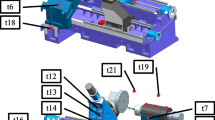
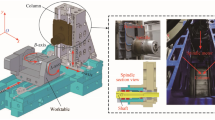
Abstract
Many studies indicate that thermal errors induced by spindle account for about 50–80 % of the total thermal errors of a machine tool due to the continuous rotation of the spindle during machining. The drawbacks of the commonly used axial thermal growth compensation methods for spindles were studied. In the present work, a robust axial thermal growth model for the spindle, based on the temperature variation, is proposed. Considering the exponential trend of the axial thermal growth of the spindle, the suggested model is based on an exponential formula. The results show that the steady value of axial thermal growth is changing with the spindle rotating speed. Therefore, the real-time steady value of axial thermal growth was predicted using the velocity and acceleration of temperature variation in the key point of the spindle. Additionally, the identification method for the parameters in the suggested model was also presented. The environmental temperature variation error (ETVE) and error induced by spindle rotation (EIBSR) were investigated using a CNC turning machine. The results recorded on the two turning machines indicated that high accuracy and strong robustness can be achieved with the suggested model, even when the rotating speed of the spindle changes randomly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesh R, Mannan MA, Poo AN (2000) Error compensation in machine tools—a review. Part II: thermal errors. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40(9):1257–1284
Yang J, Shi H, Feng B, Zhao L, Ma C, Mei XS (2015) Thermal error modeling and compensation for a high-speed motorized spindle. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 77(5-8):1005–1017
Mori M, Mizuguchi H, Fujishima M, Ido Y, Mingkai N, Konishi K (2009) Design optimization and development of CNC lathe headstock to minimize thermal deformation. CIRP Ann–Manuf Technol 58:331–334
Jiao Y, Sun LJ, Hong HB, Yin YH (2015) Material thermal conductivity determination and structure optimization of ultra-precision optical machine tool. J Mech Eng 51(1):167–175
Sun ZC, Tao T, Huang XY, Mei XS, Wang XM, Yang J, Zhao L (2015) Modeling and compensation of coupled thermal error of spindle and feed shafts. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ 49(7):105–111
Mayr J, Jedrzejewwski J, Uhlmann E, Donmez MA, Knapp W, Hartig F, Wendt K, Moriwaki T, Shore P, Schmitt R, Brecher C, Wurz T, Wegener K (2012) Thermal issues in machine tools. CIRP Ann—Manuf Technol 61(2):771–791
Li Y, Zhao WH, Lan SH, Ni J, Wu WW, Lu BH (2015) A review on spindle thermal error compensation in machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 95:20–38
Lei CL, Rui ZY (2012) Thermal error modeling and forecasting based on multivariate autoregressive model for motorized spindle. Mech Sci Technol Aerosp Eng 31(9):1526–1529
Chen JS, Hsu WY (2003) Characterizations and models for the thermal growth of a motorized high speed spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:1163–1170
Lin Z, Chang J (2007) The building of spindle thermal displacement model of high speed machine center. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 34:556–566
Wu CW, Tang CH, Chang CF, Shiao YS (2011) Thermal error compensation method for machine center. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 59:681–689
Krulewich DA (1998) Temperature integration model and measurement point selection for thermally induced machine tool errors. Mechatronics 8:395–412
Yang H, Ni J (2005) Dynamic neural network modeling for nonlinear, nonstationary machine tool thermally induced error. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45:455–465
Zhang Y, Yang JG, Jiang H (2012) Machine tool thermal error modeling and prediction by grey neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 59:1065–1072
Xiang ST, Yang JG, Zhang Y (2014) Modeling method for spindle thermal error based on mechanism analysis and thermal basic characteristics tests. J Mech Eng 50(11):144–152
Yang JG, Fan KG (2013) Research on the thermal deformation pseudo-lag and real-time compensation for CNC machine tool spindle. J Mech Eng 49(23):129–135
Yang J (1999) Thermal error mode analysis and robust modeling for error compensation on a CNC turning center. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39:1367–1381
Zhu J (2008) Robust thermal error modeling and compensation for CNC machine tools. Dissertation, University of Michigan
Shu QL, Li YL, Lv YS (2012) Application of time series analysis to thermal error modeling on NC micro-grinder. Mod Mach Tool Auto Manuf Tech 12:30–32
Li YX, Tong HC, Cao HT, Zhang HT, Yang JG (2006) Application of time series analysis to thermal error modeling on NC machine tool. J Sichuan Univ (Eng Sci Ed) 38(2):74–78
Lin WQ, Fu JZ, Chen ZC, Xu YZ (2009) Modeling of NC machine tool thermal error based on adaptive best-fitting WLS-SVM. J Mech Eng 45(3):178–182
Xu Y Z (2006) Research on thermal error modeling of machine tools based on least squares support vector machine. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Miao EM, Gong YY, Xu ZS, Zhou XS (2015) Comparative analysis of thermal error compensation model robustness of CNC machine tools. J Mech Eng 51(7):130–135
Jiang H, Yang JG, Yao XD, Zhang YS, Yuan F (2013) Modeling of CNC machine tool spindle thermal distortion with LS-SVM based on Bayesian inference. J Mech Eng 49(15):115–121
Creighton E, Honegger A, Tulsian A, Mukhopadhyay D (2010) Analysis of thermal errors in a high-speed micro-milling spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50:386–393
ISO 230-2: 2006 (2006) Test code for machine tools—part 2: determination of accuracy and repeatability of positioning numerically controlled axes. International Standards Organization, Switzerland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Liu, Y., Sun, M. et al. Spindle axial thermal growth modeling and compensation on CNC turning machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87, 2285–2292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8593-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8593-5