Abstract
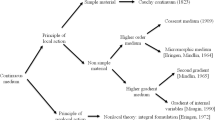
According to their peculiar mechanical properties, the description of cellular materials is of high interest. Modelling aspects to be considered are, e.g. pronounced size depending boundary layer effects as well as a deformation-driven evolution of anisotropy or porosity. In the present contribution, we pay special attention to the description of size-dependent microtopological effects on the one hand. On the other hand, we focus on the relevance of extended continuum theories describing the local deformation state of microstructured materials. We, therefore, introduce a homogenization scheme for two-scale problems replacing a heterogeneous Cauchy continuum on the microscale by a homogeneous effective micromorphic continuum on the macroscale. The transitions between both scales are obtained by appropriate projection and homogenization rules which have to be derived, on the one hand, by kinematic assumptions, i.e. the minimization of the macroscopic displacement field, and, on the other hand, by energetic considerations, i.e. the evaluation of an extended Hill–Mandel condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capriz G., Podio-Guidugli P., Williams W.: On balance equations for materials with affine structure. Meccanica 17, 80–84 (1982)
Cosserat E., Cosserat F.: Théorie des corps déformables. A. Hermann et Fils, Paris (1909)
Diebels S.: Ein mikropolares Materialgesetz für poröse Festkörper. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 79, S533–S534 (1999)
Diebels S., Steeb H.: The size effect in foams and its theoretical and numerical investigation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 458, 2869–2883 (2002)
Diebels S., Steeb H.: Stress and couple stress in foams. Comput. Math. Sci. 28, 714–722 (2003)
Diebels S., Johlitz M., Steeb H., Possart W., Batal J.: A continuum-based model capturing size effects in polymer bonds. J. Phys. 62, 34–42 (2007)
Eringen C.: Polar and Nonlocal Field Theories, Continuum Physics, vol. IV. Academic Press, Boston (1976)
Eringen C.: Microcontinuum Field Theories, vol. I: Foundations and Solids. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1999)
Feyel F., Chaboche J.L.: FE 2 multiscale approach for modelling the elastoviscoplastic behaviour of long fiber SiC/Ti composite materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 183, 309–330 (2000)
Forest S.: Mechanics of generalized continua: construction by homogenization. J. Phys. IV, 39–48 (1998)
Forest S.: Homogenization methods and the mechanics of generalized continua—Part 2. Theor. Appl. Mech. 28–29, 113–143 (2002)
Forest S.: Nonlinear microstrain theories. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 7224–7245 (2006)
Forest S., Sab K.: Cosserat overall modeling of heterogeneous materials. Mech. Res. Commun. 25, 449–454 (1998)
Germain P.: La méthode des puissances virtuelles en mécanique des milieux continus, Première partie: Théorie du second gradient. J. Mecanique 12, 235–274 (1973)
Germain P.: The method of virtual power in continuum mechanics. Part 2: Microstructure. J. Appl. Mech. 25, 556–575 (1973)
Hazanov S.: Hill condition and overall properties of composites. Arch. Appl. Mech. 68(6), 385–394 (1998)
Hill R.: Elastic properties of reinforced solids: some theoretical principles. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11, 357–372 (1963)
Hill R.: On constitutive macro-variables for heterogeneous solids at finite strain. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 326, 131–147 (1972)
Huet C.: Coupled size and boundary-condition eects in viscoelastic heterogeneous and composite bodies. Mech. Mater. 31, 787–829 (1999)
Jänicke R., Diebels S.: A numerical homogenisation strategy for micromorphic continua. Nuovo Cimento Soc. Ital. Fis. C 31(1), 121–132 (2009)
Kaczmarczyk L., Pearce C.J., Bićanić N.: Scale transition and enforcement of RVE boundary conditions in second-order homogenization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 74, 506–522 (2008)
Kirchner N., Steinmann P.: Mechanics of extended continua: modeling and simulation of elastic microstretch materials. Comput. Mech. 40(4), 651–666 (2007)
Kouznetsova, V.G.: Computational homogenization for the multi-scale analysis of multi-phase m aterial. PhD-thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands (2002)
Kouznetsova V.G., Geers M.G.D., Brekelmans W.A.M.: Size of a representative volume element in a second-order computational homogenization framework. Int. J. Multiscale Comput. Eng. 2(4), 575–598 (2004)
Larsson R., Diebels S.: A second order homogenization procedure for multi-scale analysis based on micropolar kinematics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 69, 2485–2512 (2006)
Maugin G.A.: Nonlocal theories or gradient-type theories: a matter of convenience?. Acta Mater. 31, 15–26 (1979)
Maugin G.A.: The Thermomechanics of Plasticity and Fracture. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992)
Mindlin R.D.: Micro-structure in linear elasticity. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 16, 51–78 (1964)
Neff, P.: On material constants for micromorphic continua. In: K. Hutter, Y. Wang (eds.) Proceedings of ‘International Symposium on Trends in Applications of Mathematics to Mechanics’. Shaker, Aachen (2004)
Nemat-Nasser S.: On finite plastic flow of crystalline solids and geomaterials. J. Appl. Mech. 50, 1114–1126 (1983)
Nemat-Nasser S., Hori M.: Micromechanics. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1993)
Steeb H., Diebels S.: Continua with affine microstructure: theoretical aspects and application. Proc. Appl. Math. Mech. 5, 319–320 (2005)
Tekoǧlu C., Onck P.R.: Size effects in two-dimensional voronoi foams: A comparison between generalized continua and discrete models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 3541–3564 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jänicke, R., Diebels, S., Sehlhorst, HG. et al. Two-scale modelling of micromorphic continua. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 21, 297–315 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-009-0114-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-009-0114-4