Abstract
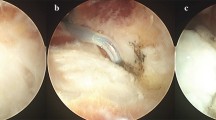
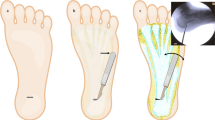
The purpose of the present study is to present the surgical technique for, and review our indications and results after, endoscopic fascial release in patients with plantar fasciitis. In five thiel-embalmed human specimens, a biportal technique for endoscopic release of the plantar fascia was established. The aim was here to evaluate the relation between the plantar fascia and the heel spur and to perform a release that would not exceed 50–70% of the diameter of the calcaneoplantar fascia. The endoscopic technique was performed within the last 5 years in ten male and seven female patients. All patients with the clinical entity of plantar fasciitis underwent conservative treatment for at least 6 months. The average age at surgery was 35 years (24–56 years). In the first five patients, surgery was performed under c-arm control. In all patients the operation could be finished endoscopically. The endoscopic portals healed without complications. The time for surgery during the learning curve ranged between 21 and 74 min (average 41 min) and was still longer compared to the open technique. The clinical follow-up ranged between 4 and 48 months (average 18.5 months). Out of 17 patients, 13 improved clinically, and they would choose the treatment option again. In the Ogilvie-Harris score, seven patients showed good and six excellent results. In two patients, the initial results were not satisfactory, because of a bony stress reaction of the calcaneus. This complication was treated by 6 weeks of partial weight bearing, without any further problems. Two other patients developed secondary pain in the lateral column. In spite of the minimal invasive approach it seems to be important to be careful in increasing the weight bearing in early rehabilitation. The technique of the endoscopic plantar fascia release (EFRPF) can be performed in a standardised and reproducible procedure. The follow-up examination showed good midterm results, but a loss of stability of the plantar arch has to be strictly avoided.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandler TJ, Kibler WB (1993) A biomechanical approach to the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of plantar fasciitis. Sports Med 15:344–352
Kibler WB, Goldberg C, Chandler TJ (1991) Functional biomechanical deficits in running athletes with plantar fasciitis. Am J Sports Med 19:66–71
Sadat-Alsi M (1998) Plantar fasciitis/calcaneal spur among security forces personnel. Mil Med 163:56–57
Cardinal E, Chhem RK, Beauregard CG, Aubin B, Pelletier M (1996) Plantar fasciitis: sonographic evaluation. Radiology 201:257–259
Kane D, Greaney T, Bresnihan B, Gibney R, FitzGerald O (1998) Ultrasound guided injection of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Ann Rheum Dis 57:383–384
Wall JR, Harkness MA, Crawford A (1993) Ultrasound diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle 14:465–470
Tudor GR, Finlay D, Allen MJ, Belton I (1997) The role of bone scintigraphy and plain radiography in intractable plantar fasciitis. Nucl Med Commun 18:853–856
Kier R (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging of plantar fasciitis and other causes of heel pain. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2:97–107
de Souza H, Reed L (1997) An inexpensive “orthosis” for plantar fasciitis. Med J Aust 167:509
Mizel MS, Marymont JV, Trepman E (1996) Treatment of plantar fasciitis with a night splint and shoe modification consisting of a steel shank and anterior rocker bottom. Foot Ankle Int 17:732–735
Powell M, Post WR, Keener J, Wearden S (1998) Effective treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis with dorsiflexion night splints: a crossover prospective randomized outcome study. Foot Ankle Int 19:10–18
Vohra PK, Giorgini RJ, Sobel E, Japour CJ, Villalba MA, Rostkowski T (1999) Long-term follow-up of heel spur surgery: a 10-year retrospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 89:81–88
Chandler TJ (1998) Iontophoresis of 0.4% dexamethasone for plantar fasciitis. Clin J Sport Med 8:68
Gill LH, Kiebzak GM (1996) Outcome of nonsurgical treatment for plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 17:527–532
Sollitto RJ, Plotkin EL, Klein PG, Mullin P (1997) Early clinical results of the use of radiofrequency lesioning in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. J Foot Ankle Surg 36:215–219
Wolgin M, Cook C, Graham C, Mauldin D (1994) Conservative treatment of plantar heel pain: long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle Int 15:97–102
Basford JR, Malanga GA, Krause DA, Harmsen WS (1998) A randomized controlled evaluation of low-intensity laser therapy: plantar fasciitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79:249–254
Krischek O, Rompe JD, Herbsthofer B, Nafe B (1998) Symptomatic low-energy shockwave therapy in heel pain and radiologically detected plantar heel spur. Z Orthop 136:169–174
Daly PJ, Kitaoka HB, Chao EY (1992) Plantar fasciotomy for intractable plantar fasciitis: clinical results and biomechanical evaluation. Foot Ankle 13:188–195
Graves RH 3rd, Levin DR, Giacopelli J, White PR, Russell RD (1994) Fluoroscopy-assisted plantar fasciotomy and calcaneal exostectomy: a retrospective study and comparison of surgical techniques. J Foot Ankle Surg 33:475–481
Barrett SL, Day SV, Pignetti TT, Robinson LB (1995) Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: a multi-surgeon prospective analysis of 652 cases. J Foot Ankle Surg 34:400–406
Barrett SL, Day SV (1991) Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy for chronic plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome: surgical technique—early clinical results. J Foot Surg 30:568–570
Brekke MK, Green DR (1998) Retrospective analysis of minimal-incision, endoscopic, and open procedures for heel spur syndrome. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 88:64–72
Hawkins BJ, Langermen RJ Jr, Gibbons T, Calhoun JH (1995) An anatomic analysis of endoscopic plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle Int 16:552–558
Santini S, Rebeccato A, Schiavon R, Nogarin L (2003) Percutaneous drilling for chronic heel pain. J Foot Ankle Surg 42:296–301
Tomczak RL, Haverstock BD (1995) A retrospective comparison of endoscopic plantar fasciotomy to open plantar fasciotomy with heel spur resection for chronic plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome. J Foot Ankle Surg 34:305–311
Heller KD (1999) Extracorporal shockwave therapy in heel spur: analysis of the literature. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 137:13–15
Maier M, Durr HR, Kohler S, Staupendahl D, Pfahler M, Refior HJ, Meier M (2000) Analgesic effect of low energy extracorporeal shock waves in tendinosis calcarea, epicondylitis humeri radialis and plantar fasciitis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 138:34–38
Abt T, Hopfenmuller W, Mellerowicz H (2002) Shock wave therapy for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis with heel spur: a prospective randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Complications of plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 140:548–554
Sammarco GJ, Idusuyi OB (1998) Stress fracture of the base of the third metatarsal after an endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: a case report. Foot Ankle Int 19:157–159
Manoli A II, Harper MC, Fitzgibbons TC, McKernan DJ (1992) Calcaneal fracture after cortical bone removal. Foot Ankle 13:523–525
Reeve F, Laughlin RT, Wright DG (1997) Endoscopic plantar fascia release: a cross-sectional anatomic study. Foot Ankle Int 18:398–401
Kinley S, Frascone S, Calderone D, Wertheimer SJ, Squire MA, Wiseman FA (1993) Endoscopic plantar fasciotomy versus traditional heel spur surgery: a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 32:595–603
Murphy GA, Pneumaticos SG, Kamaric E, Noble PC, Trevino SG, Baxter DE (1998) Biomechanical consequences of sequential plantar fascia release. Foot Ankle Int 19:149–152
Arangio GA, Chen C, Kim W (1997) Effect of cutting the plantar fascia on mechanical properties of the foot. Clin Orthop 339:227–231
Thordarson DB, Kumar PJ, Hedman TP, Ebramzadeh E (1997) Effect of partial versus complete plantar fasciotomy on the windlass mechanism. Foot Ankle Int 18:16–20
Brugh AM, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT (2002) Lateral column symptomatology following plantar fascial release: a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 41:365–371
Sellman JR (1994) Plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int 15:376–381
Jerosch J (2000) Endoscopic release of plantar fasciitis—a benign procedure? Foot Ankle Int 21:511–513
Smith WK, Noriega JA, Smith WK Jr (2001) Resection of a plantar calcaneal spur using the holmium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Ho:YAG) laser. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 91:142–146
Batt ME, Tanji JL, Skattum N (1996) Plantar fasciitis: a prospective randomized clinical trial of the tension night splint. Clin J Sport Med 6:158–162
White AD (1997) An inexpensive “orthosis” for plantar fasciitis. Med J Aust 166:616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jerosch, J., Schunck, J., Liebsch, D. et al. Indication, surgical technique and results of endoscopic fascial release in plantar fasciitis (EFRPF). Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12, 471–477 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0496-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-004-0496-6