Abstract
Purpose
The purposes of this study were (1) to evaluate the foot rotational effects on local and whole leg alignment and (2) to confirm the correlation between local and whole leg alignment. The hypotheses of this study were that (1) the alignment would become varus if the rotation of the foot changes from internal to external rotation, and (2) there would be some correlation between local and whole leg radiographs, and local knee radiographs could then be used indirectly for the assessment of whole leg alignment in patients with bilateral medial compartment knee osteoarthritis.
Methods
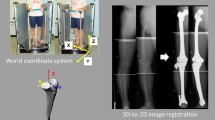
A total of 80 lower limbs with genu varum of patients who complained of medial knee pain were examined. The standing anterior–posterior view of whole leg radiographs was taken in the four foot positions, and a custom-made foot plate was used for the attainment of accurate radiographs: feet straight ahead with foot contact at the medial side (R: routine), feet straight ahead at shoulder width (N: neutral), 30° external rotated (ER) and 15° internal rotated (IR) position. In order to obtain a local radiograph of the knee, we took only whole leg radiographs and selected the area of interest on the whole leg radiograph. We evaluated the total width of the tibia plateau (Total), the length of the weight-bearing line, the ratio of weight-bearing line/Total and femorotibial angle (FTA).
Results
The absolute value of weight-bearing line was shifted laterally in the 30° ER position and shifted medially in the 15° IR position compared to the neutral position (1.8 mm lateral and 0.2 mm medial in the WLR; 3.5 mm lateral and 3 mm medial in the local radiograph). Significant statistical differences were observed in the local knee weight-bearing line; however, no significant statistical differences were observed in the weight-bearing line of the whole leg radiograph (n.s.). Results of the % (weight-bearing line/Total) were similar to those of weight-bearing line. The FTA of the local radiograph showed statistical differences, and it showed more valgus in the 30° ER position. In the correlation analysis between whole leg radiograph and local knee radiograph, moderate correlation (correlation coefficient = 0.67) was observed; however, significant statistical differences were observed in the comparison of weight-bearing line and % weight-bearing line/Total (p < 0.01 and < 0.01, respectively) between local knee and whole leg radiograph.
Conclusions
Foot position of ER could show less varus alignment and the reverse could occur in the IR position, compared to the neutral foot position. The severity of varus alignment could be underestimated in the local radiograph, compared with that of whole leg radiograph.
Level of evidence
Cohort study (diagnosis), Level II.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Ginai AZ, Verhaar JA (2003) The whole leg radiograph: standing versus supine for determining axial alignment. Acta Orthop Scand 74:565–568
Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Brouwer KH, Verhaar JA (2007) Pitfalls in determining knee alignment: a radiographic cadaver study. J Knee Surg 20:210–215
Classen T, Landgraeber S, Wegner A, Muller RD, von Knoch M (2011) Femoral component rotation in patients with leg axis deviation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:1077–1081
Hunt MA, Fowler PJ, Birmingham TB, Jenkyn TR, Giffin JR (2006) Foot rotational effects on radiographic measures of lower limb alignment. Can J Surg 49:401–406
Hunter DJ, Sharma L, Skaife T (2009) Alignment and osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(Suppl 1):85–89
Khan FA, Koff MF, Noiseux NO, Bernhardt KA, O’Byrne MM, Larson DR, Amrami KK, Kaufman KR (2008) Effect of local alignment on compartmental patterns of knee osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:1961–1969
Kraus VB, Vail TP, Worrell T, McDaniel G (2005) A comparative assessment of alignment angle of the knee by radiographic and physical examination methods. Arthritis Rheum 52:1730–1735
Lonner JH, Laird MT, Stuchin SA (1996) Effect of rotation and knee flexion on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:102–106
Marx RG, Grimm P, Lillemoe KA, Robertson CM, Ayeni OR, Lyman S, Bogner EA, Pavlov H (2011) Reliability of lower extremity alignment measurement using radiographs and PACS. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:1693–1698
Rauh MA, Boyle J, Mihalko WM, Phillips MJ, Bayers-Thering M, Krackow KA (2007) Reliability of measuring long-standing lower extremity radiographs. Orthopedics 30:299–303
Seo SS, Seo JH, Sohn MW, Kim YJ (2012) Differences in measurement of lower limb alignment among Different registration methods of navigation and radiographs in TKA using the OrthoPilot system. Orthopedics 35:50–55
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 286:188–195
Sim JA, Kwak JH, Yang SH, Choi ES, Lee BK (2010) Effect of weight-bearing on the alignment after open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:874–878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Lee, B.K., Lee, S.H. et al. Effect of foot rotation on the mechanical axis and correlation between knee and whole leg radiographs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21, 2542–2547 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2419-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2419-x