(3):219–252
Pramanik A (2014) Problems and solutions in machining of titanium alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(5):919–928
Yao CF, Wu DX, Tan L, Ren JX, Shi KN, Yang ZC (2013) Effects of cutting parameters on surface residual stress and its mechanism in high-speed milling of TB6. P I Mech Eng B-J Eng 227(4):483–493
Ezugwu EO, Wang ZM (1997) Titanium alloys and their machinability—a review. J Mater Process Technol 68(3):262–274
Shen Y, Liu YH, Zhang YZ, Tan B, Ji RJ, Cai BP, Zheng C (2014) Determining the energy distribution during electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(1):11–17
Kao JY, Tsao CC, Wang SS, Hsu CY (2010) Optimization of the EDM parameters on machining Ti–6Al–4V with multiple quality characteristics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(1):395–402
Li W, Liu J, Zhou Y, Li S, Wen SF, Wei QS, Yan CZ, Shi YS (2016) Effect of laser scanning speed on a Ti-45Al-2Cr-5Nb alloy processed by selective laser melting: microstructure, phase and mechanical properties. J Alloy Compd 688:626–636
Maurer JJ, Hudson JL, Fick SE, Moffat TP, Shaw GA (2012) Electrochemical micromachining of NiTi shape memory alloys with ultrashort voltage pulses. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 15(2):8–10
Weinmann M, Stolpe M, Weber O, Busch R, Natter H (2015) Electrochemical dissolution behaviour of Ti90Al6V4 and Ti60Al40 used for ECM applications. J Solid State Electr 19(2):485–495
Anasane SS, Bhattacharyya B (2016) Experimental investigation on suitability of electrolytes for electrochemical micromachining of titanium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5):2147–2160
Walther B, Schilm J, Michaelis A, Lohrengel MM (2007) Electrochemical dissolution of hard metal alloys. Electrochim Acta 52(27):7732–7737
Wang F, Liu YH, Zhang YZ, Tang ZM, Ji RJ, Zheng C (2014) Compound machining of titanium alloy by super high speed EDM milling and arc machining. J Mater Process Technol 214(3):531–538
Łupak M, Zaborski S (2009) Simulation of energy consumption in electrochemical grinding of hard-to-machine materials. J Appl Electrochem 39(1):101–106
Clifton D, Mount AR, Jardine DJ, Roth R (2001) Electrochemical machining of gamma titanium aluminide intermetallics. J Mater Process Technol 108(3):338–348
Qu NS, Fang XL, Li W, Zeng YB, Zhu D (2013) Wire electrochemical machining with axial electrolyte flushing for titanium alloy. Chinese J Aeronaut 26(1):224–229
He HD, Qu NS, Zeng YB, Fang XL, Yao YY (2016) Machining accuracy in pulsed wire electrochemical machining of γ-TiAl alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5):2353–2359
Xu ZY, Liu J, Zhu D, Qu NS, Wu XL, Chen XZ (2015) Electrochemical machining of burn-resistant Ti40 alloy. Chinese J Aeronaut 28(4):1263–1272
Chen XZ, Xu ZY, Zhu D, Fang XL, Zhu D (2016) Experimental research on electrochemical machining of titanium alloy Ti60 for a blisk. Chinese J Aeronaut 29(1):274–282
Weiss I, Semiatin SL (1998) Thermomechanical processing of beta titanium alloys—an overview. Mat Sci Eng A 243(1–2):46–65
Liu WD, Ao SS, Li Y, Liu ZM, Wang ZM, Luo Z, Wang ZP, Song RF (2016) Jet electrochemical machining of TB6 titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/ s00170-016-9500-9
Yao J, Chen ZT, Nie YJ, Li Q (2017) Investigation on the electrochemical machining by using metal reinforced double insulating layer cathode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89(5):2031–2040
Béjar MA, Gutiérrez F (1993) On the determination of current efficiency in electrochemical machining with a variable gap. J Mater Process Technol 37(1–4):691–699
Wang F, Zhao JS, Zhang XL, Yang ZW, Gan WM, Tian ZJ (2016) Electrochemical machining of a narrow slit by cathodic compound feeding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-9448-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhao, J., Lv, Y. et al. Electrochemical machining of deep narrow slits on TB6 titanium alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92, 3063–3071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0392-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0392-0