Abstract
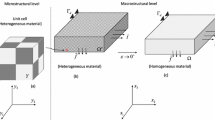
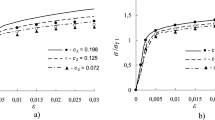
In the present paper, we will illustrate the application of the method of conditional moments by constructing the algorithm for determination of the effective elastic properties of composites from the given elastic constants of the components and geometrical parameters of inclusions. A special case of two-component matrix composite with randomly distributed unidirectional spheroidal inclusions is considered. To this end it is assumed that the components of the composite show transversally isotropic symmetry of thermoelastic properties and that the axes of symmetry of the thermoelastic properties of the matrix and inclusions coincide with the coordinate axis x 3. As a numerical example a composite based on carbon inclusions and epoxide matrix is investigated. The dependencies of Young’s moduli, Poisson’s ratios and shear modulus from the concentration of inclusions and for certain values which characterize the shape of inclusions are analyzed. The results are compared and discussed in context with other theoretical predictions and experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choy C.L., Leung W.P., Kowk K.W., Lau F.P.: Elastic moduli and thermal conductivity of injectionmolded short fiber reinforced thermoplastics. Polym. Compos. 13, 69–80 (1992)
Christensen R.M.: Mechanics of composite materials, pp. 325. Wiley-Interscience Publication, New York (1979)
Christensen R.M.: A critical evaluation for a class of micro-mechanics models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 38(3), 379–404 (1990)
Gnedenko, B.V., Belyaev, U.K., Solovyev, A.D.: Mathematical Methods in Reliability Theory, p. 524. Nauka, Moscow (1965) [in Russian]
Gnedenko, B.V.: Course of Probability Theory, p. 448. Nauka, Moscow (1988) [in Russian]
Kachanov M., Sevostianov I., Shafiro B.: Explicit cross-property correlations for porous materials with anisotropic microstructures. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 49, 1–25 (2001)
Kanaun S.K., Levin V.M.: Effective field method in mechanics of matrix composite materials. In: Markov, K.Z. (eds) Recent Advances in Mathematical Modelling of Composite Materials, pp. 1–58. World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Khoroshun L.P.: Methods of random functions in determining the macroscopic properties of microheterogeneous media. [in Russian] Prikl. Mech. 14(2), 3–17 (1978)
Khoroshun L.P., Leshchenko P.V., Nazarenko L.V.: Effective thermoelastic constants of discretely-fibrous composites with anisotropic components. Int. Appl. Mech. 24(10), 955–961 (1988)
Khoroshun, L.P., Maslov, B.P., Leshchenko, P.V.: Prediction of effective properties of piezo-composites, p. 206. Naukova Dumka. Kiev (1989) [in Russian]
Khoroshun, L.P., Maslov, B.P., Shikula, E.N., Nazarenko, L.V.: Statistical Mechanics and Effective Properties of Materials, p. 390. Naukova Dumka. Kiev (1993) [in Russian]
Kushch V., Sevostianov I.: Effective elastic moduli tensor of particulate composite with transversely isotropic phases. Int. J. Solid Struct. 41, 885–906 (2004)
Markov K.Z.: Elementary micromechanics of heterogeneous media. In: Markov, K.Z., Preziozi, L. (eds) Heterogeneous Media: Micromechanics Modeling Methods and Simulations, pp. 1–162. Birkhauser, Boston (2000)
Milton G.W., Kohn R.V.: Variational bounds on the effective moduli of anisotropic composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36(5), 597–629 (1988)
Milton G.W.: The Theory of Composites. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Mura T.: Micromechanics of defects in solids, pp. 587. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dortrecht (1987)
Ponte Castaneda P.: The effective mechanical properties of nonlinear isotropic solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 39(1), 45–71 (1991)
Ponte Castaneda P.: Exact second-order estimates for the effective mechanical properties of nonlinear composite materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44(6), 827–862 (1996)
Ponte Castaneda P., Suquet P.: Nonlinear composites. Adv. Appl. Mech. 34, 171–302 (1998)
Sanchez-Palencia E.: Non-Homogeneous Media and Vibration Theory. Springer, Berlin (1980)
Sevostianov I., Kachanov M.: Explicit cross-property correlations for anisotropic two-phase composite materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50, 253–282 (2002)
Sevostianov I.: Explicit relations between elastic and conductive properties of a material containing annular cracks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A361, 987–999 (2003)
Sevostianov I., Yilmaz N., Kushch V., Levin V.: Effective elastic properties of matrix composites with transversely-isotropic phases. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 455–476 (2005)
Sevostianov I., Kachanov M.: Explicit cross-property correlations for composites with anisotropic inhomogeneities. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55, 2181–2205 (2007)
Torquato S.: Random Heterogeneous materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic properties. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Walpole L.J.: Elastic behaviour of composite-materials—theoretical foundations. Adv. Appl. Mech. 21, 169–242 (1981)
Willis J.R.: Bounds and self-consistent estimates for the overall properties of anisotropic composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 25(2), 185–202 (1977)
Willis J.R.: The overall elastic response of composite Materials. J. Appl. Mech. 50(4B), 1202–1209 (1983)
Willis, J.R.: In mechanics of solids. The Rodney Hill 60th Anniversary Volume, pp. 653–686. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1982)
Willis, J.R.: Micromechanics and Inhomogeneity. The Toshio Mura Anniversary Volume, p. 581. Springer, New York (1989)
Withers P.J.: The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion in a transversely isotropic medium, and its relevance to composite materials. Philos. Mag. A59, 759–781 (1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Berdichevsky
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazarenko, L., Khoroshun, L., Müller, W.H. et al. Effective thermoelastic properties of discrete-fiber reinforced materials with transversally-isotropic components. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 20, 429–458 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-009-0092-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-009-0092-6