Abstract
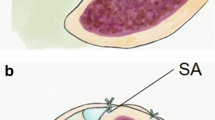
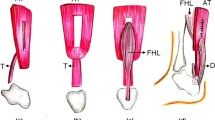
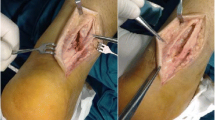
Our objective is to assess whether the tendoscopic synovectomy is effective to control the stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Our study is a retrospective one. The participants, six patients with stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, were treated with tendoscopy with synovectomy for the past 3 years. The results show that this is a safe procedure and we could achieve similar effectiveness as the traditional open procedure. There was no complication found. None of our patients have progressed to stage II or above posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. In conclusion, tendoscopic debridement is a minimal invasive surgery. It is effective to control the stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. In addition, it had the advantages of smaller scars, less wound pain and a short hospital stay.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Funk DA, Cass JR, Johnson KA (1986) Acquired adult flatfoot secondary to posterior tibial-tendon pathology. J Bone Joint Surg 68A:95–102
Holmes GB, Mann RA (1993) Possible epidemiological factors associated with rupture of the posterior tibial tendon. Foot Ankle 13:70–79
Sferra JJ, Rosenberg GA (1997) Nonoperative treatment of posterior tibial tendon pathology. Foot Ankle Clin 2:261–273
Myerson MS (1996) Adult acquired flatfoot deformity: treatment of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. J Bone Joint Surg 78A:780–792
Johnson KA (1983) Tibialis posterior tendon rupture. Clin Orthop 177:140–147
Johnson KA, Strom DE (1989) Tibialis posterior tendon dysfunction. Clin Orthop 239:197–206
van Dijk CN, Kort N, Scholten PE (1997) Tendoscopy of the posterior tibial tendon. Arthroscopy 13(6):692–698
Kaye RA, Jahss MH (1991) Tibialis posterior: a review of anatomy and biomechanics in relation to support of the medial longitudinal arch. Foot Ankle 11:244–247
Mann RA (1983) Acquired flatfoot in adults. Clin Orthop 181:46–51
Augustin JF, Lin SS, Berberian WS, Johnson JE (2003) Non-operative treatment of adult acquired flatfoot with the Arizona brace. Foot Ankle Clin 8(3):491–502
Perry, Monique B, Premkumar, Ahalya, Venzon, Shawker DJ, Thomas H, Gerber, Lynn H (2003) Ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, and posterior tibialis dysfuction. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1(408):225–231
Sitler DF, Bell SJ (2003) Soft tissue procedures. Foot Ankle Clin 8(3):503–520
Beals TC, Pomeroy GC, Manoli A (1999) Posterior tendon insufficiency: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Assoc Orthop Surg 7(2):112–118
Teasdall RD, Johnson KA (1994) Surgical treatment of stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Foot Ankle Int 15(12):646–648
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chow, H.T., Chan, K.B. & Lui, T.H. Tendoscopic debridement for stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13, 695–698 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-005-0635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-005-0635-8