Abstract
Purpose
The aim was to compare the patellar kinematics in the normal knee, fixed-bearing (FB) and mobile-bearing total knee replacement (MB-TKR). The hypothesis that a mobile-bearing TKR has a more natural patellar movement was tested.
Methods
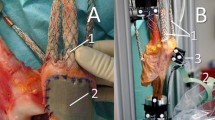
Computer navigation was used to track the patella in nine whole lower extremities in the natural knee and in the same knee with a posterior stabilised FB-TKR and a posterior stabilised MB-TKR from 0° to 90° flexion. The form and position of the trochlea in the natural knee and the patellar groove of the TKR femoral component was also analysed.
Results
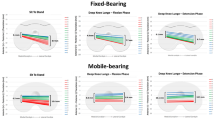
There were no differences between the FB and MB-TKRs. But the patella in the TKRs at flexion angles of more than 50° had a more medial tilt compared to the natural knee. The patella of the natural knee tended to rotate externally with flexion, this was not seen in both TKR types. There were no significant differences in absolute mediolateral translation nor in translation relative to the patellar groove. During flexion, the patella lost contact with its groove earlier in the TKRs. The radius of the patellar groove of the femoral component was larger. The groove extended more superiorly and less far posteriorly, it was also positioned further laterally compared to the natural knee.
Conclusions
There are subtle kinematic differences in patellar tracking between the natural knee and a TKR presumably due to differences in the shape and position of the patellar groove. There are no kinematic differences in patellar movement between the FB- and MB-TKR.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglin C, Brimacombe JM, Hodgson AJ, Masri BA, Greidanus NV, Tonetti J, Wilson DR (2008) Determinants of patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 23:900–910
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR (2000) Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:970–973
Kessler O, Patil S, Colwell CW Jr, D’Lima DD (2008) The effect of femoral component malrotation on patellar biomechanics. J Biomech 41:3332–3339
Lee DH, Park JH, Song DI, Padhy D, Jeong WK, Han SB (2010) Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in TKA: comparison between navigation-assisted gap balancing and conventional measured resection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:381–387
Luring C, Hüfner T, Perlick L, Bäthis H, Krettek C, Grifka J (2006) The effectiveness of sequential medial soft tissue release on coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: using a computer navigation model. J Arthroplasty 21:428–434
Masri BA, McCormack RG (1995) The effect of knee flexion and quadriceps contraction on the axial view of the patella. Clin J Sport Med 5:9–17
Miller MC, Zhang AX, Petrella AJ, Berger RA, Rubash HE (2001) The effect of component placement on knee kinetics after arthroplasty with an unconstrained prosthesis. J Orthop Res 19:614–620
Pagnano MW, Menghini RM (2006) Rotating platform knees: an emerging clinical standard: in opposition. J Arthroplasty 21(4 Suppl 1):37–39
Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Stuart MJ, Hanssen AD, Jacofsky DJ (2004) Rotating platform knees did not improve patellar tracking: a prospective, randomized study of 240 primary total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:221–227
Rees JL, Beard DJ, Price AJ, Gill HS, McLardy-Smith P, Dodd CA, Murray DW (2005) Real in vivo kinematic differences between mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 432:204–209
Skwara A, Tibesku CO, Ostermeier S, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Fuchs-Winkelmann S (2009) Differences in patellofemoral contact stresses between mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasties: a dynamic in vitro measurement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129:901–907
Song EK, Seon JK, Yoon TR, Park SJ, Cho SG, Yim JH (2007) Comparative study of stability after total knee arthroplasties between navigation system and conventional techniques. J Arthroplasty 22:1107–1111
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Depuy, Switzerland and Brainlab, Germany for their technical and logistical support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinert, G., Kendoff, D., Preiss, S. et al. Patellofemoral kinematics in mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing posterior stabilised total knee replacements: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19, 967–972 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1320-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1320-0