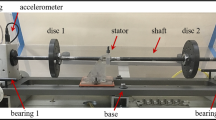
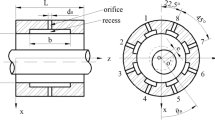
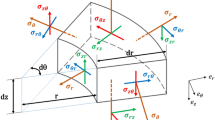
Abstract
High-speed machining spindles are high-precision mechanisms with a complex and very sensitive behavior. Frequency response functions are required to avoid unstable cutting conditions that lead to premature failure of spindle and tool. However, FRFs are affected by stiffness loss of the bearings at high speed. Indeed, the rotor’s behavior is driven by its boundary conditions which are the preloaded bearings. In order to obtain an accurate model of the preloaded bearing system, this paper focuses on the axial spindle behavior. An analytical model that computes the equilibrium state of the shaft, rear sleeve, and bearing arrangement is presented. A model enrichment method is presented with several new physical phenomena: the macroscopic deformations of the shaft and bearing rings as well as the rear sleeve’s complex behavior. The significance of these phenomena is evaluated with a sensitivity analysis and used for the model updating to obtain a just accurate enough model. The contributions of these enrichments are presented for a case study performed on an industrial spindle. A good agreement between the simulation and the experimental results are achieved that validates the model updating strategy and the phenomenologically enriched model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele E, Altintas Y, Brecher C (2010) Machine tool spindle units. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59:781–802. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.05.002
Bossmanns B, Tu JF (1999) A thermal model for high speed motorized spindles. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39(9):1345–1366. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00005-X
Cao H, Holkup T, Altintas Y (2011) A comparative study on the dynamics of high speed spindles with respect to different preload mechanisms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57(9-12):871–883. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3356-9
Cao H, Niu L, He Z (2012) Method for vibration response simulation and sensor placement optimization of a machine tool spindle system with a bearing defect. Sensors (Switzerland) 12(7):8732–8754. doi:10.3390/s120708732
Cao Y, Altintas Y (2004) A general method for the modeling of spindle-bearing systems. J Mech Des 126 (6):1089. doi:10.1115/1.1802311
Chen JS, Hwang YW (2006) Centrifugal force induced dynamics of a motorized high-speed spindle. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 30(1-2):10–19. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0032-y
De Castelbajac C, Ritou M, Laporte S, Furet B (2014) Monitoring of distributed defects on HSM spindle bearings. Appl Acoust 77:159–168. doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2013.07.008
Ertürk A, Özgüven H, Budak E (2007) Effect analysis of bearing and interface dynamics on tool point FRF for chatter stability in machine tools by using a new analytical model for spindle–tool assemblies. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(1):23–32. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.03.001
Gagnol V, Bouzgarrou B, Ray P, Barra C (2007) Model-based chatter stability prediction for high-speed spindles. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(7-8):1176–1186. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.09.002
Gao S, Cheng K, Ding H, Fu H (2016) Multiphysics-based design and analysis of the high-speed aerostatic spindle with application to micro-milling. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 230(7):852–871. doi:10.1177/1350650115619609
Holkup T, Hol ∖‘y S (2005) Prediction of thermal stability of spindle bearing systems. In: Proceedings of the 4th YSESM Youth Symposium of Experimental Solid Mechanics, pp 107– 108
Houpert L (1997) A uniform analytical approach for ball and roller bearings calculations. J Tribol 119 (4):851–859. doi:10.1115/1.2833896
Jedrzejewski J, Kwasny W (2010) Modelling of angular contact ball bearings and axial displacements for high-speed spindles. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59(1):377–382. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.026
Jones AB (1960) A general theory for elastically constrained ball and radial roller bearings under arbitrary load and speed conditions. J Basic Eng 82(2):309. doi:10.1115/1.3662587
Li H, Shin YC (2004) Analysis of bearing configuration effects on high speed spindles using an integrated dynamic thermo-mechanical spindle model. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(4):347–364. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2003.10.011
Lin CW, Tu JF, Kamman J (2003) An integrated thermo-mechanical-dynamic model to characterize motorized machine tool spindles during very high speed rotation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(10):1035–1050. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00091-9 10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00091-9
Lynagh N, Rahnejat H, Ebrahimi M, Aini R (2000) Bearing induced vibration in precision high speed routing spindles. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40(4):561–577. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00076-0
Noel D, Le Loch S, Ritou M, Furet B (2013a) HSM Spindle model updating with physical phenomena refinements. In: Volume 7A: 9th International Conference on Multibody Systems, Nonlinear Dynamics, and Control, ASME, p V07AT10A035. doi:10.1115/DETC2013-13141
Noel D, Ritou M, Furet B, Le Loch S (2013b) Complete analytical expression of the stiffness matrix of angular contact ball bearings. J Tribol 135(4):041,101. doi:10.1115/1.4024109
Ozturk E, Kumar U, Turner S, Schmitz T (2012) Investigation of spindle bearing preload on dynamics and stability limit in milling. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(1):343–346. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2012.03.134
Palmgren A (1959) Ball and roller bearing engineering, 3rd edn. SKF industries, Philadelphia
Rantatalo M, Aidanpää JO, Göransson B, Norman P (2007) Milling machine spindle analysis using FEM and non-contact spindle excitation and response measurement. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(7-8):1034–1045. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.10.004 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.10.004
Spiewak S, Nickel T (2001) Vibration based preload estimation in machine tool spindles. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41(4):567–588. doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(00)00081-X
Swanson E, Powell CD, Weissman S (2005) A practical review of rotating machinery critical speeds and modes. Sound Vib 39(5):10–17
Yamazaki T, Matsubara A, Ikenaga S (2012) Measurement of rigidity change of preload switching spindle. Int J Automot Technol 6(2):175–179
Zivkovic A, Zeljkovic M, Tabakovic S, Milojevic Z (2014) Mathematical modeling and experimental testing of high-speed spindle behavior. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-6519-7
Zverv I, Pyoun YS, Lee KB, Kim JD, Jo I, Combs A (2005) An elastic deformation model of high speed spindles built into ball bearings. J Mater Process Technol 170(3):570–578. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.05.038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabréau, C., Noël, D., Loch, S.L. et al. Phenomenological model of preloaded spindle behavior at high speed. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 3643–3654 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9702-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9702-1