Abstract
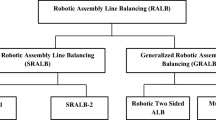
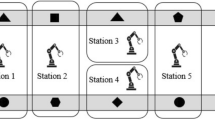
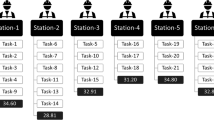
In this paper, type II robotic mixed-model two-sided assembly line balancing (RMTALB-II) problem is considered. In recent years, robots have been widely used in assembly systems as called robotic assembly lines where a set of tasks have to be assigned to stations and each station needs to select one of the different robots to process the assigned tasks. Two-sided assembly lines are especially used to produce large-sized high-volume products, such as automobiles, trucks, and buses. In this type of production line, both left side and right side of the line are used in parallel. However, little attention has been paid to solve RMTALB problems. Moreover, according to our best knowledge, there is no published work in the literature on RMTALB. This paper presents a new mixed-integer programming model for RMTALB-II to minimize the cycle time for a given number of mated stations. Since RMTALB problems are in NP-hard class of combinatorial optimization problems, a simulated annealing (SA) algorithm as metaheuristic method is proposed to solve the problem. Some problems are solved by SA and performance of the SA is evaluated by comparing their results with the optimal solution. The computational results show that SA is more efficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levitin G, Rubinovitz J, Shnits B (2006) A genetic algorithm for robotic assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168(3):811–825
Scholl A, Becker C (2006) State-of-the-art exact and heuristic solution procedures for simple assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168(3):666–693
Gao J, Sun L, Wang L, Gen M (2009) An efficient approach for type II robotic assembly line balancing problems. Comput Ind Eng 56(3):1065–1080
Bartholdi JJ (1993) Balancing two-sided assembly lines: a case study. Int J Prod Res 31(10):2447–2461
Rubinovitz J, Bukchin J (1991) Design and balancing of robotic assembly lines. In: Proceedings of the fourth world conference on robotics research, Pittsburgh, PA
Rubinovitz J, Bukchin J (1993) RALB—a heuristic algorithm for design and balancing of robotic assembly line. Ann CIRP 42(1):497–500
Tsai DM, Yao MJ (1993) A line-balanced-base capacity planning procedure for series-type robotic assembly line. Int J Prod Res 31(8):1901–1920
Kim H, Park S (1995) Strong cutting plane algorithm for the robotic assembly line balancing. Int J Prod Res 33(8):2311–2323
Yoosefelahi A, Aminnayeri M, Mosadegh H, Ardakani HD (2012) Type II robotic assembly line balancing problem: an evolution strategies algorithm for a multi-objective model. J Manuf Syst 31(2):139–151
Kim YK, Kim Y, Kim YJ (2000) Two-sided assembly line balancing: a genetic algorithm approach. Prod Plan Control 11(1):44–53
Baykasoglu A, Dereli T (2008) Two-sided assembly line balancing using an ant-colony-based heuristic. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36(5–6):582–588
Kim YK, Song WS, Kim JH (2009) A mathematical model and a genetic algorithm for two-sided assembly line balancing. Comput Oper Res 36(3):853–865
Wu EF, Jin Y, Bao JS, Hu XF (2008) A branch-and-bound algorithm for two-sided assembly line balancing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(9–10):1009–1015
Özcan U (2010) Balancing stochastic two-sided assembly lines: a chance constrained, piecewise-linear, mixed integer program and a simulated annealing algorithm. Eur J Oper Res 205(1):81–97
Rabbani M, Moghaddam M, Manavizadeh N (2012) Balancing of mixed model two sided assembly lines with multiple ushaped layout. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59(9–12):1191–1210
Noorul Haq A, Jayaprakash J, Rengarajan K (2006) A hybrid genetic algorithm approach to mixed-model assembly line balancing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28(3–4):337–341
Simaria AS, Vilarinho PM (2009) 2-ANTBAL: an ant colony optimization algorithm for balancing two-sided assembly lines. Comput Ind Eng 56(2):489–506
Ozcan U, Toklu B (2009) Balancing of mixed-model two-sided assembly lines. Comput Ind Eng 57(1):217–227
Özcan U, Toklu B (2010) Balancing two-sided assembly lines with sequence-dependent setup times. Int J Prod Res 48(18):5363–5383
McMullen PR, Frazier GV (1998) Using simulated annealing to solve a multi objective assembly line balancing problem with parallel workstations. Int J Prod Res 36(10):2717–2741
Kara Y, Ozcan U, Peker A (2007) An approach for balancing and sequencing mixed-model JIT U-lines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(11–12):1218–1231
Vilarinho PM, Simaria AS (2002) A two-stage heuristic method for balancing mixed-model assembly lines with parallel workstations. Int J Prod Res 40(6):1405–1420
Baykasoglu A (2006) Multi-rule multi-objective simulated annealing algorithm for straight and U type assembly line balancing problems. J Intell Manuf 17(2):217–232
Erel E, Sabuncuoglu I, Aksu BA (2001) Balancing of U-type assembly systems using simulated annealing. Int J Prod Res 39(13):3003–3015
Suresh G, Sahu S (1994) Stochastic assembly line balancing using simulated annealing. Int J Prod Res 32(8):1801–1810
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Veechi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–679
Arkat J, Saidi M, Abbasi B (2007) Applying simulated annealing to cellular manufacturing system design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(5–6):531–536
Safaei N, Saidi-Mehrabad M, Jabal-Ameli MS (2008) A hybrid simulated annealing for solving an extended model of dynamic cellular manufacturing system. Eur J Oper Res 185(2):563–592
Lee TO, Kim Y, Kim YK (2001) Two-sided assembly line balancing to maximize work relatedness and slackness. Comput Ind Eng 40(3):273–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghajani, M., Ghodsi, R. & Javadi, B. Balancing of robotic mixed-model two-sided assembly line with robot setup times. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74, 1005–1016 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5945-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5945-x