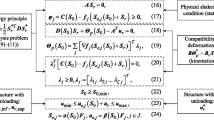Abstract
Optimization of shakedown loading under constrained residual displacement is considered for elastic and perfectly plastic circular plates. The load variation bounds, which satisfy the optimality criterion in concert with plate-strength and stiffness requirements, are identified. The actual strain fields of the plate depend on the loading history. Thus, the load optimization problem at shakedown is stated as a pair of problems that are executed in parallel: the main load optimization and the verification of the prescribed magnitudes of the bounds on the residual deflections. The problem must be solved by iteration. The Rozen projected gradient method is applied. A mechanical interpretation of the Rozen optimality criterion is given, which permits the simplification of the mathematical model for load optimization and the formulation of the solution algorithm. Numerical examples include circular annular plates with and without a rigid inclusion. The results are valid under the assumption of small displacements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkočiunas, J.; Borkowski, A.; König, J.A. 1981: Improved bounds for displacements at shakedown. Comput. Methods Appl. Eng. 28, 365–376
Atkočiunas, J. 1997: Compatibility equations of strains for degenerate shakedown problems. Comput. Struct. 63(2), 277–282
Atkočiunas, J. 1999: Mathematical models of optimization problems at shakedown. Mech. Res. Commun. 26(3), 319–326
Bazaraa, M.S.; Shetty, C.M. 1979: Nonlinear programming theory and algorithms. New York, Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto: John Wiley
Belytschko, T. 1972: Plane stress shakedown analysis by finite elements. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 14, 619–625
Borkowski, A.; Atkočiunas, J. 1975: Optimal design for cyclic loading. IUTAM, Optimization in structural design (Symposium held in Warsaw 1973), pp. 432–440. Berlin: Springer-Verlag
Borkowski, A.; Kleiber, M. 1980: On numerical approach to shakedown analysis of structures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 22(3), 101–119
Cohn, M.Z.; Parimi, S.R. 1973: Optimal design of plastic structures for fixed and shakedown loadings. J. Appl. Mech. 40, 595–599
Cohn, M.Z.; Maier, G. (eds.) 1978: Engineering plasticity by mathematical programming. New York: Pergamon Press
Corradi, L.; Zavelani, A. 1974; Linear programming approach to shakedown analysis of structures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 3, 37–53
Čyras, A. 1983: Mathematical models for the analysis and optimization of elastoplastic structures. Chichester: Ellis Horwood
Capurso, M.; Corradi, L.; Maier, G. 1978: Bounds on deformations and displacements in shakedown theory. In: Proc. Materiaux et Structures sous Chargement Cyclique (held in Palaiseau, France), pp. 213–244
Dorosz, S. 1978: An improved bound to maximum deflections of elastic-plastic structures at shakedown. J. Struct. Mech. 6, 267–287
Gallager, R.H. 1975: Finite element analysis. Fundamentals. Englewood Clifts: Prentice–Hall
Giambanco, F.; Polizzolo, L.; Polizzotto, C. 1994: Optimal shakedown design of circular plates. J. Eng. Mech. 120(12), 2535–2555
Gutkowski, W.; Bauer, J.; Iwanow, Z. 1990: Explicit formulation of Kuhn–Tucker necessary conditions in structural optimization. Comput. Struct. 3, 753–758
Jarmolajeva, E.; Atkočiunas, J. 2002: Shakedown loading optimization under constrained residual displacements – formulation and solution for circular plates. J. Civ. Eng. Manage. VIII(1), 54–67
Kalanta, S. 1995: The equilibrium finite elements in computation of elastic structures. Statyba (Civ. Eng.) 1, 25–47 (in Russian)
Kaliszky, S. 1996: Elasto-plastic analysis with limited plastic deformations and displacements. J. Mech. Struct. Mach. 24, 39–50
Kaliszky, S.; Lógó, J. 2001: Layout and shape optimization of elastoplastic discs with bounds on deformations and displacement. J. Mech. Struct. Mach. 30, 171–191
Kaneko, L.; Maier, G. 1981: Optimum design of plastic structures under displacement’s constraints. J. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 27, 369–392
König, J.A. 1966: Theory of shakedown of elasic-plastic structures. Arch. Mech. Stos. 18, 227–238
König, J.A. 1987: Shakedown of elastic-plastic structures. Amsterdam: Elsevier
Koiter, W.T. 1960: General theorems for elastic-plastic solids. In: Sheddon, I.N; Hills, R. (eds.) Progress in Solid Mechanics, pp. 165–221. Amsterdam: North Holland
Lange–Hasen, P. 1998: Comparative study of upper bound methods for the calculation of residual deformation after shakedown. Technical University of Denmark, Dept. of Struct. Engineering and Materials. Series R No. 49
Maier, G. 1970: A matrix structural theory of piecewise linear elastoplasticity with interacting yield planes. Meccanica 5, 54–66
Maier, G.; Grierson, D.E.; Best, M.J. 1977: Mathematical programming methods for deformations analysis at plastic collapse. Comput. Struct. 7, 599–612
Mróz, Z.; Weichert, D.; Dorosz, St. (eds.) 1995: Inelastic behavior of structures under variable loads. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Polizzoto, C. 1979: Upper bounds on plastic strains for elastic-perfectly plastic solids subjected to variable loads. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 21, 317–327
Ponter, A.R.S. 1972: An upper bound to the small displacements of elastic perfectly plastic structures. J. Appl. Mech. 39, 959–963
Rozvany, G.I.N. 1976: Optimal design of flexural systems. Oxford: Pergamon Press
Stein, E.; Zhang, G.; Mahnken, R. 1993: Shakedown analysis for perfectly plastic and kinematic hardening materials. CISM, Progress in computational analysis of inelastic structures. Wien, New York: Springer
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atkočiunas, J., Jarmolajeva, E. & Merkevičiutė , D. Optimal shakedown loading for circular plates. Struct Multidisc Optim 27, 178–188 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0308-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0308-5