Abstract
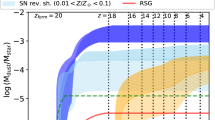
The large amounts of dust detected in sub-millimeter galaxies and quasars at high redshift pose a challenge to galaxy formation models and theories of cosmic dust formation. At z>6 only stars of relatively high mass (>3 M⊙) are sufficiently short-lived to be potential stellar sources of dust. This review is devoted to identifying and quantifying the most important stellar channels of rapid dust formation. We ascertain the dust production efficiency of stars in the mass range 3–40 M⊙ using both observed and theoretical dust yields of evolved massive stars and supernovae (SNe) and provide analytical expressions for the dust production efficiencies in various scenarios. We also address the strong sensitivity of the total dust productivity to the initial mass function. From simple considerations, we find that, in the early Universe, high-mass (>3 M⊙) asymptotic giant branch stars can only be dominant dust producers if SNe generate ≲3×10−3 M⊙ of dust whereas SNe prevail if they are more efficient. We address the challenges in inferring dust masses and star-formation rates from observations of high-redshift galaxies. We conclude that significant SN dust production at high redshift is likely required to reproduce current dust mass estimates, possibly coupled with rapid dust grain growth in the interstellar medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel T, Bryan GL, Norman ML (2002) The formation of the first star in the Universe. Science 295:93–98. doi:10.1126/science.295.5552.93, arXiv:astro-ph/0112088
Alton PB, Xilouris EM, Misiriotis A, Dasyra KM, Dumke M (2004) The emissivity of dust grains in spiral galaxies. Astron Astrophys 425:109–120. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040438, arXiv:astro-ph/0406389
Anderson JP, James PA (2008) Constraints on core-collapse supernova progenitors from correlations with H alpha emission. Mon Not R Astron Soc 390:1527–1538. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13843.x, 0809.0236
Andrews JE, Gallagher JS, Clayton GC, Sugerman BEK, Chatelain JP, Clem J, Welch DL, Barlow MJ, Ercolano B, Fabbri J, Wesson R, Meixner M, (2010) SN 2007od: a Type IIP Supernova with circumstellar interaction. Astrophys J 715:541–549. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/715/1/541, 1004.1209
Andrews JE, Clayton GC, Wesson R, Sugerman BEK, Barlow MJ, Clem J, Ercolano B, Fabbri J, Gallagher JS, Landolt A, Meixner M, Otsuka M, Riebel D, Welch DL (2011a) Evidence for pre-existing dust in the bright Type IIn SN 2010jl. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/142/2/45, 1106.0537
Andrews JE, Sugerman BEK, Clayton GC, Gallagher JS, Barlow MJ, Clem J, Ercolano B, Fabbri J, Meixner M, Otsuka M, Welch DL, Wesson R (2011b) Photometric and spectroscopic evolution of the IIP SN 2007it to day 944. Astrophys J 731:47. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/731/1/47, 1102.2431
Arendt RG, Dwek E, Moseley SH (1999) Newly synthesized elements and pristine dust in the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant. Astrophys J 521:234–245. doi:10.1086/307545, arXiv:astro-ph/9901042
Arnett WD (1988) On the early behavior of Supernova 1987A. Astrophys J 331:377–387. doi:10.1086/166564
Baade W (1943) Nova Ophiuchi of 1604 AS a Supernova. Astrophys J 97:119. doi:10.1086/144505
Ballero SK, Kroupa P, Matteucci F (2007) Testing the universal stellar IMF on the metallicity distribution in the bulges of the Milky Way and M 31. Astron Astrophys 467:117–121. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066786, arXiv:astro-ph/0702047
Bandiera R (1987) The origin of Kepler’s supernova remnant. Astrophys J 319:885–892. doi:10.1086/165505
Barlow MJ, Krause O, Swinyard BM, Sibthorpe B, Besel M, Wesson R, Ivison RJ, Dunne L, Gear WK, Gomez HL, Hargrave PC, Henning T, Leeks SJ, Lim TL, Olofsson G, Polehampton ET (2010) A Herschel PACS and SPIRE study of the dust content of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014585, 1005.2688
Bartko H, Martins F, Trippe S, Fritz TK, Genzel R, Ott T, Eisenhauer F, Gillessen S, Paumard T, Alexander T, Dodds-Eden K, Gerhard O, Levin Y, Mascetti L, Nayakshin S, Perets HB, Perrin G, Pfuhl O, Reid MJ, Rouan D, Zilka M, Sternberg A (2010) An extremely top-heavy initial mass function in the Galactic center stellar disks. Astrophys J 708:834–840. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/708/1/834, 0908.2177
Bastian N, Covey KR, Meyer MR (2010) A Universal stellar initial mass function? A critical look at variations. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 48:339–389. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-082708-101642, 1001.2965
Baugh CM, Lacey CG, Frenk CS, Granato GL, Silva L, Bressan A, Benson AJ, Cole S (2005) Can the faint submillimetre galaxies be explained in the Λ cold dark matter model? Mon Not R Astron Soc 356:1191–1200. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08553.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0406069
Beelen A, Cox P, Benford DJ, Dowell CD, Kovács A, Bertoldi F, Omont A, Carilli CL (2006) 350 μm dust emission from high-redshift quasars. Astrophys J 642:694–701. doi:10.1086/500636, arXiv:astro-ph/0603121
Beers TC, Christlieb N (2005) The discovery and analysis of very metal-poor stars in the Galaxy. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 43:531–580. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.42.053102.134057
Benetti S, Turatto M, Valenti S, Pastorello A, Cappellaro E, Botticella MT, Bufano F, Ghinassi F, Harutyunyan A, Inserra C, Magazzu A, Patat F, Pumo ML Taubenberger S, (2011) The Type Ib SN 1999dn: one year of photometric and spectroscopic monitoring. Mon Not R Astron Soc 411:2726–2738. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17873.x, 1010.3199
Benford DJ, Cox P, Omont A, Phillips TG, McMahon RG (1999) 350 micron dust emission from high-redshift objects. Astrophys J 518:L65–L68. doi:10.1086/312073, arXiv:astro-ph/9904277
Bertoldi F, Cox P (2002) Dust emission and star formation toward a redshift 5.5 QSO. Astron Astrophys 384:L11–L14. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020120, arXiv:astro-ph/0201330
Bertoldi F, Carilli CL, Cox P, Fan X, Strauss MA, Beelen A, Omont A, Zylka R (2003) Dust emission from the most distant quasars. Astron Astrophys 406:L55–L58. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030710, arXiv:astro-ph/0305116
Bianchi S, Schneider R (2007) Dust formation and survival in supernova ejecta. Mon Not R Astron Soc 378:973–982. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11829.x, 0704.0586
Blair WP, Morse JA, Raymond JC, Kirshner RP, Hughes JP, Dopita MA, Sutherland RS, Long KS, Winkler PF (2000) Hubble space telescope observations of oxygen-rich Supernova remnants in the Magellanic Clouds. II. Elemental abundances in N132D and 1E 0102.2-7219. Astrophys J 537:667–689. doi:10.1086/309077
Blair WP, Ghavamian P, Long KS, Williams BJ, Borkowski KJ, Reynolds SP, Sankrit R (2007) Spitzer space telescope observations of Kepler’s supernova remnant: a detailed look at the circumstellar dust component. Astrophys J 662:998–1013. doi:10.1086/518414, arXiv:astro-ph/0703660
Blöcker T (1995) Stellar evolution of low and intermediate-mass stars. I. Mass loss on the AGB and its consequences for stellar evolution. Astron Astrophys 297:727
Blöcker T, Schönberner D (1991) A 7-solar-mass AGB model sequence not complying with the core mass-luminosity relation. Astron Astrophys 244:L43–L46
Bonnell IA, Larson RB, Zinnecker H (2007) The origin of the initial mass function. Protostars and planets V, 149–164, arXiv:astro-ph/0603447
Borghesi A, Bussoletti E, Colangeli L, de Blasi C (1985) Laboratory study of SiC submicron particles at IR wavelengths—a comparative analysis. Astron Astrophys 153:1–8
Borkowski KJ, Williams BJ, Reynolds SP, Blair WP, Ghavamian P, Sankrit R, Hendrick SP, Long KS, Raymond JC, Smith RC, Points S, Winkler PF (2006) Dust destruction in Type Ia Supernova remnants in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys J 642:L141–L144. doi:10.1086/504472, arXiv:astro-ph/0602313
Botticella MT, Pastorello A, Smartt SJ, Meikle WPS, Benetti S, Kotak R, Cappellaro E, Crockett RM, Mattila S, Sereno M, Patat F, Tsvetkov D, van Loon JT, Abraham D, Agnoletto I, Arbour R, Benn C, di Rico G, Elias-Rosa N, Gorshanov DL, Harutyunyan A, Hunter D, Lorenzi V, Keenan FP, Maguire K, Mendez J, Mobberley M, Navasardyan H, Ries C, Stanishev V, Taubenberger S, Trundle C, Turatto M, Volkov IM (2009) SN 2008S: an electron-capture SN from a super-AGB progenitor? Mon Not R Astron Soc 398:1041–1068. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15082.x, 0903.1286
Bouchet P, De Buizer JM, Suntzeff NB, Danziger IJ, Hayward TL, Telesco CM, Packham C (2004) High-resolution mid-infrared imaging of SN 1987A. Astrophys J 611:394–398. doi:10.1086/421936, arXiv:astro-ph/0312240
Bouwens RJ, Illingworth GD, Labbe I, Oesch PA, Trenti M, Carollo CM, van Dokkum PG, Franx M Stiavelli M, González V, Magee D, Bradley L (2011) A candidate redshift z∼10 galaxy and rapid changes in that population at an age of 500 Myr. Nature 469:504–507. doi:10.1038/nature09717, 0912.4263
Bowen GH, Willson LA (1991) From wind to superwind—the evolution of mass-loss rates for Mira models. Astrophys J 375:L53–L56. doi:10.1086/186086
Boyer ML, van Loon JT, McDonald I, Gordon KD, Babler B, Block M, Bracker S, Engelbracht C, Hora J, Indebetouw R, Meade M, Meixner M, Misselt K, Sewilo M, Shiao B, Whitney B (2010) Is dust forming on the red giant branch in 47 tuc? Astrophys J 711:L99–L103. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/711/2/L99, 1002.1348
Brandt TD, Tojeiro R, Aubourg É, Heavens A, Jimenez R, Strauss MA (2010) The ages of Type Ia supernova progenitors. Astron J 140:804–816. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/140/3/804, 1002.0848
Bromm V, Larson RB (2004) The first stars. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 42:79–118. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.42.053102.134034, arXiv:astro-ph/0311019
Bromm V, Loeb A (2003) The formation of the first low-mass stars from gas with low carbon and oxygen abundances. Nature 425:812–814. doi:10.1038/nature02071, arXiv:astro-ph/0310622
Bromm V, Coppi PS, Larson RB (2002) The formation of the first stars. I. The primordial star-forming cloud. Astrophys J 564:23–51. doi:10.1086/323947, arXiv:astro-ph/0102503
Bromm V, Yoshida N, Hernquist L, McKee CF (2009) The formation of the first stars and galaxies. Nature 459:49–54. doi:10.1038/nature07990, 0905.0929
Burrows A (2009) The role of dust clouds in the atmospheres of brown dwarfs. In: Henning T, Grün E, Steinacker J (eds) Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 414, p 115, 0902.1777
Calura F, Pipino A, Matteucci F (2008) The cycle of interstellar dust in galaxies of different morphological types. Astron Astrophys 479:669–685. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078090, 0706.2197
Carilli CL, Bertoldi F, Omont A, Cox P, McMahon RG, Isaak KG (2001a) Radio observations of infrared-luminous high-redshift quasi-stellar objects. Astron J 122:1679–1687. doi:10.1086/323104, arXiv:astro-ph/0106408
Carilli CL, Bertoldi F, Rupen MP, Fan X, Strauss MA, Menten KM, Kreysa E, Schneider DP, Bertarini A, Yun MS, Zylka R (2001b) A 250 GHz survey of high-redshift quasars from the Sloan digital sky survey. Astrophys J 555:625–632. doi:10.1086/321519, arXiv:astro-ph/0103252
Cernuschi F, Marsicano FR, Kimel I (1965) On polarization of stellar light. Ann Astrophys 28:860
Chabrier G (2003a) Galactic stellar and substellar initial mass function. Publ Astron Soc Pac 115:763–795. doi:10.1086/376392, arXiv:astro-ph/0304382
Chabrier G (2003b) The Galactic disk mass function: reconciliation of the Hubble space telescope and Nearby beterminations. Astrophys J 586:L133–L136. doi:10.1086/374879, arXiv:astro-ph/0302511
Chabrier G (2005) The initial mass function: from Salpeter 1955 to 2005. In: Corbelli E, Palla F, Zinnecker H (eds) The initial mass function 50 years later. Astrophysics and space science library, vol 327, p 41, arXiv:astro-ph/0409465
Charbonnel C, Meynet G, Maeder A, Schaller G, Schaerer D (1993) Grids of stellar models—Part 3—from 0.8 to 120 M⊙ at Z=0.004. Astron Astrophys Suppl Ser 101:415
Chary R, Stern D, Eisenhardt P (2005) Spitzer constraints on the z=6.56 Galaxy lensed by Abell 370. Astrophys J 635:L5–L8. doi:10.1086/499205, arXiv:astro-ph/0510827
Cherchneff I (2006) A chemical study of the inner winds of asymptotic giant branch stars. Astron Astrophys 456:1001–1012. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064827
Cherchneff I (2011) The formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in evolved circumstellar environments. In: EAS publications series, vol 46, pp 177–189. doi:10.1051/eas/1146019, 1010.2703
Cherchneff I, Dwek E (2009) The chemistry of population III Supernova ejecta. I. Formation of molecules in the early Universe. Astrophys J 703:642–661. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/703/1/642, 0907.3621
Cherchneff I, Dwek E (2010) The chemistry of population III Supernova ejecta. II. The nucleation of molecular clusters as a diagnostic for dust in the early Universe. Astrophys J 713:1–24. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/713/1/1, 1002.3060
Cherchneff I, Barker JR, Tielens AGGM (1991) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon optical properties and contribution to the acceleration of stellar outflows. Astrophys J 377:541–552. doi:10.1086/170383
Cherchneff I, Barker JR, Tielens AGGM (1992) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon formation in carbon-rich stellar envelopes. Astrophys J 401:269–287. doi:10.1086/172059
Chevalier RA (2005) Young core-collapse Supernova remnants and their Supernovae. Astrophys J 619:839–855. doi:10.1086/426584, arXiv:astro-ph/0409013
Chevalier RA (2006) From progenitor to afterlife. arXiv:astro-ph/0607422
Chevalier RA, Klein RI (1978) On the Rayleigh–Taylor instability in stellar explosions. Astrophys J 219:994–1007. doi:10.1086/155864
Chu Y, Gruendl RA, Stockdale CJ, Rupen MP, Cowan JJ, Teare SW (2004) The nature of SN 1961V. Astron J 127:2850–2855. doi:10.1086/383556, arXiv:astro-ph/0402473
Clayton DD (1979) Sudden grain nucleation and growth in supernova and nova ejecta. Astrophys Space Sci 65:179–189. doi:10.1007/BF00643499
Clayton DD, Arnett D, Kane J, Meyer BS, (1997) Type X silicon carbide presolar grains: Type IA supernovae condensates? Astrophys J 486:824. doi:10.1086/304545
Clayton DD, Liu W, Dalgarno A, (1999) Condensation of carbon in radioactive Supernova gas. Science 283:1290. doi:10.1126/science.283.5406.1290
Clayton DD, Deneault E, Meyer BS (2001) Condensation of carbon in radioactive Supernova gas. Astrophys J 562:480–493. doi:10.1086/323467
Crockett RM, Smartt SJ, Eldridge JJ, Mattila S, Young DR, Pastorello A, Maund JR, Benn CR, Skillen I (2007) A deeper search for the progenitor of the Type Ic Supernova 2002ap. Mon Not R Astron Soc 381:835–850. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12283.x, 0706.0500
Crockett RM, Eldridge JJ, Smartt SJ, Pastorello A, Gal-Yam A, Fox DB, Leonard DC, Kasliwal MM, Mattila S, Maund JR, Stephens AW, Danziger IJ (2008) The Type IIb SN 2008ax: the nature of the progenitor. Mon Not R Astron Soc 391:L5–L9. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2008.00540.x, 0805.1913
Crockett RM, Smartt SJ, Pastorello A, Eldridge JJ, Stephens AW, Maund JR, Mattila S (2011) On the nature of the progenitors of three Type II-P supernovae: 2004et, 2006my and 2006ov. Mon Not R Astron Soc 410:2767–2786. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17652.x, 0912.3302
Crowther PA (2007) Physical properties of Wolf–Rayet stars. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 45:177–219. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.45.051806.110615, arXiv:astro-ph/0610356
Cucchiara A, Levan AJ, Fox DB, Tanvir NR, Ukwatta TN, Berger E, Krühler T, Küpcü Yoldaş A, Wu XF, Toma K, Greiner J, Olivares FE, Rowlinson A, Amati L, Sakamoto T, Roth K, Stephens A, Fritz A, Fynbo JPU, Hjorth J, Malesani D, Jakobsson P, Wiersema K, O’Brien PT, Soderberg AM, Foley RJ, Fruchter AS, Rhoads J, Rutledge RE, Schmidt BP, Dopita MA, Podsiadlowski P, Willingale R, Wolf C, Kulkarni SR, D’Avanzo P (2011) A photometric redshift of z∼9.4 for GRB 090429B. Astrophys J 736:7. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/736/1/7, 1105.4915
Dabringhausen J, Kroupa P, Baumgardt H (2009) A top-heavy stellar initial mass function in starbursts as an explanation for the high mass-to-light ratios of ultra-compact dwarf galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc 394:1529–1543. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14425.x, 0901.0915
D’Antona F, Caloi V (2004) The early evolution of globular clusters: the case of NGC 2808. Astrophys J 611:871–880. doi:10.1086/422334, arXiv:astro-ph/0405016
D’Antona F, Mazzitelli I (1996) Hot bottom burning in asymptotic giant branch stars and the turbulent convection model. Astrophys J 470:1093. doi:10.1086/177933
Danziger IJ, Gouiffes C, Bouchet P, Lucy LB (1989) Supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. IAUC 4746:1
Dartois E, Muñoz Caro GM, Deboffle D, d’Hendecourt L (2004) Diffuse interstellar medium organic polymers. Photoproduction of the 3.4, 6.85 and 7.25 μm features. Astron Astrophys 423:L33–L36. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200400032
Daulton TL, Bernatowicz TJ, Lewis RS, Messenger S, Stadermann FJ, Amari S (2002) Polytype distribution in circumstellar silicon carbide. Science 296:1852–1855. doi:10.1126/science.1071136
Davé R (2008) The galaxy stellar mass-star formation rate relation: evidence for an evolving stellar initial mass function? Mon Not R Astron Soc 385:147–160. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.12866.x, 0710.0381
Davidson K (1971) On the nature of Eta Carinae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 154:415–427
De Breuck C, Neri R, Morganti R, Omont A, Rocca-Volmerange B, Stern D, Reuland M, van Breugel W, Röttgering H, Stanford SA, Spinrad H, Vigotti M, Wright M (2003) CO emission and associated H I absorption from a massive gas reservoir surrounding the z=3 radio galaxy B3 J2330+3927. Astron Astrophys 401:911–925. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030171, arXiv:astro-ph/0302154
Decin L, Cherchneff I, Hony S, Dehaes S, De Breuck C, Menten KM (2008) Detection of “parent” molecules from the inner wind of AGB stars as tracers of non-equilibrium chemistry. Astron Astrophys 480:431–438. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078892, 0801.1118
Decin L, De Beck E, Brünken S, Müller HSP, Menten KM, Kim H, Willacy K, de Koter A, Wyrowski F (2010) Circumstellar molecular composition of the oxygen-rich AGB star IK Tauri. II. In-depth non-LTE chemical abundance analysis. Astron Astrophys 516:A69. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014136, 1004.1914
Di Carlo E, Corsi C, Arkharov AA, Massi F, Larionov VM, Efimova NV, Dolci M, Napoleone N, Di Paola A (2008) Near-infrared observations of the Type Ib Supernova SN 2006jc: evidence of interactions with dust. Astrophys J 684:471–480. doi:10.1086/590051, 0712.3855
Doane JS, Mathews WG (1993) Stellar evolution in the starburst Galaxy M82: evidence for a top-heavy initial mass function. Astrophys J 419:573. doi:10.1086/173509
Donn B, Nuth JA (1985) Does nucleation theory apply to the formation of refractory circumstellar grains? Astrophys J 288:187–190. doi:10.1086/162779
Dorschner J, Henning T (1995) Dust metamorphosis in the galaxy. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 6:271–333. doi:10.1007/BF00873686
Dorschner J, Friedemann C, Guertler J, Duley WW (1980a) Laboratory spectra of protosilicates and the interstellar silicate absorption bands. Astrophys Space Sci 68:159–174. doi:10.1007/BF00641652
Dorschner J, Friedemann C, Guertler J, Duley WW (1980b) Laboratory spectra of protosilicates and the interstellar silicate absorption bands. Astrophys Space Sci 68:159–174. doi:10.1007/BF00641652
Douvion T, Lagage PO, Cesarsky CJ, Dwek E (2001a) Dust in the Tycho, Kepler and Crab Supernova remnants. Astron Astrophys 373:281–291. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010447
Douvion T, Lagage PO, Pantin E (2001b) Cassiopeia A dust composition and heating. Astron Astrophys 369:589–593. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010053
Draine BT (1979) Time-dependent nucleation theory and the formation of interstellar grains. Astrophys Space Sci 65:313–335. doi:10.1007/BF00648499
Draine BT (1985) Tabulated optical properties of graphite and silicate grains. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 57:587–594. doi:10.1086/191016
Draine BT (1990) Mass determinations from far-infrared observations. In: Thronson HA Jr, Shull JM (eds) The interstellar medium in galaxies, astrophysics and space science library, vol 161, pp 483–492
Draine BT (2009) Interstellar dust models and evolutionary implications. In: Henning T, Grün E, Steinacker J (eds) Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 414, p 453, 0903.1658
Draine BT, Lee HM (1984) Optical properties of interstellar graphite and silicate grains. Astrophys J 285:89–108. doi:10.1086/162480
Duley WW, Williams DA (1981) The infrared spectrum of interstellar dust—surface functional groups on carbon. Mon Not R Astron Soc 196:269–274
Dunne L, Eales SA (2001) The SCUBA local Universe Galaxy survey—II 450-μm data: evidence for cold dust in bright IRAS galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc 327:697–714. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04789.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0106362
Dunne L, Eales S, Ivison R, Morgan H, Edmunds M (2003) Type II supernovae as a significant source of interstellar dust. Nature 424:285–287. doi:10.1038/nature01792, arXiv:astro-ph/0307320
Dunne L, Maddox SJ, Ivison RJ, Rudnick L, Delaney TA, Matthews BC, Crowe CM, Gomez HL, Eales SA, Dye S (2009) Cassiopeia A: dust factory revealed via submillimetre polarimetry. Mon Not R Astron Soc 394:1307–1316. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14453.x, 0809.0887
Dwek E (1998) The evolution of the elemental abundances in the gas and dust phases of the Galaxy. Astrophys J 501:643. doi:10.1086/305829, arXiv:astro-ph/9707024
Dwek E (2004) The detection of Cold Dust in Cassiopeia A: evidence for the formation of metallic needles in the ejecta. Astrophys J 607:848–854. doi:10.1086/382653, arXiv:astro-ph/0401074
Dwek E, Cherchneff I (2011) The origin of dust in the early Universe: probing the star formation history of Galaxies by their dust content. Astrophys J 727:63. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/727/2/63, 1011.1303
Dwek E, Moseley SH, Glaccum W, Graham JR, Loewenstein RF, Silverberg RF, Smith RK (1992) Dust and gas contributions to the energy output of SN 1987A on day 1153. Astrophys J 389:L21–L24. doi:10.1086/186339
Dwek E, Galliano F, Jones AP (2007) The evolution of dust in the early Universe with applications to the Galaxy SDSS J1148+5251. Astrophys J 662:927–939. doi:10.1086/518430, 0705.3799
Dwek E, Arendt RG, Bouchet P, Burrows DN, Challis P, Danziger IJ, De Buizer JM, Gehrz RD, Kirshner RP, McCray R, Park S, Polomski EF, Woodward CE (2008) Infrared and X-Ray evidence for circumstellar grain destruction by the blast wave of Supernova 1987A. Astrophys J 676:1029–1039. doi:10.1086/529038, 0712.2759
Dwek E, Galliano F, Jones A (2009) The cycle of dust in the Milky Way: Clues from the high-redshift and local Universe. In: Henning T, Grün E, Steinacker J (eds) Cosmic dust—near and far. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 414, p 183, 0903.0006
Edmunds MG (2001) An elementary model for the dust cycle in galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc 328:223–236. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04859.x
Ekström S, Meynet G, Maeder A (2008) Can very massive stars avoid pair-instability supernovae. In: Bresolin F, Crowther PA, Puls J (eds) IAU symposium, vol 250, pp 209–216. doi:10.1017/S1743921308020516, 0801.3397
Eldridge JJ, Relaño M (2011) The red supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars of NGC 604. Mon Not R Astron Soc 411:235–246. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17676.x, 1009.1871
Eldridge JJ, Tout CA (2004) The progenitors of core-collapse supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 353:87–97. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08041.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0405408
Eldridge JJ, Vink JS (2006) Implications of the metallicity dependence of Wolf–Rayet winds. Astron Astrophys 452:295–301. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065001, arXiv:astro-ph/0603188
Eldridge JJ, Genet F, Daigne F, Mochkovitch R (2006) The circumstellar environment of Wolf–Rayet stars and gamma-ray burst afterglows. Mon Not R Astron Soc 367:186–200. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09938.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0509749
Eldridge JJ, Izzard RG, Tout CA (2008) The effect of massive binaries on stellar populations and supernova progenitors. Mon Not R Astron Soc 384:1109–1118. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12738.x, 0711.3079
Elias-Rosa N, Van Dyk SD, Li W, Miller AA, Silverman JM, Ganeshalingam M, Boden AF, Kasliwal MM, Vinkó J, Cuillandre J, Filippenko AV, Steele TN, Bloom JS, Griffith CV, Kleiser IKW, Foley RJ (2010) The massive progenitor of the Type II-linear Supernova 2009kr. Astrophys J 714:L254–L259. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/714/2/L254, 0912.2880
Elmegreen BG (2009) The stellar initial mass function in 2007: a year for discovering variations. In: The evolving ISM in the Milky Way and Nearby Galaxies
Elmhamdi A, Danziger IJ, Chugai N, Pastorello A, Turatto M, Cappellaro E, Altavilla G, Benetti S, Patat F, Salvo M (2003) Photometry and spectroscopy of the Type IIP SN 1999em from outburst to dust formation. Mon Not R Astron Soc 338:939–956. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06150.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0209623
Elmhamdi A, Danziger IJ, Cappellaro E, Della Valle M, Gouiffes C, Phillips MM, Turatto M (2004) SN Ib 1990I: Clumping and dust in the ejecta? Astron Astrophys 426:963–977. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041318, arXiv:astro-ph/0407145
Elvis M, Marengo M, Karovska M (2002) Smoking quasars: a new source for cosmic dust. Astrophys J 567:L107–L110. doi:10.1086/340006, arXiv:astro-ph/0202002
Ercolano B, Barlow MJ, Sugerman BEK (2007) Dust yields in clumpy supernova shells: SN 1987A revisited. Mon Not R Astron Soc 375:753–763. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11336.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0611719
Erickson EF, Knacke RF, Tokunaga AT, Haas MR (1981) The 45 micron H2O ice band in the Kleinmann–Low Nebula. Astrophys J 245:148–153. doi:10.1086/158795
Fabian D, Posch T, Mutschke H, Kerschbaum F, Dorschner J (2001) Infrared optical properties of spinels. A study of the carrier of the 13, 17 and 32 μm emission features observed in ISO-SWS spectra of oxygen-rich AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 373:1125–1138. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010657
Fallest DW, Nozawa T, Nomoto K, Umeda H, Maeda K, Kozasa T, Lazzati D (2011) On the effects of microphysical grain properties on the yields of carbonaceous dust from type II SNe. arXiv:1105.4631
Fan X, Strauss MA, Schneider DP, Becker RH, White RL, Haiman Z, Gregg M, Pentericci L, Grebel EK, Narayanan VK, Loh Y, Richards GT, Gunn JE, Lupton RH, Knapp GR, Ivezić Ž, Brandt WN, Collinge M, Hao L, Harbeck D, Prada F, Schaye J, Strateva I, Zakamska N, Anderson S, Brinkmann J, Bahcall NA, Lamb DQ, Okamura S, Szalay A, York DG (2003) A survey of z>5.7 Quasars in the Sloan digital sky survey. II. Discovery of three additional quasars at z>6. Astron J 125:1649–1659. doi:10.1086/368246, arXiv:astro-ph/0301135
Feder D (1966) Adv Phys 15:111
Ferrarotti AS, Gail H (2001) Dust Condensation in LBV and WN stars. In: Schielicke ER (ed) Astronomische gesellschaft meeting abstracts, vol 18, p 49
Ferrarotti AS, Gail H (2002) Mineral formation in stellar winds. III. Dust formation in S stars. Astron Astrophys 382:256–281. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011580
Ferrarotti AS, Gail H (2006) Composition and quantities of dust produced by AGB-stars and returned to the interstellar medium. Astron Astrophys 447:553–576. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041198
Filippenko AV (1997) Optical spectra of Supernovae. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 35:309–355. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.35.1.309
Filippenko AV, Barth AJ, Bower GC, Ho LC, Stringfellow GS, Goodrich RW, Porter AC (1995) Was Fritz Zwicky’s “Type V” SN 1961V a Genuine Supernova? Astron J 110:2261. doi:10.1086/117687
Fink M, Hillebrandt W, Röpke FK (2007) Double-detonation supernovae of sub-Chandrasekhar mass white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 476:1133–1143. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078438, 0710.5486
Foley RJ, Smith N, Ganeshalingam M, Li W, Chornock R, Filippenko AV (2007) SN 2006jc: a Wolf–Rayet star exploding in a dense He-rich circumstellar medium. Astrophys J 657:L105–L108. doi:10.1086/513145, arXiv:astro-ph/0612711
Foley RJ, Berger E, Fox O, Levesque EM, Challis PJ, Ivans II, Rhoads JE, Soderberg AM (2010) The diversity of massive star outbursts I: observations of SN 2009ip, UGC 2773 OT2009-1, and their progenitors. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/732/1/32, 1002.0635
Fox O, Skrutskie MF, Chevalier RA, Kanneganti S, Park C, Wilson J, Nelson M, Amirhadji J, Crump D, Hoeft A, Provence S, Sargeant B, Sop J, Tea M, Thomas S, Woolard K (2009) Near-infrared photometry of the Type IIn SN 2005ip: the case for dust condensation. Astrophys J 691:650–660. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/650, 0807.3555
Fox OD, Chevalier RA, Dwek E, Skrutskie MF, Sugerman BEK, Leisenring JM (2010) Disentangling the origin and heating mechanism of Supernova dust: late-time Spitzer spectroscopy of the Type IIn SN 2005ip. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/725/2/1768, 1005.4682
Fox OD, Chevalier RA, Skrutskie MF, Soderberg AM, Filippenko AV, Ganeshalingam M, Silverman JM, Smith N, Steele TN (2011) A Spitzer survey for dust in Type IIn Supernovae. arXiv:1104.5012
Fraser M, Takáts K, Pastorello A, Smartt SJ, Mattila S, Botticella M, Valenti S, Ergon M, Sollerman J, Arcavi I, Benetti S, Bufano F, Crockett RM, Danziger IJ, Gal-Yam A, Maund JR, Taubenberger S, Turatto M (2010) On the progenitor and early evolution of the Type II Supernova 2009kr. Astrophys J 714:L280–L284. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/714/2/L280, 0912.2071
Frenklach M, Feigelson ED (1989) Formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in circumstellar envelopes. Astrophys J 341:372–384. doi:10.1086/167501
Frenklach M, Carmer CS, Feigelson ED (1989) Silicon carbide and the origin of interstellar carbon grains. Nature 339:196–198. doi:10.1038/339196a0
Freudling W, Corbin MR, Korista KT (2003) Iron Emission in z∼6 QSOs. Astrophys J 587:L67–L70. doi:10.1086/375338, arXiv:astro-ph/0303424
Fryer CL, Mazzali PA, Prochaska J, Cappellaro E, Panaitescu A, Berger E, van Putten M, van den Heuvel EPJ, Young P, Hungerford A, Rockefeller G, Yoon S, Podsiadlowski P, Nomoto K, Chevalier R, Schmidt B, Kulkarni S (2007) Constraints on Type Ib/c Supernovae and gamma-ray burst progenitors. Publ Astron Soc Pac 119:1211–1232. doi:10.1086/523768
Gail H (2003) Formation and evolution of minerals in accretion disks and stellar outflows. In: Henning TK (ed) Astromineralogy. Lecture notes in physics, vol 609, Springer, Berlin, pp 55–120
Gail H, Keller R, Sedlmayr E (1984) Dust formation in stellar winds. I—A rapid computational method and application to graphite condensation. Astron Astrophys 133:320–332
Gail H, Duschl WJ, Ferrarotti AS, Weis K (2005) Dust formation in LBV envelopes. In: Humphreys R, Stanek K (eds) The fate of the most massive stars. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 332, p 317
Gail HP (2010) Formation and evolution of minerals in accretion disks and stellar outflows. In: Henning T (ed) Lecture notes in physics, vol 815. Springer, Berlin, pp 61–141. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13259-9_2
Gal-Yam A, Leonard DC, Fox DB, Cenko SB, Soderberg AM, Moon D, Sand DJ, Li W, Filippenko AV, Aldering G, Copin Y (2007) On the progenitor of SN 2005gl and the nature of Type IIn Supernovae. Astrophys J 656:372–381. doi:10.1086/510523, arXiv:astro-ph/0608029
Gal-Yam A, Mazzali P, Ofek EO, Nugent PE, Kulkarni SR, Kasliwal MM, Quimby RM, Filippenko AV, Cenko SB, Chornock R, Waldman R, Kasen D, Sullivan M, Beshore EC, Drake AJ, Thomas RC, Bloom JS, Poznanski D, Miller AA, Foley RJ, Silverman JM, Arcavi I, Ellis RS, Deng J (2009) Supernova 2007bi as a pair-instability explosion. Nature 462:624–627. doi:10.1038/nature08579, 1001.1156
Gall C, Andersen AC, Hjorth J (2011a) Genesis and evolution of dust in galaxies in the early Universe. I. Modelling dust evolution in starburst galaxies. Astron Astrophys 528:A13. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015286, 1011.3157
Gall C, Andersen AC, Hjorth J (2011b) Genesis and evolution of dust in galaxies in the early Universe. II. Rapid dust evolution in quasars at z≳6. Astron Astrophys A 528:14. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015605, 1101.1553
Gallagher JS III, Hunter DA, Tutukov AV (1984) Star formation histories of irregular galaxies. Astrophys J 284:544–556. doi:10.1086/162437
Gallerani S, Maiolino R, Juarez Y, Nagao T, Marconi A, Bianchi S, Schneider R, Mannucci F, Oliva T, Willott CJ, Jiang L, Fan X (2010) The extinction law at high redshift and its implications. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014721, 1006.4463
Gautschy-Loidl R, Höfner S, Jørgensen UG, Hron J (2004) Dynamic model atmospheres of AGB stars. IV. A comparison of synthetic carbon star spectra with observations. Astron Astrophys 422:289–306. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20035860
Gehrz R (1989) Sources of stardust in the Galaxy. In: Allamandola LJ, Tielens AGGM (eds) Interstellar dust. IAU symposium, vol 135, p 445
Gomez HL, Dunne L, Ivison RJ, Reynoso EM, Thompson MA, Sibthorpe B, Eales SA, Delaney TM, Maddox S, Isaak K (2009) Accounting for the foreground contribution to the dust emission towards Kepler’s supernova remnant. Mon Not R Astron Soc 397:1621–1632. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15061.x, 0905.2564
Gomez HL, Vlahakis C, Stretch CM, Dunne L, Eales SA, Beelen A, Gomez EL, Edmunds MG (2010) Submillimetre variability of Eta Carinae: cool dust within the outer ejecta. Mon Not R Astron Soc 401:L48–L52. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00784.x, 0911.0176
Goodrich RW, Stringfellow GS, Penrod GD, Filippenko AV (1989) SN 1961V—an extragalactic Eta Carinae analog. Astrophys J 342:908–916. doi:10.1086/167646
Green DA, Tuffs RJ, Popescu CC (2004) Far-infrared and submillimetre observations of the Crab nebula. Mon Not R Astron Soc 355:1315–1326, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08414.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0409469
Greggio L (2005) The rates of Type Ia supernovae. I. Analytical formulations. Astron Astrophys 441:1055–1078. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20052926, arXiv:astro-ph/0504376
Greggio L, Renzini A (1983) The binary model for Type I supernovae—theoretical rates. Astron Astrophys 118:217–222
Greif TH, Bromm V (2006) Two populations of metal-free stars in the early Universe. Mon Not R Astron Soc 373:128–138. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11017.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0604367
Greif TH, Glover SCO, Bromm V, Klessen RS (2010) The first galaxies: chemical enrichment, mixing, and star formation. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/716/1/510, 1003.0472
Groenewegen MAT, van der Veen WECJ, Matthews HE (1998a) IRC + 10 216 revisited. II. The circumstellar CO shell. Astron Astrophys 338:491–504. arXiv:astro-ph/9807201
Groenewegen MAT, Whitelock PA, Smith CH, Kerschbaum F (1998b) Dust shells around carbon Mira variables. Mon Not R Astron Soc 293:18. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01113.x
Groenewegen MAT, Wood PR, Sloan GC, Blommaert JADL, Cioni M, Feast MW, Hony S, Matsuura M, Menzies JW, Olivier EA, Vanhollebeke E, van Loon JT, Whitelock PA, Zijlstra AA, Habing HJ, Lagadec E (2007) Luminosities and mass-loss rates of carbon stars in the Magellanic Clouds. Mon Not R Astron Soc 376:313–337. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11428.x
Habergham SM, Anderson JP, James PA (2010) Type Ibc supernovae in disturbed galaxies: evidence for a top-heavy IMF. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/717/1/342, 1005.0511
Hanner M (1988) Grain optical properties. In: Hanner MS (ed) Infrared observations of comets Halley and Wilson and properties of the grains, pp 22–49
Heger A, Woosley SE (2002) The nucleosynthetic signature of population III. Astrophys J 567:532–543. doi:10.1086/338487, arXiv:astro-ph/0107037
Heger A, Fryer CL, Woosley SE, Langer N, Hartmann DH (2003) How massive single stars end their life. Astrophys J 591:288–300. doi:10.1086/375341, arXiv:astro-ph/0212469
Helling C, Dehn M, Woitke P, Hauschildt PH (2008) Consistent simulations of substellar atmospheres and nonequilibrium dust cloud formation. Astrophys J 675:L105–L108. doi:10.1086/533462, 0801.3733
Henning T (ed) (2010a) Astromineralogy. Lecture notes in physics, vol 815. Springer, Berlin
Henning T (2010b) Cosmic silicates. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 48:21. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-081309-130815
Henning T, Jäger C, Mutschke H (2004) Laboratory studies of carbonaceous dust analogs. In: Witt AN, Clayton GC, Draine BT (eds) Astrophysics of dust, astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 309, p 603
Herant M, Benz W (1991) Hydrodynamical instabilities and mixing in SN 1987A—Two-dimensional simulations of the first 3 months. Astrophys J 370:L81–L84. doi:10.1086/185982
Herant M, Woosley SE (1994) Postexplosion hydrodynamics of supernovae in red supergiants. Astrophys J 425:814–828. doi:10.1086/174026
Herwig F (2004) Evolution and yields of extremely metal-poor intermediate-mass stars. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 155:651–666. doi:10.1086/425419, arXiv:astro-ph/0407592
Hildebrand RH (1983) The determination of cloud masses and dust characteristics from submillimetre thermal emission. Q J R Astron Soc 24:267
Hillebrandt W, Niemeyer JC (2000) Type IA Supernova explosion models. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 38:191–230. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.38.1.191, arXiv:astro-ph/0006305
Hines DC, Rieke GH, Gordon KD, Rho J, Misselt KA, Woodward CE, Werner MW, Krause O, Latter WB, Engelbracht CW, Egami E, Kelly DM, Muzerolle J, Stansberry JA, Su KYL, Morrison JE, Young ET, Noriega-Crespo A, Padgett DL, Gehrz RD, Polomski E, Beeman JW, Haller EE (2004) Imaging of the Supernova remnant Cassiopeia A with the multiband imaging photometer for spitzer (MIPS). Astrophys J Suppl Ser 154:290–295. doi:10.1086/422583
Hines DC, Krause O, Rieke GH, Fan X, Blaylock M, Neugebauer G (2006) Spitzer observations of high-redshift QSOs. Astrophys J 641:L85–L88. doi:10.1086/504109, arXiv:astro-ph/0604347
Hirashita H, Nozawa T, Takeuchi TT, Kozasa T (2008) Extinction curves flattened by reverse shocks in supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 384:1725–1732. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12834.x, 0801.2649
Hjorth J, Sollerman J, Møller P, Fynbo JPU, Woosley SE, Kouveliotou C, Tanvir NR, Greiner J, Andersen MI, Castro-Tirado AJ, Castro Cerón JM, Fruchter AS, Gorosabel J, Jakobsson P, Kaper L, Klose S, Masetti N, Pedersen H, Pedersen K, Pian E, Palazzi E, Rhoads JE, Rol E, van den Heuvel EPJ, Vreeswijk PM, Watson D, Wijers RAMJ (2003) A very energetic supernova associated with the γ-ray burst of 29 March 2003. Nature 423:847–850. doi:10.1038/nature01750, arXiv:astro-ph/0306347
Hofmeister AM (1997) Infrared reflectance spectra of fayalite, and absorption data from assorted olivines, including pressure and isotope effects. Phys Chem Miner 24:535–546. doi:10.1007/s002690050069
Höfner S (2006) Mass loss: the role of grains. In: IAU joint discussion, vol 11
Höfner S (2008) Winds of M-type AGB stars driven by micron-sized grains. Astron Astrophys 491:L1–L4. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810641
Höfner S (2009) Dust formation and winds around evolved stars: the good, the bad and the ugly cases. In: Henning T, Grün E, Steinacker J (eds) Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 414, p 3. 0903.5280
Höfner S, Andersen AC (2007) Winds of M- and S-type AGB stars: an unorthodox suggestion for the driving mechanism. Astron Astrophys 465:L39–L42. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066970, arXiv:astro-ph/0702445
Höfner S, Jörgensen UG, Loidl R, Aringer B (1998) Dynamic model atmospheres of AGB stars. I. Atmospheric structure and dynamics. Astron Astrophys 340:497–507
Höfner S, Gautschy-Loidl R, Aringer B, Jørgensen UG (2003) Dynamic model atmospheres of AGB stars. III. Effects of frequency-dependent radiative transfer. Astron Astrophys 399:589–601. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021757
Hoyle F, Wickramasinghe NC (1970) Dust in Supernova explosions. Nature 226:62–63. doi:10.1038/226062a0
Hughes DH, Dunlop JS, Rawlings S (1997) High-redshift radio galaxies and quasars at submillimetre wavelengths: assessing their evolutionary status. Mon Not R Astron Soc 289:766–782. arXiv:astro-ph/9705094
Hunter DJ, Valenti S, Kotak R, Meikle WPS, Taubenberger S, Pastorello A, Benetti S, Stanishev V, Smartt SJ, Trundle C, Arkharov AA, Bufano F, Cappellaro E di Carlo E, Dolci M, Elias-Rosa N, Frandsen S, Fynbo JU, Hopp U, Larionov VM, Laursen P, Mazzali P, Navasardyan H, Ries C, Riffeser A, Rizzi L, Tsvetkov DY, Turatto M, Wilke S (2009) Extensive optical and near-infrared observations of the nearby, narrow-lined type Ic !ASTROBJ?SN 2007gr!/ASTROBJ?: days 5 to 415. Astron Astrophys 508:371–389. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912896, 0909.3780
Iben I Jr, Renzini A (1981) Physical processes in red giants. In: Iben I Jr, Renzini A (eds) Proceedings of the second workshop, advanced school of astronomy, Erice, Italy, 3–13 September, 1980. Physical processes in red giants, astrophysics and space science library, vol 88
Iben I Jr, Tutukov AV (1984) Supernovae of type I as end products of the evolution of binaries with components of moderate initial mass (M not greater than about 9 solar masses). Astrophys J Suppl Ser 54:335–372. doi:10.1086/190932
Inserra C, Turatto M, Pastorello A, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Pumo ML, Zampieri L, Agnoletto I, Bufano F, Botticella MT, Della Valle M, Elias Rosa N, Iijima T, Spiro S, Valenti S, (2011) The Type IIP SN 2007od in UGC 12846: from a bright maximum to dust formation in the nebular phase. arXiv:1102.5468
Isaak KG, Priddey RS, McMahon RG, Omont A, Peroux C, Sharp RG, Withington S (2002) The SCUBA Bright Quasar Survey (SBQS): 850-μm observations of the z≳4 sample. Mon Not R Astron Soc 329:149–162. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.04966.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0109438
Ishihara D, Kaneda H, Furuzawa A, Kunieda H, Suzuki T, Koo B, Lee H, Lee J, Onaka T (2010) Origin of the dust emission from Tycho’s SNR. Astron Astrophys 521:L61. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015131, 1009.6047
Ivison RJ, Swinbank AM, Swinyard B, Smail I, Pearson CP, Rigopoulou D, Polehampton E, Baluteau J, Barlow MJ, Blain AW, Bock J, Clements DL, Coppin K, Cooray A, Danielson A, Dwek E, Edge AC, Franceschini A, Fulton T, Glenn J, Griffin M, Isaak K, Leeks S, Lim T, Naylor D, Oliver SJ, Page MJ, Pérez Fournon I, Rowan-Robinson M, Savini G, Scott D, Spencer L, Valtchanov I, Vigroux L, Wright GS (2010) Herschel and SCUBA-2 imaging and spectroscopy of a bright, lensed submillimetre galaxy at z=2.3. Astron Astrophys 518:L35. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014548, 1005.1071
Iwamoto K, Nakamura T, Nomoto K, Mazzali PA, Danziger IJ, Garnavich P, Kirshner R, Jha S, Balam D, Thorstensen J (2000) The peculiar Type IC Supernova 1997EF: another Hypernova. Astrophys J 534:660–669. doi:10.1086/308761
Jäger C, Molster FJ, Dorschner J, Henning T, Mutschke H, Waters LBFM (1998a) Steps toward interstellar silicate mineralogy. IV. The crystalline revolution. Astron Astrophys 339:904–916
Jäger C, Mutschke H, Henning T (1998b) Optical properties of carbonaceous dust analogues. Astron Astrophys 332:291–299
Jäger C, Dorschner J, Mutschke H, Posch T, Henning T (2003) Steps toward interstellar silicate mineralogy. VII. Spectral properties and crystallization behaviour of magnesium silicates produced by the sol–gel method. Astron Astrophys 408:193–204. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030916
Jäger C, Huisken F, Mutschke H, Jansa IL, Henning T (2009a) Formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and carbonaceous solids in gas-phase condensation experiments. Astrophys J 696:706–712. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/696/1/706, 0903.0775
Jäger C, Mutschke H, Henning T, Huisken F (2009b) Analogs of cosmic dust. In: Henning T, Grün E, Steinacker J (eds) Cosmic dust—near and far. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 414, p 319
Jäger C, Mutschke H, Henning T, Huisken F (2011) From PAHs to solid carbon. In: EAS Publications Series, vol 46, pp 293–304. doi:10.1051/eas/1146031
Johnson JL, Greif TH, Bromm V (2007) Local radiative feedback in the formation of the first protogalaxies. Astrophys J 665:85–95. doi:10.1086/519212, arXiv:astro-ph/0612254
Jones AP (2004) Dust destruction processes. In: Witt AN Clayton GC Draine BT (eds) Astrophysics of dust. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 309, p 347
Jones AP, D’Hendecourt LB (2004) Interstellar nanodiamonds. In: Witt AN Clayton GC Draine BT (eds) Astrophysics of dust. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 309, p 589
Jones AP, Nuth JA (2011) Dust destruction in the ISM: a re-evaluation of dust lifetimes. Astron Astrophys A 530:44. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014440
Jones AP, Tielens AGGM, Hollenbach DJ, McKee CF (1994) Grain destruction in shocks in the interstellar medium. Astrophys J 433:797–810. doi:10.1086/174689
Juarez Y, Maiolino R, Mujica R, Pedani M, Marinoni S, Nagao T, Marconi A, Oliva E (2009) The metallicity of the most distant quasars. Astron Astrophys 494:L25–L28. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200811415, 0901.0974
Justtanont K, Barlow MJ, Skinner CJ, Roche PF, Aitken DK, Smith CH (1996) Mid-infrared spectroscopy of carbon-rich post-AGB objects and detection of the PAH molecule chrysene. Astron Astrophys 309:612–628
Karakas A, Lattanzio JC (2007) Stellar models and yields of asymptotic giant branch stars. Publ Astron Soc Aust 24:103–117. doi:10.1071/AS07021, 0708.4385
Karakas AI (2010) Updated stellar yields from asymptotic giant branch models. Mon Not R Astron Soc 403:1413–1425. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16198.x, 0912.2142
Karlsson T, Johnson JL, Bromm V (2008) Uncovering the chemical signature of the first stars in the Universe. Astrophys J 679:6–16. doi:10.1086/533520, 0709.4025
Kawabata KS, Tanaka M, Maeda K, Hattori T, Nomoto K, Tominaga N, Yamanaka M (2009) Extremely luminous Supernova 2006gy at late phase: detection of optical emission from Supernova. Astrophys J 697:747–757. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/697/1/747, 0902.1440
Kawara K, Hirashita H, Nozawa T, Kozasa T, Oyabu S, Matsuoka Y, Shimizu T, Sameshima H, Ienaka N (2011) Supernova dust for the extinction law in a young infrared galaxy at z∼1. Mon Not R Astron Soc 412:1070–1080. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17960.x, 1011.0511
Kemper F, de Koter A, Waters LBFM, Bouwman J, Tielens AGGM (2002) Dust and the spectral energy distribution of the OH/IR star OH 127.8+0.0: evidence for circumstellar metallic iron. Astron Astrophys 384:585–593. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020036, arXiv:astro-ph/0201128
Kifonidis K, Plewa T, Janka H, Müller E (2003) Non-spherical core collapse supernovae. I. Neutrino-driven convection, Rayleigh–Taylor instabilities, and the formation and propagation of metal clumps. Astron Astrophys 408:621–649. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030863, arXiv:astro-ph/0302239
Kitaura FS, Janka H, Hillebrandt W (2006) Explosions of O-Ne-Mg cores, the Crab Supernova, and subluminous Type II-P Supernovae. Astron Astrophys 450:345–350. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054703, arXiv:astro-ph/0512065
Knapp GR, Young K, Lee E, Jorissen A (1998) Multiple molecular winds in evolved Stars I A survey of CO (2–1) and CO (3–2) emission from 45 nearby AGB stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 117:209. doi:10.1086/313111, arXiv:astro-ph/9711125
Kochanek CS, Szczygiel DM, Stanek KZ (2010) The Supernova impostor SN 1961V: spitzer shows that zwicky was right (again). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/737/2/76, 1010.3704
Koike C, Hasegawa H, Asada N, Hattori T (1981) The extinction coefficients in mid- and far-infrared of silicate and iron-oxide minerals of interest for astronomical observations. Astrophys Space Sci 79:77–85. doi:10.1007/BF00655906
Koike C, Shibai H, Tuchiyama A (1993) Extinction of olivine and pyroxene in the mid infrared and far infrared. Mon Not R Astron Soc 264:654
Koike C, Kaito C, Yamamoto T, Shibai H, Kimura S, Suto H (1995) Extinction spectra of corundum in the wavelengths from UV to FIR. Icarus 114:203–214. doi:10.1006/icar.1995.1055
Koike C, Tsuchiyama A, Shibai H, Suto H, Tanabé T, Chihara H, Sogawa H, Mouri H, Okada K (2000) Absorption spectra of Mg-rich Mg–Fe and Ca pyroxenes in the mid- and far-infrared regions. Astron Astrophys 363:1115–1122
Koike C, Chihara H, Tsuchiyama A, Suto H, Sogawa H, Okuda H (2003) Compositional dependence of infrared absorption spectra of crystalline silicate. II. Natural and synthetic olivines. Astron Astrophys 399:1101–1107. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021831
Koike C, Imai Y, Chihara H, Suto H, Murata K, Tsuchiyama A, Tachibana S, Ohara S (2010) Effects of forsterite grain shape on infrared spectra. Astrophys J 709:983–992. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/709/2/983
Komatsu E, Smith KM, Dunkley J, Bennett CL, Gold B, Hinshaw G, Jarosik N, Larson D, Nolta MR, Page L, Spergel DN, Halpern M, Hill RS, Kogut A, Limon M, Meyer SS, Odegard N, Tucker GS, Weiland JL, Wollack E, Wright EL (2010) Seven-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological interpretation. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/192/2/18, 1001.4538
Kotak R (2008) Core-collapse supernovae as dust producers. In: Bresolin F, Crowther PA, Puls J (eds) IAU symposium, vol 250, pp 437–442. doi:10.1017/S1743921308020802
Kotak R, Vink JS (2006) Luminous blue variables as the progenitors of supernovae with quasi-periodic radio modulations. Astron Astrophys 460:L5–L8. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065800, arXiv:astro-ph/0610095
Kotak R, Meikle P, van Dyk SD, Höflich PA, Mattila S (2005) Early-time Spitzer observations of the Type II Plateau Supernova SN 2004dj. Astrophys J 628:L123–L126. doi:10.1086/432719, arXiv:astro-ph/0506407
Kotak R, Meikle WPS, Farrah D, Gerardy CL, Foley RJ, Van Dyk SD, Fransson C, Lundqvist P, Sollerman J, Fesen R, Filippenko AV, Mattila S, Silverman JM, Andersen AC, Höflich PA, Pozzo M, Wheeler JC (2009) Dust and the Type II-Plateau Supernova 2004et. Astrophys J 704:306–323. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/704/1/306, 0904.3737
Kozasa T, Hasegawa H, Nomoto K (1989) Formation of dust grains in the ejecta of SN 1987A. Astrophys J 344:325–331. doi:10.1086/167801
Kozasa T, Hasegawa H, Nomoto K (1991) Formation of dust grains in the ejecta of SN 1987A. II. Astron Astrophys 249:474–482
Kozasa T, Nozawa T, Tominaga N, Umeda H, Maeda K, Nomoto K (2009) Dust in Supernovae: formation and evolution. arXiv:0903.0217
Krause O, Birkmann SM, Rieke GH, Lemke D, Klaas U, Hines DC, Gordon KD (2004) No cold dust within the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. Nature 432:596–598. doi:10.1038/nature03110, arXiv:astro-ph/0412092
Krause O, Birkmann SM, Usuda T, Hattori T, Goto M, Rieke GH, Misselt KA (2008) The Cassiopeia A Supernova was of Type IIb. Science 320:1195. doi:10.1126/science.1155788, 0805.4557
Kroupa P (2002) The initial mass function of stars: evidence for uniformity in variable systems. Science 295:82–91. doi:10.1126/science.1067524, arXiv:astro-ph/0201098
Krumholz MR, Cunningham AJ, Klein RI, McKee CF (2010) Radiation feedback, fragmentation, and the environmental dependence of the initial mass function. Astrophys J 713:1120–1133. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/713/2/1120, 1001.0971
Lagadec E, Zijlstra AA, Sloan GC, Matsuura M, Wood PR, van Loon JT, Harris GJ, Blommaert JADL, Hony S, Groenewegen MAT, Feast MW, Whitelock PA, Menzies JW, Cioni M (2007) Spitzer spectroscopy of carbon stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Mon Not R Astron Soc 376:1270–1284, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11517.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0611071
Lagadec E, Zijlstra AA, Sloan GC, Wood PR, Matsuura M, Bernard-Salas J, Blommaert JADL, Cioni M, Feast MW, Groenewegen MAT, Hony S, Menzies JW, van Loon JT, Whitelock PA (2009) Metal-rich carbon stars in the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy. Mon Not R Astron Soc 396:598–608. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14736.x, 0903.1045
Lakicevic M, van Loon JT, Patat F, Staveley-Smith L, Zanardo G (2011) The remnant of SN1987A revealed at (sub-)mm wavelengths. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116978, 1107.1323
Laor A, Draine BT (1993) Spectroscopic constraints on the properties of dust in active galactic nuclei. Astrophys J 402:441–468. doi:10.1086/172149
Larson RB (1998) Early star formation and the evolution of the stellar initial mass function in galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc 301:569–581. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.02045.x, arXiv:astro-ph/9808145
Larson RB (2006) Understanding the stellar initial mass function. In: Revista mexicana de astronomia y astrofisica conference series, vol 26, pp 55–59. arXiv:astro-ph/0602469
Lattanzio JC, Wood P (2003) Evolution, nucleosynthesis, and pulsation of AGB stars. In: Habing HJ, Olofsson H (eds) Asymptotic giant branch stars, pp 23–104
Ledoux C, Bergeron J, Petitjean P (2002) Dust depletion and abundance pattern in damped Ly-alpha systems: a sample of Mn and Ti abundances at z<2.2. Astron Astrophys 385:802–815. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020198, arXiv:astro-ph/0202134
Lehnert MD, Nesvadba NPH, Cuby J, Swinbank AM, Morris S, Clément B, Evans CJ, Bremer MN, Basa S (2010) Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z=8.6. Nature 467:940–942. doi:10.1038/nature09462, 1010.4312
Leipski C, Meisenheimer K, Klaas U, Walter F, Nielbock M, Krause O, Dannerbauer H, Bertoldi F, Besel M, de Rosa G, Fan X, Haas M, Hutsemekers D, Jean C, Lemke D, Rix H, Stickel M (2010) Herschel/PACS far-infrared photometry of two z>4 quasars. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014718, 1005.5016
Leitch-Devlin MA, Williams DA (1985) Sticking coefficients for atoms and molecules at the surfaces of interstellar dust grains. Mon Not R Astron Soc 213:295–306
Levesque EM, Massey P, Olsen KAG, Plez B, Josselin E, Maeder A, Meynet G (2005) The effective temperature scale of galactic red supergiants: cool, but not as cool as we thought. Astrophys J 628:973–985. doi:10.1086/430901, arXiv:astro-ph/0504337
Levesque EM, Massey P, Olsen KAG, Plez B, Meynet G, Maeder A (2006) The effective temperatures and physical properties of Magellanic cloud red supergiants: the effects of metallicity. Astrophys J 645:1102–1117. doi:10.1086/504417, arXiv:astro-ph/0603596
Li Y, Hernquist L, Robertson B, Cox TJ, Hopkins PF, Springel V, Gao L, Di Matteo T, Zentner AR, Jenkins A, Yoshida N (2007) Formation of z∼6 quasars from hierarchical Galaxy mergers. Astrophys J 665:187–208. doi:10.1086/519297, arXiv:astro-ph/0608190
Liffman K, Clayton DD (1989) Stochastic evolution of refractory interstellar dust during the chemical evolution of a two-phase interstellar medium. Astrophys J 340:853–868. doi:10.1086/167440
Livio M (2000) The progenitors of Type Ia Supernovae. In: Niemeyer JC, Truran JW (eds) Type Ia Supernovae, theory and cosmology, p 33. arXiv:astro-ph/9903264
Lodders K, Fegley BJr (1995) The origin of circumstellar silicon carbide grains found in meteorites. Meteoritics 30:661
Lucy LB, Danziger IJ, Gouiffes C, Bouchet P (1989) Dust Condensation in the Ejecta of SN 1987 A. In: Tenorio-Tagle G, Moles M, Melnick J (eds) IAU colloq. 120: structure and dynamics of the interstellar medium. Lecture notes in physics, vol 350. Springer, Berlin, p 164. doi:10.1007/BFb0114861
Lucy LB, Danziger IJ, Gouiffes C (1991) Excitation by line coincidence in the spectrum of SN 1987A. Astron Astrophys 243:223–229
Maguire K, di Carlo E, Smartt SJ, Pastorello A, Tsvetkov DY, Benetti S, Spiro S, Arkharov AA, Beccari G, Botticella MT, Cappellaro E, Cristallo S, Dolci M, Elias-Rosa N, Fiaschi M, Gorshanov D, Harutyunyan A, Larionov VM, Navasardyan H, Pietrinferni A, Raimondo G, di Rico G, Valenti S, Valentini G, Zampieri L (2010) Optical and near-infrared coverage of SN 2004et: physical parameters and comparison with other Type IIP supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 404:981–1004, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16332.x, 0912.3111
Maio U, Ciardi B, Dolag K, Tornatore L, Khochfar S (2010) The transition from population III to population II-I star formation. Mon Not R Astron Soc 407:1003–1015. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17003.x, 1003.4992
Maiolino R, Schneider R, Oliva E, Bianchi S, Ferrara A, Mannucci F, Pedani M, Roca Sogorb M (2004) A supernova origin for dust in a high-redshift quasar. Nature 431:533–535, doi:10.1038/nature02930, arXiv:astro-ph/0409577
Maíz-Apellániz J, Bond HE, Siegel MH, Lipkin Y, Maoz D, Ofek EO, Poznanski D (2004) The progenitor of the Type II-P SN 2004dj in NGC 2403. Astrophys J 615:L113–L116. doi:10.1086/426120, arXiv:astro-ph/0408265
Maness H, Martins F, Trippe S, Genzel R, Graham JR, Sheehy C, Salaris M, Gillessen S, Alexander T, Paumard T, Ott T, Abuter R, Eisenhauer F (2007) Evidence for a long-standing top-heavy initial mass function in the central parsec of the Galaxy. Astrophys J 669:1024–1041. doi:10.1086/521669, 0707.2382
Mannucci F, Della Valle M, Panagia N (2006) Two populations of progenitors for Type Ia supernovae? Mon Not R Astron Soc 370:773–783, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10501.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0510315
Maoz D (2008) On the fraction of intermediate-mass close binaries that explode as Type Ia supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 384:267–277. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12697.x, 0707.4598
Marchenko SV (2006) Dust production in the high-redshift universe. In: Lamers HJGLM, Langer N, Nugis T, Annuk K (eds) Stellar evolution at low metallicity: mass loss, explosions, cosmology. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 353, p 299
Marigo P (2001) Chemical yields from low- and intermediate-mass stars: model predictions and basic observational constraints. Astron Astrophys 370:194–217. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000247, arXiv:astro-ph/0012181
Massey P, Olsen KAG (2003) The evolution of massive stars. I. Red supergiants in the Magellanic Clouds. Astron J 126:2867–2886. doi:10.1086/379558, arXiv:astro-ph/0309272
Massey P, Plez B, Levesque EM, Olsen KAG, Clayton GC, Josselin E (2005) The reddening of red supergiants: when smoke gets in your eyes. Astrophys J 634:1286–1292. doi:10.1086/497065, arXiv:astro-ph/0508254
Mathis JS, Rumpl W, Nordsieck KH (1977) The size distribution of interstellar grains. Astrophys J 217:425–433. doi:10.1086/155591
Matsuura M, Zijlstra AA, Bernard-Salas J, Menzies JW, Sloan GC, Whitelock PA, Wood PR, Cioni M, Feast MW, Lagadec E, van Loon JT, Groenewegen MAT, Harris GJ (2007) Spitzer Space Telescope spectral observations of AGB stars in the Fornax dwarf spheroidal galaxy. Mon Not R Astron Soc 382:1889–1900. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12501.x, 0709.3199
Matsuura M, Barlow MJ, Zijlstra AA, Whitelock PA, Cioni M, Groenewegen MAT, Volk K, Kemper F, Kodama T, Lagadec E, Meixner M, Sloan GC, Srinivasan S (2009) The global gas and dust budget of the Large Magellanic Cloud: AGB stars and supernovae, and the impact on the ISM evolution. Mon Not R Astron Soc 396:918–934. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14743.x, 0903.1123
Matsuura M, Dwek E, Meixner M, Otsuka M, Babler B, Barlow MJ, Roman-Duval J, Engelbracht C, Sandstrom K, Lakicevic M, van Loon JT, Sonneborn G, Clayton GC, Long KS, Lundqvist P, Nozawa T, Gordon KD, Hony S, Panuzzo P, Okumura K, Misselt KA, Montiel E, Sauvage M (2011) Herschel detects a massive dust reservoir in Supernova 1987A. arXiv:1107.1477
Matteucci F, Recchi S (2001) On the typical timescale for the chemical enrichment from Type Ia Supernovae in galaxies. Astrophys J 558:351–358. doi:10.1086/322472, arXiv:astro-ph/0105074
Mattila S, Meikle WPS, Lundqvist P, Pastorello A, Kotak R, Eldridge J, Smartt S, Adamson A, Gerardy CL, Rizzi L, Stephens AW, van Dyk SD (2008a) Massive stars exploding in a He-rich circumstellar medium—III SN 2006jc: infrared echoes from new and old dust in the progenitor CSM. Mon Not R Astron Soc 389:141–155. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13516.x, 0803.2145
Mattila S, Smartt SJ, Eldridge JJ, Maund JR, Crockett RM, Danziger IJ (2008b) VLT detection of a red supergiant progenitor of the Type II-P Supernova 2008bk. Astrophys J 688:L91–L94. doi:10.1086/595587, 0809.0206
Mattila S, Smartt S, Maund J, Benetti S, Ergon M (2010) The disappearance of the red supergiant progenitor of Supernova 2008bk. arXiv:1011.5494
Mattsson L (2011) Dust in the early Universe: evidence for non-stellar dust production or observational errors? Mon Not R Astron Soc 414:781–791. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18447.x, 1102.0570
Mattsson L, Höfner S (2011) Dust driven mass loss from carbon stars as function of stellar parameters—II. Effects of grain size on wind properties. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015572, 1107.1771
Mattsson L, Wahlin R, Höfner S, Eriksson K (2008) Intense mass loss from C-rich AGB stars at low metallicity? Astron Astrophys 484:L5–L8. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200809689, 0804.2482
Maund JR, Smartt SJ (2009) The disappearance of the progenitors of Supernovae 1993J and 2003gd. Science 324:486. doi:10.1126/science.1170198, 0903.3772
Maund JR, Smartt SJ, Kudritzki RP, Podsiadlowski P, Gilmore GF (2004) The massive binary companion star to the progenitor of Supernova 1993J. Nature 427:129–131. arXiv:astro-ph/0401090
Maund JR, Smartt SJ, Schweizer F (2005) Luminosity and mass limits for the progenitor of the Type Ic Supernova 2004gt in NGC 4038. Astrophys J 630:L33–L36. doi:10.1086/491620, arXiv:astro-ph/0506436
Maund JR, Smartt SJ, Kudritzki R, Pastorello A, Nelemans G, Bresolin F, Patat F, Gilmore GF, Benn CR (2006) Faint supernovae and supernova impostors: case studies of SN 2002kg/NGC 2403-V37 and SN 2003gm. Mon Not R Astron Soc 369:390–406. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10308.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0603056
Maund JR, Fraser M, Ergon M, Pastorello A, Smartt SJ, Sollerman J, Benetti S, Botticella M, Bufano F, Danziger IJ, Kotak R, Magill L, Stephens AW, Valenti S (2011) The yellow supergiant progenitor of the Type II Supernova 2011dh in M51. arXiv:1106.2565
Mazzali PA, Deng J, Hamuy M, Nomoto K (2009) SN 2003bg: a broad-lined Type IIb Supernova with hydrogen. Astrophys J 703:1624–1634. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/703/2/1624, 0908.1773
McDonald I, van Loon JT, Decin L, Boyer ML, Dupree AK, Evans A, Gehrz RD, Woodward CE (2009) Giants in the globular cluster ω Centauri: dust production, mass-loss and distance. Mon Not R Astron Soc 394:831–856. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14370.x, 0812.0326
McDonald I, Boyer ML, van Loon JT, Zijlstra AA, Hora JL, Babler B, Block M, Gordon K, Meade M, Meixner M, Misselt K, Robitaille T, Sewiło M, Shiao B, Whitney B (2011) Fundamental parameters, integrated red giant branch mass loss, and dust production in the Galactic globular cluster 47 Tucanae. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 193:23. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/193/2/23, 1101.1095
McKee C (1989) Dust destruction in the interstellar medium. In: Allamandola LJ, Tielens AGGM (eds) Interstellar dust. IAU symposium, vol 135, p 431
McKee CF, Tan JC (2008) The formation of the first stars. II. Radiative feedback processes and implications for the initial mass function. Astrophys J 681:771–797. doi:10.1086/587434, 0711.1377
Meikle P, Kotak R, Farrah D, Mattila S, van Dyk SD, Andersen AC, Fesen R, Filippenko AV, Foley RJ, Fransson C, Gerardy CL, Höflich PA, Lundqvist P, Pozzo M, Sollerman J, Wheeler JC (2011) Dust and the Type II-Plateau Supernova 2004dj. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/732/2/109, 1103.2885
Meikle WPS, Mattila S, Pastorello A, Gerardy CL, Kotak R, Sollerman J, Van Dyk SD, Farrah D, Filippenko AV, Höflich P, Lundqvist P, Pozzo M, Wheeler JC (2007) A Spitzer space telescope study of SN 2003gd: still no direct evidence that core-collapse Supernovae are major dust factories. Astrophys J 665:608–617. doi:10.1086/519733, 0705.1439
Mennella V, Baratta GA, Colangeli L, Palumbo P, Rotundi A, Bussoletti E, Strazzulla G (1997) Ultraviolet spectral changes in amorphous carbon grains induced by ion irradiation. Astrophys J 481:545. doi:10.1086/304035
Meynet G, Maeder A (2003) Stellar evolution with rotation. X. Wolf–Rayet star populations at solar metallicity. Astron Astrophys 404:975–990. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030512, arXiv:astro-ph/0304069
Michałowski MJ, Murphy EJ, Hjorth J, Watson D, Gall C, Dunlop JS (2010a) Dust grain growth in the interstellar medium of 5<z<6.5 quasars. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014902, 1006.5466
Michałowski MJ, Watson D, Hjorth J (2010b) Rapid dust production in submillimetre galaxies at z>4? Astrophys J 712:942–950. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/712/2/942, 1002.2636
Miller AA, Smith N, Li W, Bloom JS, Chornock R, Filippenko AV, Prochaska JX (2010) New observations of the very luminous Supernova 2006gy: evidence for echoes. Astron J 139:2218–2229. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/6/2218, 0906.2201
Molster F, Kemper C (2005) Crystalline silicates. Space Sci Rev 119:3–28. doi:10.1007/s11214-005-8066-x
Molster FJ, Waters LBFM (2003) The mineralogy of interstellar and circumstellar dust. In: Henning TK (ed) Astromineralogy. Lecture notes in physics, vol 609. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–170
Molster FJ, Waters LBFM, Tielens AGGM (2002a) Crystalline silicate dust around evolved stars. II. The crystalline silicate complexes. Astron Astrophys 382:222–240. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011551, arXiv:astro-ph/0201304
Molster FJ, Waters LBFM, Tielens AGGM, Barlow MJ (2002b) Crystalline silicate dust around evolved stars. I. The sample stars. Astron Astrophys 382:184–221. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011550, arXiv:astro-ph/0201303
Molster FJ, Waters LBFM, Tielens AGGM, Koike C, Chihara H (2002c) Crystalline silicate dust around evolved stars. III. A correlations study of crystalline silicate features. Astron Astrophys 382:241–255. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011552, arXiv:astro-ph/0201305
Morgan HL, Edmunds MG (2003) Dust formation in early galaxies. Mon Not R Astron Soc 343:427–442. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06681.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0302566
Morgan HL, Dunne L, Eales SA, Ivison RJ, Edmunds MG (2003) Cold Dust in Kepler’s Supernova remnant. Astrophys J 597:L33–L36. doi:10.1086/379639, arXiv:astro-ph/0309233
Moriya T, Tominaga N, Tanaka M, Maeda K, Nomoto K (2010) A core-collapse supernova model for the extremely luminous Type Ic Supernova 2007bi: an alternative to the pair-instability supernova model. Astrophys J 717:L83–L86. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/717/2/L83, 1004.2967
Mortlock DJ, Warren SJ, Venemans BP, Patel M, Hewett PC, McMahon RG, Simpson C, Theuns T, Gonzáles-Solares EA, Adamson A, Dye S, Hambly NC, Hirst P, Irwin MJ, Kuiper E, Lawrence A, Röttgering HJA (2011) A luminous quasar at a redshift of z=7.085. Nature 474:616–619. doi:10.1038/nature10159, 1106.6088
Murray SD, Lin DNC (1996) Coalescence, star formation, and the cluster initial mass function. Astrophys J 467:728. doi:10.1086/177648
Mutschke H, Andersen AC, Clément D, Henning T, Peiter G (1999) Infrared properties of SiC particles. Astron Astrophys 345:187–202. arXiv:astro-ph/9903031
Nagashima M, Lacey CG, Baugh CM, Frenk CS, Cole S (2005) The metal enrichment of the intracluster medium in hierarchical galaxy formation models. Mon Not R Astron Soc 358:1247–1266. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08766.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0408529
Nakano S, Itagaki K, Puckett T, Gorelli R (2006) Possible supernova in UGC 4904. Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams 666:1
Nath BB, Laskar T, Shull JM (2008) Dust sputtering by reverse shocks in supernova remnants. Astrophys J 682:1055–1064. doi:10.1086/589224, 0804.3472
Nomoto K (1984) Evolution of 8-10 solar mass stars toward electron capture supernovae. I—Formation of electron-degenerate O + NE + MG cores. Astrophys J 277:791–805, doi:10.1086/161749
Nomoto K (1987) Evolution of 8-10 solar mass stars toward electron capture supernovae. II—Collapse of an O + NE + MG core. Astrophys J 322:206–214. doi:10.1086/165716
Nomoto K, Sugimoto D, Sparks WM, Fesen RA, Gull TR, Miyaji S (1982) The Crab Nebula’s progenitor. Nature 299:803–805. doi:10.1038/299803a0
Nomoto K, Tominaga N, Umeda H, Kobayashi C, Maeda K (2006) Nucleosynthesis yields of core-collapse supernovae and hypernovae, and galactic chemical evolution. Nucl Phys A 777:424–458. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2006.05.008, arXiv:astro-ph/0605725
Nomoto KI, Iwamoto K, Suzuki T (1995) The evolution and explosion of massive binary stars and Type Ib-Ic-IIb-IIL supernovae. Phys Rep 256:173–191. doi:10.1016/0370-1573(94)00107-E
Norman ML (2010) Pop III stellar masses and IMF. In: Whalen DJ, Bromm V, Yoshida N (eds) American institute of physics conference series, vol 1294, pp 17–27. doi:10.1063/1.3518848, 1011.4624
Nowotny W, Lebzelter T, Hron J, Höfner S (2005) Atmospheric dynamics in carbon-rich Miras. II. Models meet observations. Astron Astrophys 437:285–296. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042572, arXiv:astro-ph/0503653
Nowotny W, Höfner S, Aringer B (2010) Line formation in AGB atmospheres including velocity effects. Molecular line profile variations of long period variables. Astron Astrophys A 514:35. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200911899, 1002.1849
Nozawa T, Kozasa T, Umeda H, Maeda K, Nomoto K (2003) Dust in the early Universe: dust formation in the ejecta of population III Supernovae. Astrophys J 598:785–803. doi:10.1086/379011, arXiv:astro-ph/0307108
Nozawa T, Kozasa T, Habe A, Dwek E, Umeda H, Tominaga N, Maeda K, Nomoto K (2007) Evolution of dust in primordial supernova remnants: can dust grains formed in the ejecta survive and be injected into the early interstellar medium? Astrophys J 666:955–966. doi:10.1086/520621, 0706.0383
Nozawa T, Kozasa T, Tominaga N, Maeda K, Umeda H, Nomoto K, Krause O (2010) Formation and evolution of dust in Type IIb supernovae with application to the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant. Astrophys J 713:356–373. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/713/1/356, 0909.4145
Nozawa T, Maeda K, Kozasa T, Tanaka M, Nomoto K, Umeda H (2011) Formation of dust in the ejecta of Type Ia supernovae. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/736/1/45, 1105.0973
Ofek EO, Cameron PB, Kasliwal MM, Gal-Yam A, Rau A, Kulkarni SR, Frail DA, Chandra P, Cenko SB, Soderberg AM, Immler S (2007) SN 2006gy: an extremely luminous supernova in the Galaxy NGC 1260. Astrophys J 659:L13–L16. doi:10.1086/516749, arXiv:astro-ph/0612408
Olofsson H (1996) Circumstellar molecular envelopes of AGB and post-AGB objects. Astrophys Space Sci 245:169–200. doi:10.1007/BF00642225
Olofsson H (1997) Molecules in envelopes around AGB-stars. Astrophys Space Sci 251:31–39. doi:10.1023/A:1000747630702
Omont A, Cox P, Bertoldi F, McMahon RG, Carilli C, Isaak KG (2001) A 1.2 mm MAMBO/IRAM–30 m survey of dust emission from the highest redshift PSS quasars. Astron Astrophys 374:371–381. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010721, arXiv:astro-ph/0107005
Omont A, Beelen A, Bertoldi F, Cox P, Carilli CL, Priddey RS, McMahon RG, Isaak KG (2003) A 1.2 mm MAMBO/IRAM-30 m study of dust emission from optically luminous z∼2 quasars. Astron Astrophys 398:857–865. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021652, arXiv:astro-ph/0211655
Origlia L, Rood RT, Fabbri S, Ferraro FR, Fusi Pecci F, Rich RM (2007) The first empirical mass-loss law for population II giants. Astrophys J 667:L85–L88. doi:10.1086/521980, 0709.3271
Origlia L, Rood RT, Fabbri S, Ferraro FR, Fusi Pecci F, Rich RM, Dalessandro E (2010) Dust is forming along the red giant branch of 47 tuc. Astrophys J 718:522–526. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/718/1/522, 1005.4618
Orofino V, Blanco A, Mennella V, Bussoletti E, Colangeli L, Fonti S (1991) Experimental extinction properties of granular mixtures of silicon carbide and amorphous carbon. Astron Astrophys 252:315–319
O’Shea BW, Norman ML (2007) Population III star formation in a ΛCDM Universe. I. The effect of formation redshift and environment on protostellar accretion rate. Astrophys J 654:66–92. doi:10.1086/509250, arXiv:astro-ph/0607013
Ossenkopf V, Henning T, Mathis JS (1992) Constraints on cosmic silicates. Astron Astrophys 261:567–578
Pakmor R, Kromer M, Röpke FK, Sim SA, Ruiter AJ, Hillebrandt W (2010) Sub-luminous Type Ia supernovae from the mergers of equal-mass white dwarfs with mass ∼0.9 M⊙. Nature 463:61–64. doi:10.1038/nature08642, 0911.0926
Palik ED (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids. In: Palik ED (ed) Academic press handbook series. Academic Press, New York.
Pascoli G, Polleux A (2000) Condensation and growth of hydrogenated carbon clusters in carbon-rich stars. Astron Astrophys 359:799–810
Pastorello A, Zampieri L, Turatto M, Cappellaro E, Meikle WPS, Benetti S, Branch D, Baron E, Patat F, Armstrong M, Altavilla G, Salvo M, Riello M (2004) Low-luminosity Type II supernovae: spectroscopic and photometric evolution. Mon Not R Astron Soc 347:74–94. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07173.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0309264
Pastorello A, Sauer D, Taubenberger S, Mazzali PA, Nomoto K, Kawabata KS, Benetti S, Elias-Rosa N, Harutyunyan A, Navasardyan H, Zampieri L, Iijima T, Botticella MT, di Rico G, Del Principe M, Dolci M, Gagliardi S, Ragni M, Valentini G (2006) SN 2005cs in M51—I. The first month of evolution of a subluminous SN II plateau. Mon Not R Astron Soc 370:1752–1762. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10587.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0605700
Pastorello A, Smartt SJ, Mattila S, Eldridge JJ, Young D, Itagaki K, Yamaoka H, Navasardyan H, Valenti S, Patat F, Agnoletto I, Augusteijn T, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Boles T, Bonnet-Bidaud J, Botticella MT, Bufano F, Cao C, Deng J, Dennefeld M, Elias-Rosa N, Harutyunyan A, Keenan FP, Iijima T, Lorenzi V, Mazzali PA, Meng X, Nakano S, Nielsen TB, Smoker JV, Stanishev V, Turatto M, Xu D, Zampieri L (2007) A giant outburst two years before the core-collapse of a massive star. Nature 447:829–832. doi:10.1038/nature05825, arXiv:astro-ph/0703663
Pastorello A, Kasliwal MM, Crockett RM, Valenti S, Arbour R, Itagaki K, Kaspi S, Gal-Yam A, Smartt SJ, Griffith R, Maguire K, Ofek EO, Seymour N, Stern D, Wiethoff W (2008) The Type IIb SN 2008ax: spectral and light curve evolution. Mon Not R Astron Soc 389:955–966. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13618.x, 0805.1914
Patat F, Taubenberger S, Benetti S, Pastorello A, Harutyunyan A (2011) Asymmetries in the Type IIn SN 2010jl. Astron Astrophys 527:L6, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201016217, 1011.5926
Pei YC, Fall SM, Bechtold J (1991) Confirmation of dust in damped Lyman-alpha systems. Astrophys J 378:6–16. doi:10.1086/170401
Perley DA, Bloom JS, Klein CR, Covino S, Minezaki T, Woźniak P, Vestrand WT, Williams GG, Milne P, Butler NR, Updike AC, Krühler T, Afonso P, Antonelli A, Cowie L, Ferrero P, Greiner J, Hartmann DH, Kakazu Y, Küpcü Yoldaş A, Morgan AN, Price PA, Prochaska JX, Yoshii Y (2010) Evidence for supernova-synthesized dust from the rising afterglow of GRB071025 at z∼5. Mon Not R Astron Soc 406:2473–2487. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16772.x
Pettini M, Smith LJ, Hunstead RW, King DL (1994) Metal enrichment, dust, and star formation in galaxies at high redshifts. 3: Zn and CR abundances for 17 damped Lyman-alpha systems. Astrophys J 426:79–96. doi:10.1086/174041
Piovan L, Chiosi C, Merlin E, Grassi T, Tantalo R, Buonomo U, Cassarà LP (2011a) Formation and evolution of the dust in Galaxies. II. The Solar neighbourhood. arXiv:1107.4561
Piovan L, Chiosi C, Merlin E, Grassi T, Tantalo R, Buonomo U, Cassarà LP (2011b) Formation and evolution of the dust in Galaxies. III. The disk of the Milky Way. arXiv:1107.4567
Pipino A, Fan XL, Matteucci F, Calura F, Silva L, Granato G, Maiolino R (2011) The chemical evolution of elliptical galaxies with stellar and QSO dust production. Astron Astrophys 525:61. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014843, 1008.3875
Pitman KM, Hofmeister AM (2006) Thin film absorbance spectra of forsterite and fayalite dust grains. In: Mackwell S, Stansbery E (eds) 37th annual lunar and planetary science conference. Lunar and planetary institute science conference abstracts, vol 37, p 1338
Pitman KM, Dijkstra C, Hofmeister AM, Speck AK (2010) IR absorbance spectra of olivine (Pitman+, 2010). VizieR Online Data Catalog 740:60460
Poelarends AJT, Herwig F, Langer N, Heger A (2008) The supernova channel of super-AGB stars. Astrophys J 675:614–625. doi:10.1086/520872, 0705.4643
Posch T, Baier A, Mutschke H, Henning T (2007) Carbonates in space: the challenge of low-temperature data. Astrophys J 668:993–1000. doi:10.1086/521390, 0706.3963
Pozzo M, Meikle WPS, Fassia A, Geballe T, Lundqvist P, Chugai NN, Sollerman J (2004) On the source of the late-time infrared luminosity of SN 1998S and other Type II supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 352:457–477. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07951.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0404533
Pozzo M, Meikle WPS, Rayner JT, Joseph RD, Filippenko AV, Foley RJ, Li W, Mattila S, Sollerman J (2006) Optical and infrared observations of the Type IIP SN2002hh from days 3 to 397. Mon Not R Astron Soc 368:1169–1195. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10204.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0602372
Priddey RS, McMahon RG (2001) The far-infrared-submillimetre spectral energy distribution of high-redshift quasars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 324:L17–L22. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04548.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0102116
Priddey RS, Isaak KG, McMahon RG, Robson EI, Pearson CP (2003) Quasars as probes of the submillimetre cosmos at z>5—I. Preliminary SCUBA photometry. Mon Not R Astron Soc 344:L74–L78. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.07076.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0308132
Prieto JL, Kistler MD, Thompson TA, Yüksel H, Kochanek CS, Stanek KZ, Beacom JF, Martini P, Pasquali A, Bechtold J (2008) Discovery of the dust-enshrouded progenitor of SN 2008S with Spitzer. Astrophys J 681:L9–L12. doi:10.1086/589922, 0803.0324
Puls J, Vink JS, Najarro F (2008) Mass loss from hot massive stars. Astron Astrophys 16:209–325. doi:10.1007/s00159-008-0015-8, 0811.0487
Raiteri CM, Villata M, Navarro JF (1996) Simulations of Galactic chemical evolution. I. O and Fe abundances in a simple collapse model. Astron Astrophys 315:105–115
Ramstedt S, Schöier FL, Olofsson H, Lundgren AA (2008) On the reliability of mass-loss-rate estimates for AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 487:645–657. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078876, 0806.0517
Ramstedt S, Schöier FL, Olofsson H (2009) Circumstellar molecular line emission from S-type AGB stars: mass-loss rates and SiO abundances. Astron Astrophys 499:515–527. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200911730, 0903.1672
Renzini A, Voli M (1981) Advanced evolutionary stages of intermediate-mass stars. I—Evolution of surface compositions. Astron Astrophys 94:175–193
Reynolds SP (1985) An evolutionary history for the Crablike, pulsar-powered supernova remnant 0540-69.3. Astrophys J 291:152–155. doi:10.1086/163050
Reynolds SP, Borkowski KJ, Hwang U, Hughes JP, Badenes C, Laming JM, Blondin JM (2007) A deep Chandra observation of Kepler’s supernova remnant: a Type Ia event with circumstellar interaction. Astrophys J 668:L135–L138. doi:10.1086/522830, 0708.3858
Rho J, Kozasa T, Reach WT, Smith JD, Rudnick L, DeLaney T, Ennis JA, Gomez H, Tappe A (2008) Freshly formed dust in the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant as revealed by the Spitzer space telescope. Astrophys J 673:271–282. doi:10.1086/523835, 0709.2880
Rho J, Reach WT, Tappe A, Hwang U, Slavin JD, Kozasa T, Dunne L (2009) Spitzer observations of the Young core-collapse supernova remnant 1E0102-72.3: infrared ejecta emission and dust formation. Astrophys J 700:579–596. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/700/1/579
Riechers DA, Walter F, Bertoldi F, Carilli CL, Aravena M, Neri R, Cox P, WeißA, Menten KM (2009) Imaging atomic and highly excited molecular gas in a z=6.42 quasar host galaxy: copious fuel for an eddington-limited starburst at the end of cosmic reionization. Astrophys J 703:1338–1345. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/703/2/1338, 0908.0018
Rieke GH, Loken K, Rieke MJ, Tamblyn P (1993) Starburst modeling of M82—Test case for a biased initial mass function. Astrophys J 412:99–110. doi:10.1086/172904
Robson I, Priddey RS, Isaak KG, McMahon RG (2004) Submillimetre observations of z>6 quasars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 351:L29–L33. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07923.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0405177
Rouleau F, Martin PG (1991) Shape and clustering effects on the optical properties of amorphous carbon. Astrophys J 377:526–540. doi:10.1086/170382
Ryder SD, Murrowood CE, Stathakis RA (2006) A post-mortem investigation of the Type IIb Supernova 2001ig. Mon Not R Astron Soc 369:L32–L36. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2006.00168.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0603336
Sahu DK, Anupama GC, Srividya S, Muneer S (2006) Photometric and spectroscopic evolution of the Type IIP supernova SN 2004et. Mon Not R Astron Soc 372:1315–1324. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10937.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0608432
Sakon I, Onaka T, Wada T, Ohyama Y, Kaneda H, Ishihara D, Tanabé T, Minezaki T, Yoshii Y, Tominaga N, Nomoto K, Nozawa T, Kozasa T, Tanaka M, Suzuki T, Umeda H, Ohyabu S, Usui F, Matsuhara H, Nakagawa T, Murakami H (2009) Properties of newly formed dust by SN 2006JC based on near- to mid-infrared observation with AKARI. Astrophys J 692:546–555. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/692/1/546, 0711.4801
Salpeter EE (1955) The luminosity function and stellar evolution. Astrophys J 121:161. doi:10.1086/145971
Salvaterra R, Della Valle M, Campana S, Chincarini G, Covino S, D’Avanzo P, Fernández-Soto A, Guidorzi C, Mannucci F, Margutti R, Thöne CC, Antonelli LA, Barthelmy SD, de Pasquale M, D’Elia V, Fiore F, Fugazza D, Hunt LK, Maiorano E, Marinoni S, Marshall FE, Molinari E, Nousek J, Pian E, Racusin JL, Stella L, Amati L, Andreuzzi G, Cusumano G, Fenimore EE, Ferrero P, Giommi P, Guetta D, Holland ST, Hurley K, Israel GL, Mao J, Markwardt CB, Masetti N, Pagani C, Palazzi E, Palmer DM, Piranomonte S, Tagliaferri G, Testa V (2009) GRB090423 at a redshift of z∼8.1. Nature 461:1258–1260. doi:10.1038/nature08445, 0906.1578
Sandstrom K, Bolatto A, Leroy A, Stanimirovic S, Simon JD, Staveley-Smith L, Shah R (2008) The far-IR radio continuum correlation in the small Magellanic cloud. In: Chary R-R, Teplitz HI, Sheth K (eds) Infrared diagnostics of galaxy evolution. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 381, p 268
Scalo J (1998) The IMF revisited: a case for variations. In: Gilmore G, Howell D (eds) The stellar initial mass function (38th herstmonceux conference). Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 142, p 201. arXiv:astro-ph/9712317
Scalo J (2005) Fifty years of IMF variation: the intermediate-mass stars. In: Corbelli E, Palla F, Zinnecker H (eds) The initial mass function 50 years later. Astrophysics and space science library, vol 327, p 23. arXiv:astro-ph/0412543
Scalo JM (1986) The stellar initial mass function. FCPh 11:1–278
Schaerer D, Meynet G, Maeder A, Schaller G (1993) Grids of stellar models II—From 0 8 to 120 solar masses at Z=0.008. Astron Astrophys Suppl Ser 98:523–527
Schaller G, Schaerer D, Meynet G, Maeder A (1992) New grids of stellar models from 0 8 to 120 solar masses at Z=0.020 and Z=0.001. Astron Astrophys Suppl Ser 96:269–331
Schneider R, Ferrara A, Salvaterra R (2004) Dust formation in very massive primordial supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 351:1379–1386. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07876.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0307087
Schneider R, Omukai K, Inoue AK, Ferrara A (2006) Fragmentation of star-forming clouds enriched with the first dust. Mon Not R Astron Soc 369:1437–1444. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10391.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0603766
Schöier FL, Olofsson H (2001) Models of circumstellar molecular radio line emission. Mass loss rates for a sample of bright carbon stars. Astron Astrophys 368:969–993. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010072, arXiv:astro-ph/0101477
Schwartz PR (1982) The spectral dependence of dust emissivity at millimeter wavelengths. Astrophys J 252:589–593. doi:10.1086/159585
Schwarzschild M, Spitzer L (1953) On the evolution of stars and chemical elements in the early phases of a galaxy. The Observatory 73:77–79
Scoville N, Young JS (1983) The molecular gas distribution in M51. Astrophys J 265:148. doi:10.1086/160660
Sedlmayr E (1994) From molecules to grains. In: Jorgensen UG (ed) IAU colloq. 146: molecules in the stellar environment. Lecture notes in physics, vol 428. Springer, Berlin, p 163. doi:10.1007/3-540-57747-5_42
Sharp CM, Wasserburg GJ (1995) Molecular equilibria and condensation temperatures in carbon-rich gases. GeCoA 59:1633–1652. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00069-C
Shigeyama T, Nomoto K (1990) Theoretical light curve of SN 1987A and mixing of hydrogen and nickel in the ejecta. Astrophys J 360:242–256. doi:10.1086/169114
Sibthorpe B, Ade PAR, Bock JJ, Chapin EL, Devlin MJ, Dicker S, Griffin M, Gundersen JO, Halpern M, Hargrave PC, Hughes DH, Jeong W, Kaneda H, Klein J, Koo B, Lee H, Marsden G, Martin PG, Mauskopf P, Moon D, Netterfield CB, Olmi L, Pascale E, Patanchon G, Rex M, Roy A, Scott D, Semisch C, Truch MDP, Tucker C, Tucker GS, Viero MP, Wiebe DV (2009) AKARI and BLAST observations of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant and surrounding interstellar medium. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/719/2/1553, 0910.1094
Siess L (2007) Evolution of massive AGB stars. II. Model properties at non-solar metallicity and the fate of super-AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 476:893–909. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078132
Siess L (2008) The most massive AGB stars. In: Deng L, Chan KL (eds) IAU symposium, vol 252, pp 297–307. doi:10.1017/S1743921308023077
Silvia DW, Smith BD, Shull JM (2010) Numerical simulations of supernova dust destruction. I. Cloud-crushing and post-processed Grain sputtering. Astrophys J 715:1575–1590. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/715/2/1575, 1001.4793
Sloan GC, Kraemer KE, Wood PR, Zijlstra AA, Bernard-Salas J, Devost D, Houck JR (2008) The Magellanic zoo: mid-infrared Spitzer spectroscopy of evolved stars and circumstellar dust in the Magellanic clouds. Astrophys J 686:1056–1081. doi:10.1086/591437, 0807.2998
Sloan GC, Matsuura M, Zijlstra AA, Lagadec E, Groenewegen MAT, Wood PR, Szyszka C, Bernard-Salas J, van Loon JT (2009) Dust formation in a Galaxy with primitive abundances. Science 323:353. doi:10.1126/science.1165626
Smartt SJ (2009) Progenitors of core-collapse supernovae. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 47:63–106. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-082708-101737, 0908.0700
Smartt SJ, Maund JR, Hendry MA, Tout CA, Gilmore GF, Mattila S, Benn CR (2004) Detection of a red supergiant progenitor star of a Type II-Plateau supernova. Science 303:499–503. doi:10.1126/science.1092967, arXiv:astro-ph/0401235
Smartt SJ, Eldridge JJ, Crockett RM, Maund JR (2009) The death of massive stars—I. Observational constraints on the progenitors of Type II-P supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 395:1409–1437. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14506.x, 0809.0403
Smith LJ, Gallagher JS (2001) M82-F: a doomed super star cluster? Mon Not R Astron Soc 326:1027–1040. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04627.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0104429
Smith N, Owocki SP (2006) On the role of continuum-driven eruptions in the evolution of very massive stars and population III stars. Astrophys J 645:L45–L48. doi:10.1086/506523, arXiv:astro-ph/0606174
Smith N, Humphreys RM, Gehrz RD (2001) Post-eruption detection of variable 12 in NGC 2403 (SN 1954j): another η carinae variable. Publ Astron Soc Pac 113:692–696. doi:10.1086/320812
Smith N, Gehrz RD, Hinz PM, Hoffmann WF, Hora JL, Mamajek EE, Meyer MR (2003) Mass and kinetic energy of the Homunculus Nebula around η carinae. Astron J 125:1458–1466. doi:10.1086/346278
Smith N, Li W, Foley RJ, Wheeler JC, Pooley D, Chornock R, Filippenko AV, Silverman JM, Quimby R, Bloom JS, Hansen C (2007) SN 2006gy: discovery of the most luminous supernova ever recorded, powered by the death of an extremely massive star like η Carinae. Astrophys J 666:1116–1128. doi:10.1086/519949, arXiv:astro-ph/0612617
Smith N, Foley RJ, Bloom JS, Li W, Filippenko AV, Gavazzi R, Ghez A, Konopacky Q, Malkan MA, Marshall PJ, Pooley D, Treu T, Woo J (2008a) Late-time observations of SN 2006gy: still going strong. Astrophys J 686:485–491. doi:10.1086/590141, 0802.1743
Smith N, Foley RJ, Filippenko AV (2008b) Dust formation and He II λ4686 emission in the dense shell of the Peculiar Type Ib Supernova 2006jc. Astrophys J 680:568–579. doi:10.1086/587860, 0704.2249
Smith N, Silverman JM, Chornock R, Filippenko AV, Wang X, Li W, Ganeshalingam M, Foley RJ, Rex J, Steele TN (2009) Coronal lines and dust formation in SN 2005ip: not the brightest, but the hottest Type IIn supernova. Astrophys J 695:1334–1350. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/695/2/1334, 0809.5079
Smith N, Chornock R, Silverman JM, Filippenko AV, Foley RJ (2010a) Spectral evolution of the extraordinary Type IIn Supernova 2006gy. Astrophys J 709:856–883. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/709/2/856, 0906.2200
Smith N, Miller A, Li W, Filippenko AV, Silverman JM, Howard AW, Nugent P, Marcy GW, Bloom JS, Ghez AM, Lu J, Yelda S, Bernstein RA, Colucci JE (2010b) Discovery of precursor luminous blue variable outbursts in two recent optical transients: the fitfully variable missing links UGC 2773-OT and SN 2009ip. Astron J 139:1451–1467. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/4/1451, 0909.4792
Soderberg AM, Chakraborti S, Pignata G, Chevalier RA, Chandra P, Ray A, Wieringa MH, Copete A, Chaplin V, Connaughton V, Barthelmy SD, Bietenholz MF, Chugai N, Stritzinger MD, Hamuy M, Fransson C, Fox O, Levesque EM, Grindlay JE, Challis P, Foley RJ, Kirshner RP, Milne PA, Torres MAP (2010) A relativistic type Ibc supernova without a detected γ-ray burst. Nature 463:513–515. doi:10.1038/nature08714, 0908.2817
Stanimirović S, Bolatto AD, Sandstrom K, Leroy AK, Simon JD, Gaensler BM, Shah RY, Jackson JM (2005) Spitzer space telescope detection of the Young supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219. Astrophys J 632:L103–L106. doi:10.1086/497985, arXiv:astro-ph/0509786
Stockdale CJ, Rupen MP, Cowan JJ, Chu Y, Jones SS (2001) The fading radio emission from SN 1961V: evidence for a Type II peculiar supernova? Astron J 122:283–287. doi:10.1086/321136, arXiv:astro-ph/0104235
Sugerman BEK, Ercolano B, Barlow MJ, Tielens AGGM, Clayton GC, Zijlstra AA, Meixner M, Speck A, Gledhill TM, Panagia N, Cohen M, Gordon KD, Meyer M, Fabbri J, Bowey JE, Welch DL, Regan MW, Kennicutt RC (2006) Massive-star supernovae as major dust factories. Science 313:196–200. doi:10.1126/science.1128131, arXiv:astro-ph/0606132
Szalai T, Vinkó J, Balog Z, Gáspár A, Block M, Kiss LL (2011) Dust formation in the ejecta of the Type II-P Supernova 2004dj. Astron Astrophys A 527:61. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015624, 1012.2035
Tanvir NR, Fox DB, Levan AJ, Berger E, Wiersema K, Fynbo JPU, Cucchiara A, Krühler T, Gehrels N, Bloom JS, Greiner J, Evans PA, Rol E, Olivares F, Hjorth J, Jakobsson P, Farihi J, Willingale R, Starling RLC, Cenko SB, Perley D, Maund JR, Duke J, Wijers RAMJ, Adamson AJ, Allan A, Bremer MN, Burrows DN, Castro-Tirado AJ, Cavanagh B, de Ugarte Postigo A, Dopita MA, Fatkhullin TA, Fruchter AS, Foley RJ, Gorosabel J, Kennea J, Kerr T, Klose S, Krimm HA, Komarova VN, Kulkarni SR, Moskvitin AS, Mundell CG, Naylor T, Page K, Penprase BE, Perri M, Podsiadlowski P, Roth K, Rutledge RE, Sakamoto T, Schady P, Schmidt BP, Soderberg AM, Sollerman J, Stephens AW, Stratta G, Ukwatta TN, Watson D, Westra E, Wold T, Wolf C (2009) A γ-ray burst at a redshift of z∼8.2. Nature 461:1254–1257. doi:10.1038/nature08459, 0906.1577
Tegmark M, Silk J, Rees MJ, Blanchard A, Abel T, Palla F (1997) How small were the first cosmological objects? Astrophys J 474:1. doi:10.1086/303434, arXiv:astro-ph/9603007
Temim T, Gehrz RD, Woodward CE, Roellig TL, Smith N, Rudnick L, Polomski EF, Davidson K, Yuen L, Onaka T (2006) Spitzer space telescope infrared imaging and spectroscopy of the Crab Nebula. Astron J 132:1610–1623. doi:10.1086/507076, arXiv:astro-ph/0606321
Thompson TA, Prieto JL, Stanek KZ, Kistler MD, Beacom JF, Kochanek CS (2009) A new class of luminous transients and a first census of their massive stellar progenitors. Astrophys J 705:1364–1384. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/705/2/1364, 0809.0510
Thronson HA Jr, Telesco CM (1986) Star formation in active dwarf galaxies. Astrophys J 311:98–112. doi:10.1086/164756
Tian WW, Leahy DA (2011) Tycho SN 1572: a naked Ia Supernova remnant without an associated ambient molecular cloud. Astrophys J 729:L15. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/729/2/L15, 1012.5673
Tielens AGGM (1998) Interstellar depletions and the life cycle of interstellar dust. Astrophys J 499:267. doi:10.1086/305640
Tinsley BM (1980) Evolution of the stars and gas in galaxies. In: Gordon CW, Canuto V (eds) Fundamentals of cosmic physics, vol 5, pp 287–388
Todini P, Ferrara A (2001) Dust formation in primordial Type II supernovae. Mon Not R Astron Soc 325:726–736. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04486.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0009176
Truelove JK, McKee CF (1999) Evolution of nonradiative supernova remnants. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 120:299–326. doi:10.1086/313176
Trundle C, Kotak R, Vink JS, Meikle WPS (2008) SN 2005gj: evidence for LBV supernovae progenitors? Astron Astrophys 483:L47–L50. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200809755, 0804.2392
Tumlinson J (2006) Chemical evolution in hierarchical models of cosmic structure. I. Constraints on the early stellar initial mass function. Astrophys J 641:1–20. doi:10.1086/500383, arXiv:astro-ph/0507442
Umana G, Buemi CS, Trigilio C, Hora JL, Fazio GG, Leto P (2009) The dusty nebula surrounding HR car: a spitzer view. Astrophys J 694:697–703. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/694/1/697, 0901.2447
Umeda H, Nomoto K (2002) Nucleosynthesis of zinc and iron peak elements in population III Type II supernovae: comparison with abundances of very metal poor halo stars. Astrophys J 565:385–404. doi:10.1086/323946, arXiv:astro-ph/0103241
Valiante R, Schneider R, Bianchi S, Andersen AC (2009) Stellar sources of dust in the high-redshift Universe. Mon Not R Astron Soc 397:1661–1671. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15076.x, 0905.1691
Valiante R, Schneider R, Salvadori S, Bianchi S (2011) The origin of dust in high redshift QSOs: the case of SDSS J1148+5251. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19168.x, 1106.1418
van den Hoek LB, Groenewegen MAT (1997) New theoretical yields of intermediate mass stars. Astron Astrophys Suppl Ser 123:305–328. doi:10.1051/aas:1997162
Van Dyk SD, Peng CY, King JY, Filippenko AV, Treffers RR, Li W, Richmond MW (2000) SN 1997bs in M66: another extragalactic η Carinae analog? Publ Astron Soc Pac 112:1532–1541. doi:10.1086/317727, arXiv:astro-ph/0009027
Van Dyk SD, Filippenko AV, Li W (2002) Possible recovery of SN 1961V in Hubble space telescope archival images. Publ Astron Soc Pac 114:700–707. doi:10.1086/341695, arXiv:astro-ph/0203508
Van Dyk SD, Filippenko AV, Chornock R, Li W, Challis PM (2005) Supernova 1954J (variable 12) in NGC 2403 unmasked. Publ Astron Soc Pac 117:553–562. doi:10.1086/430238, arXiv:astro-ph/0503324
Van Dyk SD, Li W, Filippenko AV, Humphreys RM, Chornock R, Foley R, Challis PM (2006) The Type IIn Supernova 2002kg: the outburst of a luminous blue variable star in NGC 2403. arXiv:astro-ph/0603025
Van Dyk SD, Davidge TJ, Elias-Rosa N, Taubenberger S, Li W, Howerton S, Pignata G, Morrell N, Hamuy M, Filippenko AV (2010) Supernova 2008bk and its red supergiant progenitor. arXiv:1011.5873
van Loon JT, Cohen M, Oliveira JM, Matsuura M, McDonald I, Sloan GC, Wood PR, Zijlstra AA (2008) Molecules and dust production in the Magellanic clouds. Astron Astrophys 487:1055–1073. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810036, 0806.3557
Vassiliadis E, Wood PR (1993) Evolution of low- and intermediate-mass stars to the end of the asymptotic giant branch with mass loss. Astrophys J 413:641–657. doi:10.1086/173033
Ventura P, D’Antona F (2009) Massive AGB models of low metallicity: the implications for the self-enrichment scenario in metal-poor globular clusters. Astron Astrophys 499:835–846. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811139
Vinkó J, Sárneczky K, Balog Z, Immler S, Sugerman BEK, Brown PJ, Misselt K, Szabó GM, Csizmadia S, Kun M, Klagyivik P, Foley RJ, Filippenko AV, Csák B, Kiss LL (2009) The young, massive, star cluster sandage-96 after the explosion of Supernova 2004dj in NGC 2403. Astrophys J 695:619–635. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/695/1/619, 0812.1589
Vlahakis C, Dunne L, Eales S (2005) The SCUBA local universe Galaxy survey—III. Dust along the Hubble sequence. Mon Not R Astron Soc 364:1253–1285. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09666.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0510768
Wachter A, Winters JM, Schröder K, Sedlmayr E (2008) Dust-driven winds and mass loss of C-rich AGB stars with subsolar metallicities. Astron Astrophys 486:497–504. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200809893, 0805.3656
Wagner RM, Vrba FJ, Henden AA, Canzian B, Luginbuhl CB, Filippenko AV, Chornock R, Li W, Coil AL, Schmidt GD, Smith PS, Starrfield S, Klose S, Tichá J, Tichý M, Gorosabel J, Hudec R, Simon V (2004) Discovery and evolution of an unusual luminous variable star in NGC 3432 (Supernova 2000ch). Publ Astron Soc Pac 116:326–336. doi:10.1086/382997, arXiv:astro-ph/0404035
Walter F, Carilli C, Bertoldi F, Menten K, Cox P, Lo KY, Fan X, Strauss MA (2004) Resolved molecular gas in a quasar host galaxy at redshift z=6.42. Astrophys J 615:L17–L20. doi:10.1086/426017, arXiv:astro-ph/0410229
Wanajo S, Nomoto K, Janka H, Kitaura FS, Müller B (2009) Nucleosynthesis in electron capture supernovae of asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys J 695:208–220. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/695/1/208, 0810.3999
Wang R, Carilli CL, Neri R, Riechers DA, Wagg J, Walter F, Bertoldi F, Menten KM, Omont A, Cox P, Fan X (2010) Molecular gas in z∼6 quasar host Galaxies. Astrophys J 714:699–712. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/714/1/699, 1002.1561
Wang X, Yang Y, Zhang T, Ma J, Zhou X, Li W, Lou Y, Li Z (2005) The progenitor of SN 2004dj in a star cluster. Astrophys J 626:L89–L92. doi:10.1086/431903, arXiv:astro-ph/0505305
Webbink RF (1984) Double white dwarfs as progenitors of R Coronae Borealis stars and Type I supernovae. Astrophys J 277:355–360. doi:10.1086/161701
Weingartner JC, Draine BT (2001) Dust grain-size distributions and extinction in the Milky Way, Large Magellanic Cloud, and Small Magellanic Cloud. Astrophys J 548:296–309. doi:10.1086/318651, arXiv:astro-ph/0008146
Weis K, Bomans DJ (2005) SN 2002kg—the brightening of LBV V37 in NGC 2403. Astron Astrophys 429:L13–L16. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200400105, arXiv:astro-ph/0411504
Wesson R, Barlow MJ, Ercolano B, Andrews JE, Clayton GC, Fabbri J, Gallagher JS, Meixner M, Sugerman BEK, Welch DL, Stock DJ (2010) The destruction and survival of dust in the shell around SN2008S. Mon Not R Astron Soc 403:474–482. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15871.x, 0907.0246
Whelan J, Iben I Jr (1973) Binaries and supernovae of Type I. Astrophys J 186:1007–1014. doi:10.1086/152565
Williams BJ, Borkowski KJ, Reynolds SP, Raymond JC, Long KS, Morse J, Blair WP, Ghavamian P, Sankrit R, Hendrick SP, Smith RC, Points S, Winkler PF (2008) Ejecta, dust, and synchrotron radiation in SNR B0540-69.3: a more Crab-like remnant than the Crab. Astrophys J 687:1054–1069. doi:10.1086/592139, 0807.4155
Willson LA (2007) What do we really know about mass loss on the AGB. In: Kerschbaum F, Charbonnel C, Wing RF (eds) Why galaxies care about AGB Stars: their importance as actors and probes. Astronomical society of the pacific conference series, vol 378, p 211
Wilson TL, Batrla W (2005) An alternate estimate of the mass of dust in Cassiopeia A. Astron Astrophys 430:561–566. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041220, arXiv:astro-ph/0412533
Winters JM, Le Bertre T, Jeong KS, Helling C, Sedlmayr E (2000) A systematic investigation of the mass loss mechanism in dust forming long-period variable stars. Astron Astrophys 361:641–659
Woitke P (2006) Too little radiation pressure on dust in the winds of oxygen-rich AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 460:L9–L12. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066322, arXiv:astro-ph/0609392
Wooden DH, Rank DM, Bregman JD, Witteborn FC, Tielens AGGM, Cohen M, Pinto PA, Axelrod TS (1993) Airborne spectrophotometry of SN 1987A from 1.7 to 12.6 microns—time history of the dust continuum and line emission. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 88:477–507. doi:10.1086/191830
Woosley SE, Weaver TA (1986) The physics of supernova explosions. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 24:205–253. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.24.090186.001225
Woosley SE, Weaver TA (1995) The evolution and explosion of massive stars. II. Explosive hydrodynamics and nucleosynthesis. Astrophys J Suppl Ser 101:181. doi:10.1086/192237
Yang X, Chen P, He J (2004) Molecular and dust features of 29 SiC carbon AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 414:1049–1063. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031673
Yoshida N, Omukai K, Hernquist L, Abel T (2006) Formation of primordial stars in a ΛCDM Universe. Astrophys J 652:6–25. doi:10.1086/507978, arXiv:astro-ph/0606106
Yoshida N, Oh SP, Kitayama T, Hernquist L (2007a) Early cosmological H II/He III regions and their impact on second-generation star formation. Astrophys J 663:687–707. doi:10.1086/518227, arXiv:astro-ph/0610819
Yoshida N, Omukai K, Hernquist L (2007b) Formation of massive primordial stars in a reionized gas. Astrophys J 667:L117–L120. doi:10.1086/522202, 0706.3597
Yoshida N, Omukai K, Hernquist L (2008) Protostar formation in the early Universe. Science 321:669. doi:10.1126/science.1160259, 0807.4928
Yoshida T, Umeda H (2011) A progenitor for the extremely luminous Type Ic Supernova 2007bi. Mon Not R Astron Soc 412:L78–L82. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2011.01008.x, 1101.0635
Yun MS, Carilli CL (2002) Radio-to-far-infrared spectral energy distribution and photometric redshifts for dusty starburst Galaxies. Astrophys J 568:88–98. doi:10.1086/338924, arXiv:astro-ph/0112074
Zeidler S, Posch T, Mutschke H, Richter H, Wehrhan O (2011) Near-infrared absorption properties of oxygen-rich stardust analogs. The influence of coloring metal ions. Astron Astrophys A 526:68. doi:10.1007/s00159-011-0043-7, 1101.0695
Zhukovska S, Gail H, Trieloff M (2008) Evolution of interstellar dust and stardust in the solar neighbourhood. Astron Astrophys 479:453–480. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077789, 0706.1155
Zijlstra AA, Matsuura M, Wood PR, Sloan GC, Lagadec E, van Loon JT, Groenewegen MAT, Feast MW, Menzies JW, Whitelock PA, Blommaert JADL, Cioni M, Habing HJ, Hony S, Loup C, Waters LBFM (2006) A Spitzer mid-infrared spectral survey of mass-losing carbon stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Mon Not R Astron Soc 370:1961–1978. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10623.x, arXiv:astro-ph/0602531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gall, C., Hjorth, J. & Andersen, A.C. Production of dust by massive stars at high redshift. Astron Astrophys Rev 19, 43 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00159-011-0043-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00159-011-0043-7