Abstract
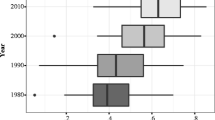
There are two types of variance generally associated with the phenomenon of racial residential segregation. One type involves differing racial compositions between spatial locations. The other is concerned with varying residential spatial distributions between ethnic groups. This paper presents a spatial analytical approach to identify and measure the two types of variance through a decomposition of an entropy index regarding racial diversity. A region’s racial diversity entropy is found to comprise three factors: (a) the overall spatial distribution of regional population; (b) the ratio between the number of ethnic groups and that of spatial areal units within the region, and (c) the differential between two types of variance aforementioned. For demonstrative purpose census data from Los Angeles County are studied using this approach. The results suggest the second type of variance to be the primary contributor to the increasing racial diversity in Los Angeles. Implications regarding affordable homeownership and inclusionary housing policies are discussed accordingly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apparicio P et al (2008) Segregation Analyzer: a C#. Net application for calculating residential segregation indices. European Journal of Geography 414
Batten DF (1983) Spatial analysis of interacting economies: the role of entropy and information theory in spatial input and output modelling. Kluwer-Nijhoff, Boston
Batty M (1976) Entropy in spatial aggregation. Geogr Anal 8: 1–21
Bernanke BS (2007) GSE portfolios, systemic risk, and affordable housing. Speech before the independent community bankers of America’s annual convention and techworld. Honolulu, Hawaii
Casey ES (2001) Between geography and philosophy. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 91(4): 683–693
Clark WAV (1992) Residential prefernces and residential choices in a multiethnic context. Demography 29(3): 451–466
Ethington PJ et al (2000) Los Angeles County union census tract data series, version 1.01, 1940–1990. University of Southern California, Los Angeles
Heikkila E, Hu L (2006) Adjusting spatial entropy measures for scale and resolution effects. Envrion Plann B 33(6): 845–861
Krieger M (1971) Modeling urban change. Socioecon Plann Sci 5(1): 41–55
Krieger M (1991) Segmentation and filtering into neighborhoods as processes of percolation and diffusion: stochastic processes (randomness) as the null hypothesis. Environ Plann A 23: 1609–1626
Logan JR et al (2002) Immigrant enclaves and ethnic communities in New York and Los Angeles. Am Sociol Rev 67(2): 299–322
Massey DS, Denton NA (1988) The dimensions of residential segregation. Soc Forces 67(2): 281–315
Massey DS, Denton NA (1989) Hypersegregation in U.S. metropolitan areas: black and hispanic segregation along five dimensions. Demography 26(3): 373–391
Massey DS, Denton NA (1993) Amercian apartheid: segregation and the making of the underclass. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Mateos P et al (2009) Uncertainty in the analysis of ethnicity classifications: issues of extent and aggregation of ethnic groups. J Ethnic Migr Stud 35(9): 1437–1460
Myers D (2007) Immigrants and boomers: forging a new social contract for the future of America. Russell Sage Foundation, New York
Openshaw S (1984) The modifiable areal unit problem. Geo Books, Norwich
Rearden SF et al (2009) Race and space in the 1990s: changes in the geographic scale of racial residential segregation, 1990–2000. Soc Sci Res 38(1): 55–70
Rearden SF, Firebaugh G (2002) Measures of multiplegroup segregation. Sociol Methodol 32: 33–67
Reardon SF, O’Sullivan D (2004) Measures of spatial segregation. Pennsylvania State University, Pennsylvania
Schelling TC (1971) Dynamic models of segregation. J Math Sociol 1: 143–186
Squires GD, O’Connor S (2001) Color and money: politics and prospects for community reinvestment in urban America. State University of New York Press, Albany
Theil H (1967) Econmics and information theory. North Holland, Amsterdam
Theil H (1972) Statistical decomposition analysis. North Holland, Amsterdam
Voas D, Williamson P (2000) The scale of dissimilarity: concepts, measurement and an application to socio economic variation across England and Wales. Trans Inst Br Geogr 25(4): 465–481
White MJ (1986) Segregation and diversity: measures in population distribution. Popul Index 52(2): 198–221
Wilkes R, Iceland J (2004) Hypersegregation in the twenty-first century. Demography 41(1): 23–36
Wong DWS (2003a) Implementing spatial segregation measures in GIS. Comput Environ Urban Syst 27(1): 53–70
Wong DWS (2003b) Spatial decomposition of segregation indices: a framework toward measuring segregation at multiple levels. Geogr Anal 35(3): 179–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y. Decomposing the entropy index of racial diversity: in search of two types of variance. Ann Reg Sci 48, 897–915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-010-0426-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-010-0426-0