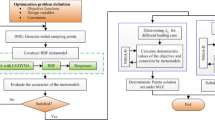
Abstract
Multi-objective optimization (MOO) problems involving expensive black-box functions are common in various engineering design problems. Currently, metamodel-based multi-objective optimization methods using static metamodels are routinely used to solve these MOO problems. The major challenge to static metamodel-based MOO methods lies in solution accuracy, which heavily depends on the accuracy of the metamodels. While sequential or successive methods can be used to improve the accuracy of a metamodel in a small local region, they are not appropriate for MOO problems because the Pareto optima do not fall into the same small region in the design space. In this study, a novel metamodel-based MOO method using adaptive radial basis functions (ARBFs) was developed for efficiently and effectively solving MOO problems. The ARBFs are globally metamodels that are adaptively improved at various local regions where the Pareto optimal designs are located. The performance of this novel method was first evaluated using six mathematical functions. In addition, the ARBF-based MOO method was also used in a practical application, i.e., the crashworthiness optimization of a new kind of thin-walled structure named functionally graded multi-cell tube (FGMT) that was shown to be a good energy absorber in vehicle bodies.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen WG, Wierzbicki T (2001) Relative merits of single-cell, multi-cell and foam-filled thin-walled structures in energy absorption. Thin Wall Struct 39(4):287–306
Chen G, Han X, Liu G, Jiang C, Zhao Z (2012) An efficient multi-objective optimization method for black-box functions using sequential approximate technique. Appl Soft Comput 12(1):14–27
Coello CAC, Lamont GB, Veldhuizen DAV (2007) Evolutionary algorithms for solving multi-objective problems (2nd edition). Springer Science, New York
Deb K (2001) Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. Wiley, New York
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Fang HB, Wang Q (2008) On the effectiveness of assessing model accuracy at design points for radial basis functions. Commun Numer Methods Eng 24(3):219–235
Fang HB, Rais-Rohani M, Liu Z, Horstemeyer MF (2005) A comparative study of metamodeling methods for multi-objective crashworthiness optimization. Comput Struct 83(25–26):2121–2136
Gu XG, Sun GY, Li GY, Mao LC, Li Q (2013) A comparative study on multiobjective reliable and robust optimization for crashworthiness design of vehicle structure. Struct Multidisc Optim 48(3):669–684
Hallquist JO (1998) LS-DYNA theoretical manual. Livemore Software Technology Corporation, California
Hallquist JO (2003) LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual. Livemore Software Technology Corporation, California
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76(8):1905–1915
Hassing PM, Fang HB, Wang Q (2010) Identification of material parameters for McGinty’s model using adaptive RBFs and optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 42(2):233–242
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems (2nd edition). MIT Press, Cambridge
Hou SJ, Li Q, Long SY, Yang XJ, Li W (2008) Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design. Int J Impact Eng 35(11):1355–1367
Hou SJ, Li Q, Long SY, Yang XJ, Li W (2009) Crashworthiness design for foam filled thin-wall structures. Mater Design 30:2024–2032
Hou SJ, Han X, Sun GY, Long SY, Lei W, Yang XJ, Li Q (2011) Multiobjective optimization for tapered circular tubes. Thin Wall Struct 49(7):855–863
Huband S, Hingston P, Barone L, While L (2006) A review of multi-objective test problems and a scalable test problem toolkit. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10(5):477–506
Jusuf A, Dirgantara T, Gunawan L, Putra IS (2015) Crashworthiness analysis of multi-cell prismatic structures. Int J Impact Eng 78:34–50
Kim HS (2002) New extruded multi-cell aluminum profile for maximum crash energy absorption and weight efficiency. Thin Wall Struct 40(4):311–327
Kitayma S, Srirat J, Arakawa M, Yamazaki K (2013) Sequential approximate multi-objective optimization using radial basis function network. Struct Multidisc Optim 48(3):501–515
Li GY, Xu FX, Sun GY, Li Q (2015) Crashworthiness study on functionally graded thin-walled structures. Int J Crashworthiness 20(3):280–300
Liao XT, Li Q, Yang XJ, Li W, Zhang WG (2008) A two-stage multi-objective optimization of vehicle crashworthiness under frontal impact. Int J Crashworthiness 13(3):279–288
Lu GX, Yu TX (2003) Energy absorption of structures and materials. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Messac A, Mullur AA (2008) A computationally efficient metamodeling approach for expensive multiobjective optimization. Optim Eng 9(1):37–67
Montgomery DC (2009) Design and analysis of experiments, 7th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Park JS (1994) Optimal Latin-hypercube designs for computer experiments. J Statistical Planning Inference 39(1):95–111
Santosa SP, Wierzbicki T, Hanssen AG, Langseth M (2000) Experimental and numerical studies of foam-filled sections. Int J Impact Eng 24(5):509–534
Shan S, Wang GG (2004) An efficient Pareto set identification approach for multiobjective optimization on black-box functions. J Mech Des 127(5):866–874
Sun GY, Song XG, Baek S, Li Q (2014) Robust optimization of foam-filled thin-walled structure based on sequential Kriging metamodel. Struct Multidisc Optim 49(6):897–913
Sun GY, Tian XY, Fang JG, Xu FX, Li GY, Huang XD (2015) Dynamical bending analysis and optimization design for functionally graded thickness (FGT) tube. Int J Impact Eng 78:128–137
Tabatabaei M, Hakanen J, Hartikainen M, Miettinen K, Sindhya K (2015) A survey on handling computationally expensive multiobjective optimization problems using surrogates: non-nature inspired methods. Struct Multidisc Optim 52(1):1–25
Tang ZL, Liu ST, Zhang ZH (2012) Energy absorption properties of non-convex multi-corner thin-walled columns. Thin Wall Struct 51:112–120
Tang ZL, Liu ST, Zhang ZH (2013) Analysis of energy absorption characteristics of cylindrical multi-cell columns. Thin Wall Struct 62:75–84
Tran TN, Hou SJ, Han X, Tan W, Nguyen NT (2014a) Theoretical prediction and crashworthiness optimization of multi-cell triangular tubes. Thin Wall Struct 82:183–195
Tran TN, Hou SJ, Han X, Nguyen NT, Chau MQ (2014b) Theoretical prediction and crashworthiness optimization of multi-cell square tubes under oblique impact loading. Int J Mech Sci 89:177–193
Wang GG, Shan S (2007) Review of metamodeling techniques in support of engineering design optimization. Int J Mech Des 129(4):370–380
Yang BS, Yeun YS, Ruy WS (2002) Managing approximation models in multiobjective optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 24(2):141–156
Yun Y, Yoon M, Nakayama H (2009) Multi-objective optimization based on meta-modeling by using support vector regression. Optim Eng 10(2):167–181
Zhang X, Zhang H (2013) Energy absorption of multi-cell stub columns under axial compression. Thin Wall Struct 68:156–163
Zhang X, Zhang H (2014) Axial crushing of circular multi-cell columns. Int J Impact Eng 65:110–125
Zhang X, Cheng GD, Zhang H (2006) Theoretical prediction and numerical simulation of multi-cell square thin-walled structures. Thin Wall Struct 44(11):1185–1191
Zhang ZH, Liu ST, Tang ZL (2011) Comparisons of honeycomb sandwich and foam-filled cylindrical columns. Thin Wall Struct 49(9):1071–1079
Zhang Y, Sun GY, Xu XP, Li GY, Li Q (2014a) Multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of hollow and conical tubes for multiple load cases. Thin Wall Struct 82:331–342
Zhang X, Wen ZZ, Zhang H (2014b) Axial crushing and optimal design of square tubes with graded thickness. Thin Walled Struct 84:263–274
Zitzler K, Deb K, Thiele L (2000) Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: empirical results. Evol Comput 8(2):173–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, H., Fang, H., Wen, G. et al. An adaptive RBF-based multi-objective optimization method for crashworthiness design of functionally graded multi-cell tube. Struct Multidisc Optim 53, 129–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1313-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1313-1