Abstract
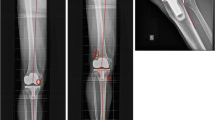
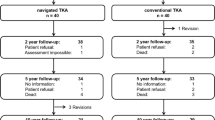
Despite the frequent use of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and better radiological results for coronal alignment reported in many studies, there is still no evidence of improved clinical outcomes when compared to conventional TKA. We compared alignment after navigated TKA and conventional TKA in 80 randomized patients. Seventy three patients were available for physical and radiological examination at 20 month after surgery. Both groups showed similar Knee Society Score results, with medians of 89 points (navigated 49–95 points, conventional 48–95 points, n.s.) in the Knee Score and 70 points (navigated 45–100 points, conventional 40–100 points, n.s.) in the Function Score. The median improvement in the Knee Society Knee Score was 45 points (−3 to 88 points) in the navigated group and 35 points (−13 to 62 points) in the conventional group (P = 0.03), and the Knee Society Function Score improvement was 15 points (−10 to 50 points) in the navigated group versus 10 points (−10 to 50 points) in the conventional group (n.s.). The current health state at follow-up using the EuroQuol questionnaire was similar in both groups, with medians of 67 points in the navigated group and 65 points in the conventional group. This investigation did show slightly greater functional improvement at short-term follow-up in the navigated TKA group. Longer follow-up will be required to assess the possible benefit of computer-assisted navigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauwens K, Matthes G, Wich M, Gebhard F, Hanson B, Ekkernkamp A, Stengel D (2007) Navigated total knee replacement. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89A:261–269
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE (2004) Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:26–34
Cerha O, Kirschner S, Gunther KP, Lützner J (2009) Cost analysis for navigation in knee endoprosthetics. Orthopäde 38:1235–1240
Dattani R, Patnaik S, Kantak A, Tselentakis G (2009) Navigation knee replacement. Int Orthop 33:7–10
DesJardins JD, Banks SA, Benson LC, Pace T, LaBerge M (2007) A direct comparison of patient and force-controlled simulator total knee replacement kinematics. J Biomech 40:3458–3466
Ewald FC (1989) The Knee Society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:9–12
Hakki S, Coleman S, Saleh K, Bilotta VJ, Hakki A (2009) Navigational predictors in determining the necessity for collateral ligament release in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91B:1178–1182
Harman MK, Banks SA, Kirschner S, Lützner J (2009) Axial alignment of mobile-bearing TKR: does it affect knee rotation and bearing motion? 10th EFORT Congress, http://www.efort.org/cdrom2009/FreePaperContent.asp?Pid=F208
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73B:709–714
Kamat YD, Aurakzai KM, Adhikari AR, Matthews D, Kalairajah Y, Field RE (2009) Does computer navigation in total knee arthroplasty improve patient outcome at midterm follow-up? Int Orthop 33:1567–1570
Kim YH, Kim JS, Choi Y, Kwon OR (2009) Computer-assisted surgical navigation does not improve the alignment and orientation of the components in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91A:14–19
Krackow KA, Pepe CL, Galloway EJ (1990) A mathematical analysis of the effect of flexion and rotation on apparent varus/valgus alignment at the knee. Orthopedics 13:861–868
Lee DH, Park JH, Song DI, Padhy D, Jeong WK, Han SB Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in TKA: comparison between navigation-assisted gap balancing and conventional measured resection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (Epub ahead of print). doi:10.1007/s00167-009-0983-x
Lotke PA, Ecker ML (1977) Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59:77–79
Lützner J, Krummenauer F, Wolf C, Günther K-P, Kirschner S (2008) Computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty—a prospective, randomized study with radiographic and CT evaluations. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90B:1039–1044
Molfetta L, Caldo D (2008) Computer navigation versus conventional implantation for varus knee total arthroplasty: a case-control study at 5 years follow-up. Knee 15:75–79
IH N (2004) NIH Consensus Statement on total knee replacement. J Bone and Joint Surg Am 86A:1328–1335
Novak EJ, Silverstein MD, Bozic KJ (2007) The cost-effectiveness of computer-assisted navigation in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89A:2389–2397
Oberst M, Bertsch C, Wurstlin S, Holz U (2003) CT analysis of leg alignment after conventional vs. navigated knee prosthesis implantation. Initial results of a controlled, prospective and randomized study. Unfallchirurg 106:941–948
Oppe M, Rabin R, de Charro F (2008) EQ-5D User Guide. www euroqol org
Rasanen P, Paavolainen P, Sintonen H, Koivisto AM, Blom M, Ryynanen OP, Roine RP (2007) Effectiveness of hip or knee replacement surgery in terms of quality-adjusted life years and costs. Acta Orthop 78:108–115
Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Tullos HS (1993) The effect of femoral component position on the kinematics of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:122–129
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Slover JD, Tosteson AN, Bozic KJ, Rubash HE, Malchau H (2008) Impact of hospital volume on the economic value of computer navigation for total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90A:1492–1500
Spencer JM, Chauhan SK, Sloan K, Taylor A, Beaver RJ (2007) Computer navigation versus conventional total knee replacement: no difference in functional results at two years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:477–480
Yaffe MA, Koo SS, Stulberg SD (2008) Radiographic and navigation measurements of TKA limb alignment do not correlate. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2736–2744
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Heike Voigt for her valuable assistance in clinical data management and evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have received funding from Stryker Orthopaedics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lützner, J., Günther, KP. & Kirschner, S. Functional outcome after computer-assisted versus conventional total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18, 1339–1344 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1153-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1153-x