Abstract
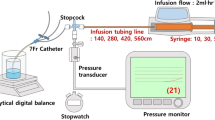
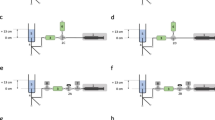
Objective: To evaluate the effect of different infusion pump models on continuity of drug delivery during vertical displacement of syringe pumps. Design: Zero-drug delivery time (ZDDT), retrograde aspiration volume, and infusion bolus were recorded using the same syringe in three different models of syringe pump after lowering and elevating the pump. Compliance of each infusion assembly was measured using the occlusion release technique at 38 mmHg. Results: Lowering the pump by 50 cm at an infusion rate of 1 ml/h resulted in ZDDT values ranging from 2.78±0.29 to 5.99±1.09 min. Elevating the syringe pump to its original position caused infusion boluses between 44.1±3.2 and 77.1±5.1 µl. The results demonstrated that there are large differences between syringe pump models (F=66.8, df=2/33, p<0.0001) and between pumps of the same model (F=21.3, df=1/34, p<0.0001). A similar pattern was found in retrograde aspiration volume and infusion bolus. Conclusion: All tested pumps led to clinically relevant flow irregularities during vertical displacement of the syringe pump. Thus, vertical displacement of any syringe pump connected to an infusion line delivering highly potent drugs at low infusion rates should be avoided. The variability across syringe pumps indicates that syringe pump design remains an area of potential further improvement for reducing the risk of adverse patient events.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Final revision received: 26 October 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neff, T., Fischer, J., Schulz, G. et al. Infusion pump performance with vertical displacement: effect of syringe pump and assembly type. Intensive Care Med 27, 287–291 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000784
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000784