Abstract
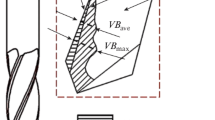
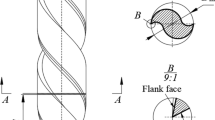
For the improvement of machining precision and stability of the grinding process it is very important to perform research on wear detection of the wheel. Conventional wear detection methods depended on the wheel’s optical projection, and its detection error was relatively large due to more subjective factors in the detection process. Meanwhile, non-contact acquisition and processing of the object could be realized by the use of digital image processing technology, and the processing precision and stability was relatively good. Thus, the technology of digital image acquisition and recognition was applied in the research of wear detection of the wheel in precision NC curve grinding. In this work, the working process of new-type curve point grinding based on normal tracing is first introduced in detail; second, the evaluation method of the wheel’s wear is presented, and a description of the wear detection system of the wheel which was built. Lastly a location algorithm of sub-pixels was studied in order to improve the detection precision of the wheel’s wear. Experimental results of wear detection of the wheel showed great improvement of machining precision and verified the effectiveness of wear detection of the wheel based on digital image acquisition and recognition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu QF, Lu HW, Liu XL (2002) Precision measurement and movement measurement based on image. Scientific Technology Press
Wu Q, Hu DJ (2006) Research on NC point-grinding of the curve based on normal tracing. Key Eng Mater 304–305(2):488–491
Zhao CM, Liu WJ (2004) Quick point grinding processing and its application on automobile manufacturing. Manuf Technol Mach Tool 6:67–68
Gu YS (1995) Advanced external circle grinding processing. Automob Process Mater 10:8–9
Anonymous (1997) Germans study O.D. grinding process. Automot Manuf Prod 4(109):39
Junker (2004) Technical file of NC point grinding. Junker Corp.
Tabatabai AJ, Mitchell OR (1984) Edge location to subpixel values in digital imagery. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 6(2):188–201
Jensen K, Anastassiou D (1995) Subpixel edge location and the interpolation of still images. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(3):285–295
Huertas A, Medioni G (1986) Detection of intensity changes with subpixel accuracy using Laplacian-Gaussian masks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 8(5):651–664
Liu X, Ehrich RW (1995) Subpixel edge location in binary images using dithering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(6):629–634
Kisworo M, Venkatesh S, West G (1994) Modeling edges at subpixel accuracy using the local energy approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 16(4):405–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YH., Wu, Q. & Hu, DJ. Research on wear detection of wheel in precision NC curve point grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35, 994–999 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0783-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0783-0