Abstract
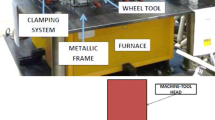
Hot single point incremental forming (SPIF) with induction heating and cryogenic cooling has been applied to form the Ti-6Al-4V sheets. The influence of both the forming temperature and the cooling rate after deformation, on microstructure evolution and microhardness of Ti-6Al-4V sheets, has been extensively studied. We propose the use and development of a new system of heating by induction. The system is composed of a medium–high frequency generator and a continuously water-cooled heating head, which is placed under the sheet and linked axially to the punch movement, heating the material locally by generating an eddy current within the material. Furthermore, a cooling system integrated with the movement of the forming punch allows us to apply a cryogenic fluid to the recently deformed sheet metal. Both localized heating and cooling systems are particularly suitable for such a process as SPIF, whose primary characteristic is the incremental forming of localized sheet zones. The meta-dynamic and static recrystallization processes have been suppressed in the sheet material, evident by the final microstructure and mechanical properties. Finally, a comparison between parts is made, both with and without cooling during hot SPIF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filice L, Fratini L, Micari F (2002) Analysis of material formability in incremental forming. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 51:199–202. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61499-1
Jackson K, Allwood J (2009) The mechanics of incremental sheet forming. J Mater Proc Technol 209(3):1158–1174. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.03.025
Gate S, Ou H, McCartney G (2016) Review on the influence of process parameters in incremental sheet forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol:1–21. doi:10.1007/s00170-016-8426-6
Xu D, Wu W, Malhotra R, Chena J, Lu B, Cao J (2013) Mechanism investigation for the influence of tool rotation and laser surface texturing (LST) on formability in single point incremental forming. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 73:37–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2013.06.007
Centeno G, Bagudanch I, Martínez-Donaire AJ, García-Romeu ML, Vallellano C (2014) Critical analysis of necking and fracture limit strains and forming forces in single-point incremental forming. Mat Des 63:20–29. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2014.05.066
Hirt G, Ames J, Bambach M, Kopp R (2004) Forming strategies and process modelling for CNC incremental sheet forming. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 1:203–206. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60679-9
Li J, Shen J, Wang B (2013) A multipass incremental sheet forming strategy of a car taillight bracket. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57:2229–2236. doi:10.1007/s00170-013-5179-3
Lingam R, Prakash O, Belk JH, Reddy NV (2016) Automatic feature recognition and tool path strategies for enhancing accuracy in double sided incremental forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol; 1–17. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-8880-1.
Jeswiet J, Micari F, Hirt G, Bramley A, Duflou J, Allwood J (2005) Asymmetric single point incremental forming of sheet metal. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 54(2):88–114. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60021-3
Vanhove H, Mohammad AS, Guo Y, Duflou JR (2014) High-speed single point incremental forming of an automotive aluminium alloy. Key Eng Mat 622-623:433–439. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.622-623.433
Ambrogio G, Gagliardi F, Bruschi S, Filice L (2013) On the high-speed single point incremental forming of titanium alloys. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62:243–246. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2013.03.053
Allwood JM, Braun D, Music O (2013) The effect of partially cut-out blanks on geometric accuracy in incremental sheet forming. J Mater Proc Technol 210:1501–10. doi: dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.04.008
Hussain G, Gao L, Zhang Y (2008) Formability evaluation of pure titanium sheet in the cold incremental forming process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:920–926. doi:10.1007/s00170-007-1043-7
Liu J, Tan MJ, Wollmar Jarfors AE, Aue-u-lan Y, Castagne S (2010) Formability in AA5083 and AA6061 alloys for light weight applications. Mat Des 31:S66–S70. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2009.10.052
Fan G, Sun F, Meng X, Gao L, Tong G (2010) Electric hot incremental forming of Ti-6Al-4V titanium sheet. Int J Adv Manufact Technol 49(9):941–947. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2472-2
Van Sy L, Nam NT (2013) Hot incremental forming of magnesium and aluminum alloy sheets by using direct heating system. J Eng Manuf 227(8):1099–1110. doi:10.1177/0954405413484014
Palumbo G, Brandizzi M (2012) Experimental investigations on the single point incremental forming of a titanium alloy component combining static heating with high tool rotation speed. Mat Des 40:43–51. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2012.03.031
Xu DK, Lu B, Cao TT, Zhang H, Chen J, Long H, Cao J (2016) Enhancement of process capabilities in electrically-assisted double sided incremental forming. Mat Des 92:268–280. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.009
Ji YH, Park JJ (2008) Formability of magnesium AZ31 sheet in the incremental forming at warm temperature. J Mater Proc Technol 201:354–358. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.11.206
Ambrogio G, Filice L, Manco GL (2008) Warm incremental forming of magnesium alloy AZ31. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57:257–260. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.066
Duflou JR, Callebaut B, Verbert J, De Baerdemaeker H (2007) Laser assisted incremental forming: formability and accuracy improvement. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 56:273–276. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2007.05.063
Göttmann A, Bailly D, Bergweiler G, Bambach M, Stollenwerk J, Hirt G (2013) A novel approach for temperature control in SPIF supported by laser and resistance heating. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67:2195–2205. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4640-z
Otsu M, Matsuo H, Matsuda M, Takashima K (2014) Friction stir incremental forming of aluminum alloy sheets. Steel Res Int 81:942–945. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.10.327
Xu D, Wu W, Malhotra R, Chen J, Lu B, Cao J (2013) Mechanism investigation for the influence of tool rotation and laser surface texturing (LST) on formability in single point incremental forming. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 73:37–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2013.06.007
Fan G, Gao L, Hussain G, Wu Z (2008) Electric hot incremental forming: a novel technique. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1688–1692. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.07.010
Ambrogio G, Filice L, Gagliardi F (2012) Formability of lightweight alloys by hot incremental sheet forming. Mat Des 34:501–508. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2011.08.024
Xu D, Lu B, Cao T, Chen J, Long H, Cao J (2014) A comparative study on process potentials for frictional stir-welding and electric hot-assisted incremental sheet forming. Proc Eng 2014;81:2324–9. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.10.328.
Della Torre E, Magnetic hysteresis. Wiley-IEEE Press Home, 2005.
Donachie M. Titanium: a technical guide. The Materials Information Society 2004 Ohio (USA).
Ambrogio G, Bruschi S, Gagliardi F, Ghiotti A, Filice L (2014) Surface and microstructure considerations in high speed single point incremental forming of Ti6Al4V sheets. Key Eng Mater 611-612:1071–1078
Murty SN, Nayan N, Kumar P, Narayanan PR, Sharma SC, George KM (2014) Microstructure–texture–mechanical properties relationship in multi-pass warm rolled Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mat Sci Eng A 589:174–181. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2013.09.087
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ambrogio, G., Gagliardi, F., Chamanfar, A. et al. Induction heating and cryogenic cooling in single point incremental forming of Ti-6Al-4V: process setup and evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91, 803–812 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9794-7