Abstract
Purpose
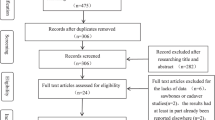
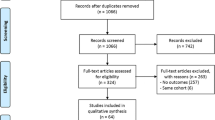
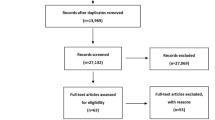
Whether navigated total knee arthroplasty can improve the limb and component alignment is a matter of debate. This systematic literature review analyzed the differences on alignment outcomes between navigated total knee arthroplasty and conventional total knee arthroplasty.
Methods
Multiple databases, online registers of randomized controlled trials were searched. Published and unpublished randomized controlled trials were included, and data on methodological quality, population, intervention, and outcomes were abstracted in duplicate. Data were pooled across studies, and odds ratios for categorical outcomes were calculated according to study sample size.
Results
Twenty-one randomized controlled trials of varying methodological quality involving 2,414 patients were included. Statistically significant differences were observed between navigated group and conventional group in mechanical axis malalignment of >3° (odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.17–0.38) and mechanical axis malalignment of >2° (odds ratio, 0.33; 95% confidence interval, 0.26–0.42). Navigated group had a lower risk of malalignment for both coronal femoral component and coronal tibial component of >3° and >2°. Both sagittal femoral component alignment and tibial slope showed statistical significance in favor of navigated arthroplasty at >2° and 3° malalignment.
Conclusion
Meta-analysis indicates significant improvement in alignment of the limb and the component position with use of computer navigation system. Its clinical benefits are unclear and remain to be defined on a larger scale randomized controlled trials with long-term follow-up.
Level of evidence
Therapeutic study (Systematic review of Level-I studies with inconsistent results), Level II.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M et al (2004) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. A comparison of computer-assisted surgery with the conventional technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:682–687
Bauwens K, Matthes G, Wich M et al (2007) Navigated total knee replacement: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:261–269
Beneyto FM, Vaquero DH, Vilalta JMS et al (2006) Navigation in total knee arthroplasty. A multicenter study. Int Orthop 30:536–540
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ et al (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Bhandari M, Morrow F, Kulkarni AV et al (2001) Meta-analysis in orthopedic surgery: a systematic review of the methodologies. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:15–24
Bohling U, Schamberger H, Grittner U et al (2005) Computerized and technical navigation in total knee-arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol 5:69–75
Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W et al (2004) Computerassisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jigbased technique. A randomized, prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:372–377
Chin PL, Yang KY, Yeo SJ, Lo NN (2005) Randomized control trial comparing radiographic total knee arthroplasty implant placement using computer navigation versus conventional technique. J Arthroplast 20:618–626
Decking R, Markmann Y, Fuchs J et al (2005) Leg axis after computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized trial comparing computer-navigated and manual implantation. J Arthroplast 20:282–288
Dutton AQ, Yeo SJ, Yang KY et al (2008) Computer-assisted minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with standard total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:2–9
Ensini A, Catani F, Leardini A et al (2007) Alignments and clinical results in conventional and navigated total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 457:156–162
Garg A, Walker PS (1990) Prediction of total knee motion using a three dimensional computer-graphics model. J Biomech 23:45–58
Hart R, Janecek M, Chaker A, Bucek P (2003) Total knee arthroplasty implanted with and without kinematic navigation. Int Orthop 27:366–369
Hernández-Vaquero D, Suarez-Vazquez A, Sandoval-Garcia MA et al (2010) Computer assistance increases precision of component placement in total knee arthroplasty with articular deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:1237–1241
Hsu WH, Hsu RW, Weng YJ (2010) Effect of preoperative deformity on postoperative leg axis in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:1323–1327
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D et al (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Jenny JY, Boeri C (2001) Computer-assisted implantation of total knee prostheses: a case-control comparative study with classical instrumentation. Comput Aided Surg 6:217–220
Kim YH, Kim JS, Choi Y, Kwon OR (2009) Computer-assisted surgical navigation does not improve the alignment and orientation of the components in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:14–19
Krackow KA, Pepe CL, Galloway EJ (1990) A mathematical analysis of the effect of flexion and rotation on apparent varus/valgus alignment at the knee. Orthopedics 13:861–868
Lützner J, Krummenauer F, Wolf C et al (2008) Computer-assisted and conventional total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:1039–1044
Mason JB, Fehring TK, Estok R et al (2007) Meta-analysis of alignment outcomes in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplast 22:1097–1106
Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U et al (2007) A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:236–242
Mullaji A, Kanna R, Marawar S et al (2007) Comparison of limb and component alignment using computer-assisted navigation versus image intensifier–guided conventional total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 22:953–959
Oberst M, Bertsch C, Wurstlin S, Holz U (2003) CT analysis of leg alignment after conventional vs. navigated knee prosthesis implantation. Initial results of a controlled, prospective, and randomized study. Unfallchirurg 106:941–948
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E et al (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 8:419–426
Saragaglia D, Picard F, Chaussard C et al (2001) Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty: comparison with a conventional procedure. Results of 50 cases in a prospective randomized study. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 87:18–28
Schmitt J, Hauk C, Kienapfel H, Pfeiffer M, Efe T, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Heyse TJ (2011) Navigation of total knee arthroplasty: rotation of components and clinical results in a prospectively randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:16
Seon JK, Song EK (2006) Navigation-assisted less invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 21:777–782
Sparmann J, Wolke B, Czupalla H et al (2003) Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:830–835
Stulberg SD, Picard F, Saragaglia D (2003) Computer-assisted total knee replacement arthroplasty. Oper Tech Orthop 10:25–39
van Strien T, der Zwaag E, Kaptein B et al (2009) Computer assisted versus conventional cemented total knee prostheses alignment accuracy and micromotion of the tibial component. Int Orthop 33:1255–1261
Victor J, Hoste D (2004) Image-based computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty leads to lower variability in coronal alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:131–139
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty R et al (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Wang, M., Liu, Y. et al. Alignment outcomes in navigated total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20, 1075–1082 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1695-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1695-6