Abstract
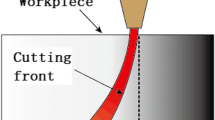
The abrasive water jet (AWJ) retardation inside the cut material, the characteristic phenomenon of the AWJ cutting, causes declination of the kerf sidewalls especially in corners and curvatures. This paper is aimed at a description of the origin of these negative consequences of jet retardation. The model for calculation of the limit traverse speed from both the jet parameters and material properties has been derived using laws of conservation. The equation expressing dependence of the angle between the tangent to the striation curve and the impinging jet axis on the depth of jet penetration into material has been used for evaluation of the product distortion in the cutting process. Proposed model has been applied for setting up the tilting angle of the cutting head during the AWJ cutting process to reduce the product shape distortion. The model was supplemented by geometrical analysis of curved parts of cut trajectories. The resulting equation makes possible to calculate the shift of the jet trajectory at the outlet side of the workpiece from its regular position determined by projection of the trajectory at the inlet side of the workpiece along the jet axis. The model is capable to determine the appropriate tilting angles of the cutting head for compensation of the jet retardation and the taper. The experimental data measured on metal samples seem to be in a good accordance with the proposed model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashish M (1984) Modeling study of metal cutting with abrasive waterjets. J Eng Mater Technol-Trans ASME 106:88–100
Hashish M (1989) A model for abrasive waterjet (AWJ) machining. J Eng Mater Technol-Trans ASME 111:154–162
Zeng J, Kim TJ (1992) Development of an abrasive waterjet kerf cutting model for brittle materials. In: Lichtarowicz A (ed) Jet cutting technology. Kluwer, Netherlands, pp 483–501
Zeng J, Kim TJ (1996) An erosion model of polycrystalline ceramics in abrasive waterjet cutting. Wear 193:207–217
Kovacevic R, Yong Z (1996) Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining: part 1—theoretical basis. In: Gee C (ed) Jetting Technology. Mech Eng Pub Ltd, Bury St Edmunds, pp 73–82
Yong Z, Kovacevic R (1996) Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining: part 2—simulation of machining. In: Gee C (ed) Jetting technology. Mech Eng Pub Ltd, Bury St Edmunds, pp 83–89
Hlaváč LM (1998) JETCUT—software for prediction of high-energy waterjet efficiency. In: Louis H (ed) Jetting technology. Prof Eng Pub Ltd, Bury St Edmunds, pp 25–37
Chen FL, Wang J, Lemma E, Siores E (2003) Striation formation mechanism on the jet cutting surface. J Mater Process Technol 141:213–218
Henning A, Westkämper E (2006) Analysis of the cutting front in abrasive waterjet cutting. In: Longman P (ed) Water jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, pp 425–434
Monno M, Pellegrini G, Ravasio C (2006) An experimental investigation of the kerf realised by AWJ: the influence of the pressure fluctuations. In: Longman P (ed) Water jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, pp 309–321
Deam RT, Lemma E, Ahmed DH (2004) Modelling of the abrasive water jet cutting process. Wear 257:877–891. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2004.04.002
Orbanic H, Junkar M (2008) Analysis of striation formation mechanism in abrasive water jet cutting. Wear 265:821–830. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2008.01.018
Hlaváč LM (2009) Investigation of the abrasive water jet trajectory curvature inside the kerf. J Mater Process Technol 209:4154–4161. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.10.009
Hloch S, Fabian S, Straka L (2006) Factor analysis and mathematical modelling of AWJ cutting. In: Kyttner R (ed) Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of DAAAM Baltic Industrial Engineering—adding innovation capacity of labour force and entrepreneur. Tallinn, Estonia, pp 127–132
Hloch S, Gombár M, Fabian S, Straka L (2006) Factor analysis of abrasive waterjet process factors influencing the cast aluminum surface roughness. In: Venkatesh VC, El-Tayeb NSM (eds) Proceedings of ICOMAST2006 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Technology. GKH Press, Melaka, Malaysia, pp 145–149
Hlaváč L (1992) Physical description of high energy liquid jet interaction with material. In: Rakowski Z (ed) Geomechanics 91. Balkema, Netherlands, pp 341–346
Hlaváč LM, Hlaváčová IM, Gembalová L, Kaličinský J, Fabian S, Měšťánek J, Kmec J, Mádr V (2009) Experimental method for the investigation of the abrasive water jet cutting quality. J Mater Process Technol 209:6190–6195. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.04.011
Hashish M (2004) Precision cutting of thick materials with AWJ. In: Gee C (ed) Water jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, pp 33–45
Ma C, Deam RT (2006) A correlation for predicting the kerf profile from abrasive water jet cutting. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 30:337–343. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2005.08.003
Fabian S, Servátka M (2009) New access at improvement of samples surface relief representation accuracy cut with AWJ technology with binding on increase of experiments evaluation objectivity and effectiveness. In: Fabian S (ed) Scientific papers operation and diagnostics of machines and production systems operational states (Vol. 2), 1st edn. RAM, Germany, pp 9–15
Janurová E, Hlaváč LM, Mádr V, Slivečka L (2007) Optical device development for measurement of wall quality after abrasive water jet cutting. In: Hloch S et al (eds) Technology Systems Operation. Prešov, Slovakia, pp 199–202
Hlaváč LM (2008) Letter to the editor. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1525–1526. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.04.006
Shanmugam DK, Wang J, Liu H (2008) Minimisation of kerf tapers in abrasive waterjet machining of alumina ceramics using a compensation technique. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1527–1534. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.07.001
Srinivasu DS, Axinte DA, Shipway PH, Folkes J (2009) Influence of kinematic operating parameters on kerf geometry in abrasive waterjet machining of silicon carbide ceramics. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:1077–1088. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.07.007
Alberdi A, Rivero A, Lopez de Lacalle LN, Etxeberria I, Suarez A (2010) Effect of process parameter on the kerf geometry in abrasive water jet milling. Int J Adv Manufac 51(5–8):467–480. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2662-y
Wang JM, Gao N, Gong WJ (2010) Abrasive waterjet machining simulation by SPH method. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 50:227–234. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2521-x
Hlaváč LM, Gembalová L, Hlaváčová IM, Mádr V, Měšťánek J (2008) Quality evaluation of the AWJ cutting through the declination angle. In: Longman P (ed) Water Jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, Bedford, England, pp 31–44
Hlaváčová IM, Hlaváč LM, Gembalová L, Matýsek D (2008) Propagation of the abrasive water jet in free air and through material. In: Longman P (ed) Water Jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, Bedford, England, pp 21–30
Hlaváč LM, Hlaváčová IM, Gembalová L, Jonšta P (2010) Experimental investigation of depth dependent kerf width in abrasive water jet cutting. In: Trieb FH (ed) Water Jetting. BHR Group, Cranfield, Bedford, England, pp 459–467
Hlaváč LM, Hlaváčová IM, Jandačka P, Zegzulka J, Viliamsová J, Vašek J, Mádr V (2010) Comminution of Material Particles by Water Jets – Influence of the Inner Shape of the Mixing Chamber. Int J Miner Process 95:25–29. doi:10.1016/j.minpro.2010.03.003
Hlaváč LM, Martinec P (1998) Almandine garnets as abrasive material in high-energy waterjet - physical modelling of interaction, experiment, and prediction. In: Louis H (ed) Jetting Technology, Prof. Eng. Pub. Ltd., Bury St Edmunds & London, pp 211–223
Jandačka P, Hlaváč LM, Mádr V, Šancer J, Staněk F (2009) Measurement of Specific Fracture Energy and Surface Tension of Brittle Materials in Powder Form. Int J Fract 159:103–110. doi:10.1007/s10704-009-9376-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hlaváč, L.M., Strnadel, B., Kaličinský, J. et al. The model of product distortion in AWJ cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62, 157–166 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3788-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3788-2