Abstract
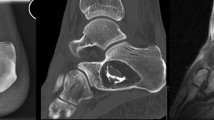
The calcaneo-fibular impingement syndrome is frequent after calcaneal fracture and is linked to the decreased space between the tip of the fibula and the lateral wall of the calcaneus. The reasons for the painful symptoms are mixed with both bony and soft tissue involvement. The abnormal bony contact between the lateral calcaneal cortex and the tip of the fibula depends mainly on the size and localization of the lateral exostosis of the calcaneal wall. The soft tissue impingement is due to the fibrosis and scar tissues in the lateral gutter and to the compression of the peroneal tendons in the retromalleolar groove and under the tip of the malleolus. A 2-portal endoscopic technique is described for the treatment of calcaneo-fibular impingement with bone resection, soft tissue debridement and peroneal tendons release. One of the advantages of this endoscopic technique is the possibility of an assessment and treatment of associated lesions in the same procedure. A subtalar joint fusion can be done before if needed under arthroscopic control. As this endoscopic technique is very efficient to relieve symptoms of calcaneo-fibular impingement and is focused on the most relevant symptoms, it can thus be indicated for most of cases of calcaneal malunions, whatever the type of malunion and depending of the painful symptoms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braly GW, Bishop JO, Tullos HS (1985) Lateral decompression for malunited os calcis fractures. Foot Ankle 6:90–92
Carr JB, Hansen ST, Bernischke SK (1988) Subtalar distraction bone block fusion for late complications of os calcis fractures. Foot Ankle 9:81–86
Carr JB (1993) Mechanism and pathoanatomy of the intraarticular calcaneal fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:36–40
Chandler JT, Bonar SK, Anderson RB, Davis WH (1999) Results of in situ subtalar arthrodesis for late sequelae of calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int 20:18–24
Clare MP, Lee WE 3rd, Sanders RW (2005) Intermediate to long-term results of a treatment protocol for calcaneal fracture malunions. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:963–973
Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T (1993) Intraarticular calcaneal fractures results of closed treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:47–54
Huang PJ, Fu YC, Cheng YM, Lin SY (1999) Subtalar arthrodesis for late sequelae of calcaneal fractures: fusion in situ versus fusion with sliding corrective osteotomy. Foot Ankle Int 20:166–170
Isbister JF (1974) Calcaneo-fibular abutment following crush fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 56:274–278
Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M (1994) Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 15:349–353
Kitaoka HB, Schaap EJ, Chao EY, An KN (1994) Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus treated non-operatively: clinical results and analysis of motion and ground reaction and temporal forces. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:1531–1540
Lim EV, Leung JP (2001) Complications of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 391:7–16
Lui TH (2007) Endoscopic lateral calcaneal ostectomy for calcaneofibular impingement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127:265–267
Lui TH (2008) Posterior ankle impingement syndrome caused by malunion of joint depressed type calcaneal fracture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:687–689
Reddy V, Fukuda T, Ptaszek AJ (2007) Calcaneus malunion and nonunion. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 12:125–135
Robinson JF, Murphy GA (2002) Arthrodesis as salvage for calcaneal malunions. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 7:107–120
Romash MM (1993) Reconstructive osteotomy of the calcaneus with subtalar arthrodesis for malunited calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:157–167
Savva N, Saxby TS (2007) In situ arthrodesis with lateral-wall ostectomy for the sequelae of fracture of the os calcis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:919–924
Stapleton JJ, Belczyk R, Zgonis T (2009) Surgical treatment of calcaneal fracture malunions and posttraumatic deformities. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 26:79–90
Stephens HM, Sanders R (1996) Calcaneal malunions: results of a prognostic computed tomography classification system. Foot Ankle Int 17:395–401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, T., Deranlot, J. & Hardy, P. Endoscopic treatment of calcaneo-fibular impingement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19, 131–136 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1149-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1149-6