Abstract
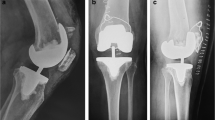
The patellar component of a total knee replacement (TKR) is the most frequent source of non-septic complications after total knee arthroplasty. Fracture of patellar pegs in all polyethylene patellar components is a very rare occurrence. We report such a case of a patellar polyethylene fracture in a 72-year-old female patient 10 years after TKR. Due to patellar malalignment and high level of activity, the patellar components failed in this patient. This was treated arthroscopically by removing the components that failed and leaving the patella unresurfaced. We followed up the patient postoperatively and her symptoms were substantially resolved.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley JC, Scott RD (1988) Further observations on metal-backed component failure. Clin Orthop 236:82–87
Bayley JC, Scott RD, Ewald FC, Holmes GB Jr (1988) Failure of the metal-backed patellar component after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:668–674
Boyd AD Jr, Ewald FC, Thomas WH, Poss R, Sledge CB (1993) Long-term complications after total knee arthroplasty with or without resurfacing of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:674–681
Clayton ML, Thirupathi R (1982) Patellar complications after total condylar arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 170:152–155
Edwards TB, D’Ambrosia RD (2002) Fracture of a three peg, nonmetal-backed, polyethylene patellar component. Orthopedics 25:856–857
Francke EI, Lachiewicz PF (2000) Failure of a cemented all-polyethylene patellar component of a press-fit condylar total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:234–237
Huang CH, Lee YM, Lai JH, Liau JJ, Cheng CK (1999) Failure of the all-polyethylene patellar component after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:940–944
Kitsugi T, Gustilo RB, Bechtold JE (1994) Results of nonmetal-backed, high-density polyethylene, biconvex patellar prostheses. A 5–7-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty 9:151–162
Lombardi AV, Engh GA, Volz RG, Albrigo JL, Brainard BJ (1988) Fracture/dissociation of the polyethylene in metal-backed patellar components in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:675–679
Larson CM, McDowell CM, Lachiewicz PF (2001) One-peg versus three-peg patella component fixation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 392:94–100
Merkow RL, Soudry M, Insall JN (1985) Patellar dislocation following total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67:1321–1327
McNamara JL, Collier JP, Mayor MB, Jensen RE (1994) A comparison of contact pressures in tibial and patellar total knee components before and after service in vivo. Clin Orthop 299:104–113
Oishi CS, Kaufman KR, Irby SE, Colwell CW Jr (1996) Effects of patellar thickness on compression and shear forces in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 331:283–290
Ranawat CS, Boachie-Adjei O (1988) Survivorship analysis and results of total condylar knee arthroplasty. Eight- to 11-year follow-up period. Clin Orthop 226:6–13
Ranawat CS, Luessenhop CP, Rodriguez JA (1997) The press-fit condylar modular total knee system. Four-to-six-year results with a posterior-cruciate-substituting design. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:342–348
Rosenberg AG, Andriacchi TP, Barden R, Galante JO (1988) Patellar component failure in cementless total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 236:106–114
Scott RD, Reilly DT (1980) Pros and cons of patellar resurfacing in total knee replacement. Orthop Trans 4:328–329
Schai PA, Thornhill TS, Scott RD (1998) Total knee arthroplasty with the PFC system. Results at a minimum of ten years and survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:850–858
Thomas WH, Ewald FC, Poss R, Sledge CB (1980) Duopatella total knee replacement. Orthop Trans 4:329–330
Wasilewski SA, Frank U (1989) Fracture of polyethylene of patellar component in total knee arthroplasty, diagnosed by arthroscopy. J Arthroplasty 4(suppl):S19–S522
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafi, M., Kim, Y.Y., Lee, Y.S. et al. Patellar polyethylene peg fracture: a case report and review of the literature. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13, 472–475 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0566-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0566-9