Abstract
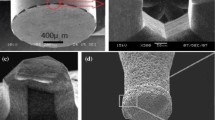
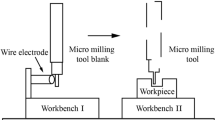
Micromachining has become a necessary manufacturing process. Micro-milling tool and its evolution play a vital role in the development of micromachining. This study optimizes the grinding process of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) compact for manufacturing PCD micro-tool. The optimization is conducted by using four parameters, i.e., grain size of PCD compact, grain size of abrasive wheel, grinding speed, and feed rate designed by the Taguchi orthogonal array. The study then evaluates two grinding characteristics, i.e., grinding forces and cutting edge radius of the PCD compact. The results of ANOVA show that the most influential parameter on grinding PCD compact is the grain size of the PCD compact, followed by the grain size of the abrasive wheel, feed rate, and grinding speed. As an example, a quadrilateral PCD micro-milling tool with a cutting edge diameter of 80 μm is fabricated by using the optimized parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dornfeld D, Min S, Takeuchi Y (2006) Recent advances in mechanical micromachining. Ann Manuf Technol 55:745–768
Chae J, Park SS, Freiheit T (2006) Investigation of micro-cutting operations. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46:313–332
Morgan CJ, Vallance RR, Marsh ER (2006) Micro-machining and micro-grinding with tools fabricated by micro electro-discharge machining. International Journal of Nanomanufacturing 1:242–258
Perveen A, Jahan MP, Rahman M, Wong YS (2012) A study on microgrinding of brittle and difficult-to-cut glasses using on-machine fabricated poly crystalline diamond (PCD) tool. J Mater Process Technol 212:580–593
Morgan CJ, Vallance RR, Marsh ER (2004) Micro machining glass with polycrystalline diamond tools shaped by micro electro discharge machining. J Micromech Microeng 14:1687–1692
Adams DP, Vasile MJ, Benavides G, Campbell AN (2001) Micro milling of metal alloy with focused ion beam-fabricated tools. Precision Engineering 25:107–113
Fleischer J, Deuchert M, Ruhs C, Ku¨hlewein C, Halvadjiysky G, Schmidt C (2008) Design and manufacturing of micro milling tools. Microsystem Technologies 14:1771–1175
Cheng X, Wang Z, Nakamoto K, Yamazaki K (2010) A study on the micro tooling for micro/nano milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2856-3
Zhang Z, Peng H, Yan J (2013) Micro-cutting characteristics of EDM fabricated high-precision polycrystalline diamond tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 65:99–106
Nakamoto K, Katahira K, Rahman M, Wong YS (2012) A study on the quality of micro-machined surfaces on tungsten carbide generated by PCD Micro end-milling. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61:567–570
Fonda P, Katahira K, Kobayashi Y, Yamazaki K. WEDM condition parameter optimization for PCD micro tool geometry fabrication process and quality improvement. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-3977-7
Uhlmann E, Schauer K (2005) Dynamic load and strain analysis for the optimization of micro end mills. Annals of the ICRP 54:75–78
Jin M, Goto I, Ti W, Kurosawa J, Murakawa M (2007) Development of cBN ball-nosed end mill with newly designed cutting edge. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:48–54
Mamalis AG, Horvath M, Grabchenko AI (2000) Diamond grinding of super-hard materials. J Mater Process Technol 97:120–125
Denkena B, Köhler J, Ventura CEH (2014) Grinding of PCBN cutting inserts. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 42:91–96
Ross PJ (1988) Taguchi techniques for quality engineering. Mc Graw-Hill, New York
Ghani JA, Choudhury IA, Hassan HH (2004) Application of Taguchi method in the optimization of end milling parameters. J Mater Process Technol 145:84–92
Zhang JZ, Chen JC, Daniel KE (2007) Surface roughness optimization in an end-milling operation using the Taguchi design method. J Mater Process Technol 184:233–239
Tzeng CJ, Lin YH, Yang YK, Jeng MC (2009) Optimization of turning operations with multiple performance characteristics using the Taguchi method and Grey relational analysis. J Mater Process Technol 209:53–2759
Denkena B, Köhler J, Ventura C (2014) Influence of grinding parameters on the quality of highcontent PCBN cutting compact. J Mater Process Technol 214:276–284
Hsiang CC, Cheng WY, Yin LB (2013) The optimal design of micro end mill for milling SKD61 tool steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:165–173
Chen Y, Zhang L (2013) Polishing of diamond materials: mechanisms, modeling and implementation. Engineering Materials and Processes. Springer, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, Z., Li, L., He, N. et al. An experimental study on grinding parameters for manufacturing PCD micro-milling tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73, 1799–1806 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5969-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5969-2