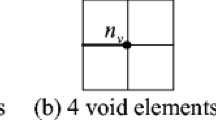
Abstract
The most popular way to introduce the notion of topology into the structural analysis of the topology optimization problem is through the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method. The fundamental principle behind its use requires a density design variable dependent material constitutive law that penalizes intermediate density material in combination with an active volume constraint. Here, the SIMP method with filtering is reevaluated, and an alternative topology optimization problem formulation, called the SINH (pronounced “cinch”) method, is developed that exploits this principle. The main advantages of the SINH method are that the optimization problem is consistently defined, the topology description is unambiguous, and the method leads to predominantly solid–void designs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathe K-J (1996) Finite element procedures. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolations in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69:635–654
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization: theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Borrvall T (2001) Topology optimization of elastic continua using restriction. Arch Comput Methods Eng 8(4):351–385
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2001) Topology optimization using regularized intermediate density control. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190:4911–4928
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(9):2143–2158
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2001) Topology optimization of nonlinear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(26–27):3443–3459
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2003) An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57(10):1413–1430
Buhl T, Pedersen CBW, Sigmund O (2000) Stiffness design of geometrically nonlinear structures using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 19:93–104
Cardoso EL, Fonseca JSO (2003) Complexity control in the topology optimization of continuum structures. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng XXV(3):293–301
Guedes JM, Taylor JE (1997) On the prediction of material properties and topology for optimal continuum structures. Struct Optim 14:193–199
Guo X, Gu YX (2004) A new density-stiffness interpolation scheme for topology optimization of continuum structures. Eng Comput, 21(1):9–22
Haber RB, Jog CS, Bendsøe MP (1996) New approach to variable-topology shape design using a constraint on perimeter. Struct Optim 11(1–2):1–12
Hansen LV (2005) Topology optimization of free vibrations of fiber laser packages. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 29(5):341–348
CS Jog (2001) ArticleTitleA robust dual algorithm for topology design of structures in discrete variables Int J Numer Methods Eng 50 IssueID7 1607–1618 Occurrence Handle10.1002/nme.88 Occurrence Handle1006.74076 Occurrence Handle1907920
CS Jog (2002) ArticleTitleTopology design of structures using a dual algorithm and a constraint on the perimeter Int J Numer Methods Eng 54 IssueID7 1007–1019 Occurrence Handle10.1002/nme.457 Occurrence Handle1098.74659 Occurrence Handle1907920
Martínez JM (2005) A note on the theoretical convergence properties of the SIMP method. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 29(4):319–323
Pedersen NL (2002) Topology optimization of laminated plates with prestress. Comput Struct 80(7–8):559–570
Pedersen CBW, Buhl T, Sigmund O (2001) Topology synthesis of large-displacement compliant mechanisms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(12):2683–2705
Petersson J, Sigmund O (1998) Slope constrained topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41(8):1417–1434
Poulsen T (2003) A new scheme for imposing a minimum length scale in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57(6):741–760
Rietz A (2001) Sufficiency of a finite exponent in SIMP (power law) methods. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 21:159–163
Rozvany GIN (2001) Aims, scope, methods, history and unified terminology of computer-aided topology optimization in structural mechanics. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 21:90–108
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim 4:250–254
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Sigmund O (1994) Optimization of topology. In: Adeli H (ed) Advances in design optimization. Chapman & Hall, London
Sigmund O (1994) Design of material structures using topology optimization. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Denmark
Sigmund O (1995) Tailoring materials with prescribed elastic properties. Mech Mater 20:351–368
Sigmund O (1997) On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization. Mech Struct Mach 25(4):493–524
O Sigmund J Petersson (1998) ArticleTitleNumerical instabilities in topology optimization: a survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima Struct Optim 16 68–75 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01214002
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001a) On the trajectories of penalization methods for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 21:128–139
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001b) An alternative interpolation scheme for minimum compliance topology optimization. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 22:116–124
Svanberg K (1987) Method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (1991) The COC algorithm. Part II. Topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89:309–336
Zhou M, Shyy YK, Thomas HL (2001) Checkerboard and minimum member size control in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscipl Optim 21:152–158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruns, T. A reevaluation of the SIMP method with filtering and an alternative formulation for solid–void topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 30, 428–436 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-005-0537-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-005-0537-x