Abstract
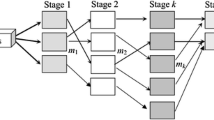
We consider the scheduling problem in hybrid flow shops that consist of two stages in series, each of which has multiple identical parallel machines. Each job has reentrant flow, i.e., the job visits each production stage several times. The problem is to determine the allocation of jobs to machines as well as the sequence of the jobs assigned to each machine for the objective of minimizing makespan subject to the maximum allowable due dates in the form of a constraint set with a certain allowance. To solve the problem, two types of algorithms are suggested: (a) a branch and bound algorithm that gives optimal semi-permutation schedules; and (b) heuristic algorithms that give non-permutation schedules. To show their performances, computational experiments were done on a number of test problems and the results are reported. In particular, one of the heuristics is competitive to the branch and bound algorithm with respect to the solution quality while requiring much shorter computation times.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linn R, Zhang W (1999) Hybrid flow shop scheduling. Comput Ind Eng 37:57– 61 doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(99)00023-6
Lee G-C, Kim Y-D (2004) A branch-and-bound algorithm for a two-stage hybrid flow shop scheduling problem minimizing total tardiness. Int J Prod Res 42:4731–4743 doi:10.1080/0020754041233127044
Tsubone H, Ohba M, Uetake T (1996) The impact of lot sizing and sequencing on manufacturing performance in a two-stage hybrid flow shop. Int J Prod Res 34:3037–3053 doi:10.1080/00207549608905076
Gupta JND, Tunc EA (1991) Scheduling for a two-stage hybrid flowshop with parallel machines at the second stage. Int J Prod Res 29:1480–1502
Lee CY, Vairaktarakis GL (1994) Minimizing makespan in hybrid flow shops. Oper Res Lett 16:149–158 doi:10.1016/0167-6377(94)90026-4
Chen B (1995) Analysis of classes of heuristics for scheduling a two-stage flow shop with parallel machines at one stage. J Oper Res Soc 46:231–244
Lee J-S, Park S-H (1999) Scheduling heuristics for a two-stage hybrid flowshop with nonidentical parallel machines. J Korean Inst Ind Engineers 25:254–265
Riane F, Artiba A, Elmaghraby SE (1998) A hybrid three-stage flowshop problem: efficient heuristics to minimize makespan. Eur J Oper Res 109:321–329 doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(98)00060-5
Brah SA, Hunsucker JL (1991) Branch and bound algorithm for the flow shop with multiple processors. Eur J Oper Res 51:88–99 doi:10.1016/0377-2217(91)90148-O
Mourisli O, Pochet Y (2000) A branch-and-bound algorithm for the hybrid flow shop. Int J Prod Econ 64:113–125 doi:10.1016/S0925-5273(99)00051-1
Gupta JND, Tunc EA (1998) Minimizing tardy jobs in a two-stage hybrid flowshop. Int J Prod Res 36:2397–2417 doi:10.1080/002075498192599
Azizoglu M, Cakmak E, Kondakci S (2001) A flexible flow shop problem with total flow time minimization. Eur J Oper Res 132:528–538 doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00142-9
Lee G-C, Kim Y-D, Choi S-W (2004) Bottleneck-focused scheduling for a hybrid flow shop. Int J Prod Res 42:165–181 doi:10.1080/00207540310001602892
Choi H-S, Lee D-H (2007) A branch and bound algorithm for two-stage hybrid flow shops: minimizing the number of tardy jobs. J Korean Inst Ind Engineers 33:213–220
Jungwattanakit J, Reodecha M, Chaovalitwongse P, Werner F (2008) Algorithms for flexible flow shop problems with unrelated parallel machines, setup times, and dual criteria. Int J Adv Manuf Technol (in press) doi:10.1007/s00170-007-0977-0
Guo ZX, Wong WK, Leung SYS, Fan JT, Chan SF (2008) A genetic-algorithm-based optimization model for scheduling flexible assembly lines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:156– 168 doi:10.1007/s00170-006-0818-6
Bertel S, Billaut JC (2004) A genetic algorithm for an industrial multiprocessor flow shop scheduling problem with recirculation. Eur J Oper Res 159:651–662 doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(03)00434-X
Choi S-W, Kim Y-D, Lee G-C (2005) Minimizing total tardiness of orders with reentrant lots in a hybrid flowshop. Int J Prod Res 43:2149–2167 doi:10.1080/00207540500050071
Wang MY, Sethi SP, Van de Velde SL (1997) Minimizing makespan in a class of reentrant shops. Oper Res 45:702–712
Hwang H, Sun JU (1997) Production sequencing problem with reentrant work flows and sequence dependent setup times. Comput Ind Eng 33:773–776 doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(97)00250-7
Drobouchevitch IG, Strusevich VA (1999) A heuristic algorithm for two-machine re-entrant shop scheduling. Ann Oper Res 86:417–439 doi:10.1023/A:1018927407164
Pan JCH, Chen JS (2003) Minimizing makespan in re-entrant permutation flow-shops. J Oper Res Soc 54:642–653 doi:10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601556
Chen JS (2006) A branch and bound procedure for the reentrant permutation flow-shop scheduling problem. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29:1186–1193 doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0017-x
Park YS, Kim SY, Jun CH (2002) Mean value analysis of re-entrant line with batch machines and multi-class jobs. Comput Oper Res 29:1009–1024 doi:10.1016/S0305-0548(00)00099-X
Uzsoy R, Lee C-Y, Martin-Vega LA (1992) A review of production planning and scheduling models in the semiconductor industry part I: system characteristics, performance evaluation and production planning. IIE Trans 24:47–60 doi:10.1080/07408179208964233
Uzsoy R, Lee C-Y, Martin-Vega LA (1994) A review of production planning and scheduling models in the semiconductor industry part II: shop-floor control. IIE Trans 26:44–55 doi:10.1080/07408179408966627
Wein LM (1988) Scheduling semiconductor wafer fabrication. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 1:115–130 doi:10.1109/66.4384
Glassey CR, Resende MCG (1988) A scheduling rule for job release in semiconductor fabrication. Oper Res Lett 7:213–217 doi:10.1016/0167-6377(88)90033-8
Kim Y-D, Lee D-H, Kim J-U, Roh H-K (1998) A simulation study on lot release control, dispatching and batch scheduling in semiconductor wafer fabrication facilities. J Manuf Syst 17:107–117
Pan JCH, Chen JS (2005) Mixed binary integer programming formulations for the reentrant job shop scheduling problem. Comput Oper Res 32:1197–1212
McNaughton R (1965) Scheduling with deadlines and loss functions on k parallel machines. Manage Sci 11:460–475
Campbell HG, Dudek RA, Smith ML (1970) A heuristic algorithm for the n job m machine sequencing problem. Manage Sci 16:630–637
Baker KR (1974) Introduction to sequencing and scheduling. Wiley, New York
Nawaz M, Enscore E, Ham I (1983) A heuristic algorithm for the m machine, n job flow shop sequence problem. OMEGA Int J Manage Sci 11:91–95 doi:10.1016/0305-0483(83)90088-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, HS., Kim, HW., Lee, DH. et al. Scheduling algorithms for two-stage reentrant hybrid flow shops: minimizing makespan under the maximum allowable due dates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42, 963–973 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1656-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1656-5