Abstract
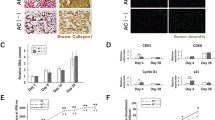
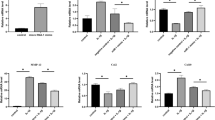
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of microRNA-21 (miR-21) on the proliferation and matrix synthesis of chondrocytes embedded in atelocollagen gel. Articular cartilage was harvested aseptically from the knee and hip joints of rats. In the experimental group, double-stranded miR-21 was transfected into the chondrocytes, and in the control group, scrambled siRNA was used. After that, chondrocytes were cultured in atelocollagen gel for 3 weeks. At 1, 2, and 3 weeks after transfection, the cell numbers were counted, and the expression levels of Col2a1 and aggrecan were measured by real-time PCR. Histological analysis by toluidine blue staining was performed at 3 weeks. The cell number in the experimental group rapidly increased compared to the control group. The expression levels of Col2a1 and aggrecan in the experimental group were higher than in the control. Histological analysis revealed that many more cells with a metachromatic stain were present in the experimental group than in the control. This study demonstrated that miR-21 promotes high proliferation and matrix synthesis of chondrocytes embedded in atelocollagen gel.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27:2128–2136
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Brittberg M, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Ohlsson C, Isaksson O, Peterson L (1994) Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med 331:889–895
Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ (1998) Articular cartilage: tissue design and chondrocyte-matrix interactions. Instr Course Lect 47:477–486
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033
De Croos JN, Dhaliwal SS, Gryynpas MD, Pilliar RM, Kandal RA (2006) Cyclic compressive mechanical stimulation induces sequential catabolic and anabolic gene changes in chondrocytes resulting in increased extracellular matrix accumulation. Matrix Biol 25:323–331
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391:806–811
Iwasaki M, Nakata K, Nakahara H, Nakase T, Kimura T, Kimata K, Caplan AI, Ono K (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 stimulates chondrogenesis and inhibits osteogenesis in high density culture of periosteum-derived cells. Endocrinology 132:1603–1608
Kawasaki K, Ochi M, Uchio Y, Adachi N, Matsusaki M (1999) Hyaluronic acid enhances proliferation and chondroitin sulfate synthesis in cultured chondrocytes embedded in collagen gels. J Cell Physiol 179:142–148
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Loffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Pfeifer G, Stocsits C, Hackermuller J, Kretzschmar AK, Burger R, Gramatzki M, Blumert C, Bauer K, Cvijic H, Ullmann AK, Stadler PF, Horn F (2007) Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood 110:1330–1333
Madry H, Kaul G, Cucchiarini M, Stein U (2005) Enhanced repair of articular cartilage defects in vivo by transplanted chondrocytes overexpressing insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). Gene Ther 12:1171–1179
Matsusaki M, Ochi M, Uchio Y, Shu N, Kurioka H, Kawasaki K, Adachi N (1998) Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on proliferation and phenotype expression of chondrocytes embedded in collagen gel. Gen Pharmacol 31:759–764
Meng F, Henson R, Weh-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob S, Patel T (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133:647–658
Minakuchi Y, Takeshita F, Kosaka N, Sasaki H, Yamamoto Y, Kouno M, Honma K, Nagahara S, Hanai K, Sano A, Kato T, Terada M, Ochiya T (2004) Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e109
Miyanishi K, Trindade MC, Lindsey DP, Beaupre GS, Carter DR, Goodman SB, Schurman DJ, Smith RL (2006) Dose- and time-dependent effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on transforming growth factor-beta3-induced chondrogenesis by adult human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Tissue Eng 12:2253–2262
Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Shi Ming, Shibuya H, Adachi N, Ochi M (2009) Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J Cell Mol Med in press. PMID: 19754672
Nagata Y, Nakasa T, Mochizuki Y, Ishikawa M, Miyaki S, Shibuya H, Yamasaki K, Adachi N, Asahara H, Ochi M (2009) Induction of apoptosis in the synovium of autoantibody-mediated arthritis in mice by the intra-articular injection of double-stranded microRNA-15a. Arthritis Rheum 60:2677–2683
Ochi M, Uchio Y, Tobita M, Kuriwaka M (2001) Current concepts in tissue engineering technique for repair of cartilage defect. Artif Organs 25:172–179
Qian B, Katsaros D, Lu L, Preti M, Durando A, Arisio R, Mu L, Yu H (2008) High miR-21 expression in breast cancer associated with poor disease-free survival in early stage disease and high TGF-beta1. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117:131–140
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M, Nakagama H (2007) Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15472–15477
Zamore PD, Haley B (2005) Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science 309:1519–1524
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Yin-Yuan M (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282:14328–14336
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have received any financial support from any organizations to influence this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kongcharoensombat, W., Nakasa, T., Ishikawa, M. et al. The effect of microRNA-21 on proliferation and matrix synthesis of chondrocytes embedded in atelocollagen gel. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18, 1679–1684 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1111-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1111-7