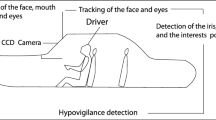
Abstract
Driver fatigue is one of the leading causes of road accidents. It affects the mental vigilance of the driver and reduces his personal capacity to drive a vehicle in full safety. These factors increase the risk of human errors which could involve deaths and wounds. Consequently, the development of an automatic system, which controls the driver fatigue and prevents him from accidents in advance, has received a growing interest. In this work, we have proposed a fusion system for drowsiness detection based on blinking measurement and the 3D head pose estimation. We have studied the driver’s eye behaviors by analysing a non-stationary and non-linear signal and we estimate the head rotation in the three directions \(Yaw\), \(Pitch\), and \(Roll\) by exploiting only three interest points of the face. Our suggested system of fusion presents three levels of drowsiness: awake, tired, and very tired. This system is evaluated by both \(DEAP\) and \(MiraclHB\) databases. The evaluation shows many promising results and shows the effectiveness of the suggested approach.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horng, W.-B., Chen, C.-Y., Chang, Y., Fan, C.-H.: Driver fatigue detection based on eye tracking and dynamk template matching, IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control 2004, pp. 7–12. IEEE Conference Publications, Taiwan (2004)
Singh, S., Papanikolopoulos, N.: Monitoring driver fatigue using facial analysis techniques, International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. IEEE Conference Publications, Tokyo (1999)
Ueno, H., Kaneda, M., Tsukino, M.: Development of drowsiness detection system, Vehicle Navigation and Information Systems Conference. IEEE Conference Publications, Yokohama (1994)
Ma, H., Yang, Z., Song, Y., Jia, P.: A fast method for monitoring driver fatigue using monocular camera, Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Information Sciences. Atlantis, China (2008)
Ji, Q., Zhu, Z., Lan, P.: Real time non-intrusive monitoring and prediction of driver fatigue. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 53, 1052–1068 (2004)
Du, Y., Ma, P., Su, X., Zhang, Y.: Driver fatigue detection based on eye state analysis, Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Information Sciences. Atlantis, China (2008)
Johns, M., Tucker, A., Chapman, R., Crowley, K., Michael, N.: Monitoring eye and eyelid movements by infrared reflectance oculography to measure drowsiness in drivers. Somnologie Schlafforschung und Schlafmedizin 11, 234–242 (2007)
Omi, T., Nagai, Fumiya., Komura, Takashi.: Driver drowsiness detection focused on eyelid behaviour, 34th Congress on Science and Technology of Thailand, pp. 1–8. Thailand (2008)
Picot, A., Charbonnier, S., Caplier, A., Vu, N.-S.: Using retina modelling to characterize blinking: comparison between EOG and video analysis. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23, 1195–1208 (2012)
Viola, P., Jones, M.: Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 511–518. IEEE Computer Society, USA (2001)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W.: Eye blinking analysis based approach for drowsy driver detection, 5th International Conference on Web and Information Technologies, pp. 235–244. Hammamet, Tunisia (2013)
Allen, J.G., Xu, R.Y.D., Jin, J.S.: Object tracking using CamShift algorithm and multiple quantized feature spaces, Proceedings of the Pan-Sydney area workshop on Visual information processing, pp. 3–7. Australian Computer Society, Australia (2004)
Comaniciu, D., Meer, P.: Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24, 603–619 (2002)
Díaz, F.J., Burón, A.M., Solana, J.M.: Haar wavelet based processor scheme for image coding with low circuit complexity. Comput. Electr. Eng. 33, 109–126 (2007)
Smereka, M., Duleba, I.: Circular object detection using a modified Hough Transform. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 18, 85–91 (2008)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W.: Hypovigilance detection based on eyelids behaviour study. Int. J. Recent Contrib. Eng. Sci. IT 1, 39–45 (2013)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W., Hamadou, A.B.: Drowsiness detection based on video analysis approach, 8th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pp. 413–416. SciTePress, Spain (2013)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., Wu, M.C., Shih, H.H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N.-C., Tung, C.C., Liu, H.H.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society A Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 454, pp. 903–995. (1998)
Kojima, N., Kozuka, K., Nakano, T., Yamamoto, S.: Detection of consciousness degradation and concentration of a driver for friendly information service. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Vehicle Electronics Conference, pp. 31–36. IEEE Conference Publications, Tottori (2001)
Suykens, J.A.K., Vandewalle, J.: Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 9, 293–300 (1999)
Bottou L., Cortes C., Denker J.S.: Comparison of classifier methods: a case study in handwritten digit recognition. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 77–82. IEEE Conference Publications, Los Alamitos (1994)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W.: A blinking measurement method for driver drowsiness detection, 8th International Conference on Computer Recognition Systems, pp. 651–660. Springer, Poland (2013)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W.: A visual based approach for drowsiness detection, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 1324–1329. IEEE Conference Publications, Australia (2013)
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W.: Vision based approach for driver drowsiness detection based on 3D head orientation, 7th International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, pp. 43–50. Springer, Korea (2013)
Koelstra, S., Muhl, C., Soleymani, M., Lee, J.-S., Yazdani, A., Ebrahimi, T., Pun, T., Nijholt, A., Patras, I.: A database for emotion analysis using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3, 18–31 (2011)
MiraclHB (Multimedia InfoRmation Systems and Advanced Computing Laboratory Hypovigilance data Base). http://www.belhassen-akrout.com. Accessed 1 July 2013
Senaratne, R., Jap, B., Lal, S., Hsu, A., Halgamuge, S., Fischer, P.: Comparing two video-based techniques for driver fatigue detection: classification versus optical flow approach. Mach. Vis. Appl. 22, 597–618 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akrout, B., Mahdi, W. Spatio-temporal features for the automatic control of driver drowsiness state and lack of concentration. Machine Vision and Applications 26, 1–13 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0644-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0644-z