Abstract
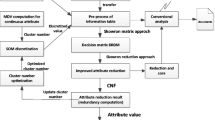
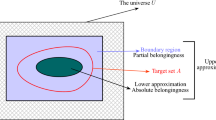
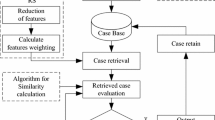
Multistage manufacturing systems (MMS) have been investigated extensively. However, quality and dimensional problems are still one of the most important research topics, especially rapid diagnosis of dimensional failures is of critical concern. Due to the knowledge and experience intension nature of fault diagnosis, the diagnostic results depend on the preference of the decision makers on the hidden relations between possible faults and presented symptoms. In this paper, a rough set-based fault diagnosis method is proposed, and a rapid fault diagnosis system with rough set is developed. The novel approach uses rough sets theory as a knowledge extraction tool to deal with the data that are obtained from both sensors and statistical process control charts and then extracts a set of minimal diagnostic rules encoding the preference pattern of decision making by experts in the field. By means of knowledge acquisition, the machining process failures in MMS can then be identified. A practical system is presented to illustrate the efficiency and effectivity of our method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Q, Shi J (2004) Stream of variation modeling and analysis of serial-parallel multistage manufacturing systems. J Manuf Sci Eng 126:611–618
Hu S, Koren Y (1997) Stream of variation theory for automotive body assembly. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 46(1):1–6
Huang Q, Zhou S, Shi J (2002) Diagnosis of multi-operational machining processes through variation propagation analysis. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 18:233–239
Ceglarek D, Huang W, Zhou S, Ding Y, Kumar R, Zhou Y (2004) Time-based competition in manufacturing: stream-of-variation analysis methodology-review. Int J Flex Manuf Syst 16(1):11–44
Zhang M, Djurdjanovic D, Ni J (2007) Diagnosibility and sensitivity analysis for multi-station machining processes. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(3–4):646–657
Barhak J, Djurdjanovic D, Spicer P, Katz R (2005) Integration of reconfigurable inspection with stream of variations methodology. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(4–5):407–419
Agapiou JS, Eric S, Gu F, Pulak B (2003) Modeling machining errors on a transfer line to predict quality. J Manuf Process 5(1):1–12
Ramesh R, Mannan MA, Poo A (2000) Error compensation in machine tools—a revire part I: geometric, cutting-force induced and fixture dependent errors. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40:1235–1256
Huang WZ, Lin J, Kong Z, Ceglarek D (2007) Stream-of-varition(SOVA) modeling-part II:a generic 3D variation model for rigid body assembly in multistation assembly processes. J Manuf Sci Eng 129(8):832–842
Wang Q, Li J (2004) A rough set-based fault ranking prototype system for fault diagnosis. Eng Appl Artif Intell 17:909–917
Pawlak Z (1991) Rough sets: theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer, Dordrecht. ISBN 0-7923-1472-7
Pawlak Z, Skowron A (2007) Rough sets and boolean reasoning. Inf Sci 177:41–73
Pawlak Z, Skowron A (2007) Rough sets: some extensions. Inf Sci 177:28–40
Shen L, Francis EH, Qu L, Shen Y (2000) Fault diagnosis using rough sets theory. Comput Ind 43:61–72
Khoo L, Tor SB, Li JR (2001) A rough set approach to the ordering of basic events in a fault tree for fault diagnosis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 17:769–774
Mannar K, Ceglarek D (2004) Continuous failure diagnosis for assembly systems using rough set approach. Ann CIRP 53:39–42
Koutras MV, Bersimis S, Maravelakis PE (2007) Statistical process control using shewhart control charts with supplementary runs rules. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 9:207–224
Zhang G, Sun J (2003) Quality management. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Pawlak Z, Grzymala J, Slowinski R, Ziarko W (1995) Rough sets. Commun ACM 38(11):88–95
Shen Q, Jensen R (2007) Rough sets, their extensions and applications. Int J Autom Comput 4(3):217–228
Francis EH, Shen L (2003) Faults diagnosis based on rough set theory. Eng Appl Artif Intell 16(1):39–43
Liu Q (2001) Rough set and rough reasoning. Science Press, Beijing
Zhao Z, Peng Y (2003) Knowledge-based engineering design: theory, method and practice. Mech Sci Technol Aerosp Eng 22(1):151–153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, N., Chen, L. & Li, A. Fault diagnosis of multistage manufacturing systems based on rough set approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48, 1239–1247 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2324-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2324-0