Abstract
Purpose
Central venous catheter (CVC)-related thrombosis (CRT) is a known complication in critically ill patients. However, its clinical significance remains unclear. The objective of the study was to evaluate the occurrence and evolution of CRT from CVC insertion to removal.
Methods
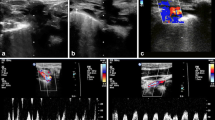
A prospective multicenter study was conducted in 28 intensive care units (ICUs). Duplex ultrasound was performed daily from CVC insertion until at least 3 days after CVC removal or before patient discharge from the ICU to detect CRT and to follow its progression. CRT diameter and length were measured and diameter > 7 mm was considered extensive.
Results
The study included 1262 patients. The incidence of CRT was 16.9% (95% confidence interval 14.8–18.9%). CRT was most commonly found in the internal jugular vein. The median time from CVC insertion to CRT onset was 4 (2–7) days, and 12% of CRTs occurred on the first day and 82% within 7 days of CVC insertion. CRT diameters > 5 mm and > 7 mm were found in 48% and 30% of thromboses. Over a 7-day follow-up, CRT diameter remained stable when the CVC was in place, whereas it gradually decreased after CVC removal. The ICU length of stay was longer in patients with CRT than in those without CRT, and the mortality was not different.
Conclusion
CRT is a frequent complication. It can occur as soon as the CVC is placed and mostly during the first week following catheterization. Half of the thromboses are small but one-third are extensive. They are often non-progressive and may be resolved after CVC removal.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Deidentified individual participant data are available indefinitely in the electronic database. Data can be accessed with the approval of the authors. Request for data can be made to the corresponding author (qinlu@zju.edu.cn) and will be discussed during a meeting of the study group of Central Venous Catheter-related Thrombosis.
References
Baumann Kreuziger L, Jaffray J, Carrier M (2017) Epidemiology, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of catheter-related thrombosis in children and adults. Thromb Res 157:64–71
Parienti JJ, Mongardon N, Megarbane B, Mira JP, Kalfon P, Gros A, Marque S, Thuong M, Pottier V, Ramakers M et al (2015) Intravascular complications of central venous catheterization by insertion site. N Engl J Med 373(13):1220–1229
Takashima M, Schults J, Mihala G, Corley A, Ullman A (2018) Complication and failures of central vascular access device in adult critical care settings. Crit Care Med 46(12):1998–2009
Timsit JF, Rupp M, Bouza E, Chopra V, Karpanen T, Laupland K, Lisboa T, Mermel L, Mimoz O, Parienti JJ et al (2018) A state of the art review on optimal practices to prevent, recognize, and manage complications associated with intravascular devices in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med 44(6):742–759
Hrdy O, Strazevska E, Suk P, Vach R, Karlik R, Jarkovsky J, Sas I, Gal R (2017) Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in intensive care patients - incidence and risk factors: a prospective observational study. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 161(4):369–373
Lee AY, Kamphuisen PW (2012) Epidemiology and prevention of catheter-related thrombosis in patients with cancer. J Thromb Haemost 10(8):1491–1499
Ostlund A, Flaring U, Norberg A, Dahlberg A, Berner J, Kaiser S, Vermin L, Svenningsson A, Frisk T, Larsson P et al (2019) Incidence of and risk factors for venous thrombosis in children with percutaneous non-tunnelled central venous catheters. Br J Anaesth 123(3):316–324
Wang J, Wang L, Shang H, Yang X, Guo S, Wang Y, Cui C (2020) Jugular venous catheter-associated thrombosis and fatal pulmonary embolism: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 99(26):e20873
Wilson TJ, Brown DL, Meurer WJ, Stetler WR Jr, Wilkinson DA, Fletcher JJ (2012) Risk factors associated with peripherally inserted central venous catheter-related large vein thrombosis in neurological intensive care patients. Intensive Care Med 38(2):272–278
Bonizzoli M, Batacchi S, Cianchi G, Zagli G, Lapi F, Tucci V, Martini G, Di Valvasone S, Peris A (2011) Peripherally inserted central venous catheters and central venous catheters related thrombosis in post-critical patients. Intensive Care Med 37(2):284–289
Govindan S, Snyder A, Flanders SA, Chopra V (2018) Peripherally inserted central catheters in the ICU: a retrospective study of adult medical patients in 52 hospitals. Crit Care Med 46(12):e1136–e1144
Haddad H, Lee KS, Higgins A, McMillan D, Price V, El-Naggar W (2014) Routine surveillance ultrasound for the management of central venous catheters in neonates. J Pediatr 164(1):118–122
Joks M, Czyz A, Poplawski D, Komarnicki M (2014) Incidence and risk factors for central venous catheter-related thrombosis in hematological patients. Med Oncol 31(1):772
Luciani A, Clement O, Halimi P, Goudot D, Portier F, Bassot V, Luciani JA, Avan P, Frija G, Bonfils P (2001) Catheter-related upper extremity deep venous thrombosis in cancer patients: a prospective study based on Doppler US. Radiology 220(3):655–660
Hubsch PJ, Stiglbauer RL, Schwaighofer BW, Kainberger FM, Barton PP (1988) Internal jugular and subclavian vein thrombosis caused by central venous catheters. Evaluation using Doppler blood flow imaging. J Ultrasound Med 7(11):629–636
Bosson JL, Riachi M, Pichot O, Michoud E, Carpentier PH, Franco A (1998) Diameters of acute proximal and distal deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs. Int Angiol 17(4):260–267
Stevens SM, Woller SC, Baumann Kreuziger L, Bounameaux H, Doerschug K, Geersing GJ, Huisman MV, Kearon C, King CS, Knighton AJ et al (2021) Executive summary: antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: second update of the CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest 160(6):2247–2259
Malinoski D, Ewing T, Bhakta A, Schutz R, Imayanagita B, Casas T, Woo N, Margulies D, Barrios C, Lekawa M et al (2013) Which central venous catheters have the highest rate of catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis: a prospective analysis of 2,128 catheter days in the surgical intensive care unit. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 74(2):454–460
Faustino EV, Spinella PC, Li S, Pinto MG, Stoltz P, Tala J, Card ME, Northrup V, Baker KE, Goodman TR et al (2013) Incidence and acute complications of asymptomatic central venous catheter-related deep venous thrombosis in critically ill children. J Pediatr 162(2):387–391
Li S, Silva CT, Brudnicki AR, Baker KE, Tala JA, Pinto MG, Polikoff LA, Qin L, Faustino EV, Northeast Pediatric Critical Care Research C (2016) Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound for catheter-related thrombosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 46(2):219–228
Brownie ER, Abuirqeba AA, Ohman JW, Rubin BG, Thompson RW (2020) False-negative upper extremity ultrasound in the initial evaluation of patients with suspected subclavian vein thrombosis due to thoracic outlet syndrome (Paget-Schroetter syndrome). J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 8(1):118–126
Citla Sridhar D, Abou-Ismail MY, Ahuja SP (2020) Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in children and adults. Thromb Res 187:103–112
Wall C, Moore J, Thachil J (2016) Catheter-related thrombosis: a practical approach. J Intensive Care Soc 17(2):160–167
Saber W, Moua T, Williams EC, Verso M, Agnelli G, Couban S, Young A, De Cicco M, Biffi R, van Rooden CJ et al (2011) Risk factors for catheter-related thrombosis (CRT) in cancer patients: a patient-level data (IPD) meta-analysis of clinical trials and prospective studies. J Thromb Haemost 9(2):312–319
Nm Bhat M, Venkataraman R, Ramakrishnan N, Abraham BK, Rajagopalan S (2019) Value of routine sonographic screening of internal jugular vein to detect catheter related thrombosis in intensive care unit. Indian J Crit Care Med 23(7):326–328
Zwicker JI, Connolly G, Carrier M, Kamphuisen PW, Lee AY (2014) Catheter-associated deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity in cancer patients: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost 12(5):796–800
Frank DA, Meuse J, Hirsch D, Ibrahim JG, van den Abbeele AD (2000) The treatment and outcome of cancer patients with thromboses on central venous catheters. J Thromb Thrombolysis 10(3):271–275
Drakos P, Ford BC, Labropoulos N (2020) A systematic review on internal jugular vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 8(4):662–666
Houghton DE, Billett HH, Gaddh M, Onadeko O, George G, Wang TF, Oo TH, Feng M, Dasgupta M, Jaglal M et al (2021) Risk of pulmonary emboli after removal of an upper extremity central catheter associated with a deep vein thrombosis. Blood Adv 5(14):2807–2812
Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, Blaivas A, Jimenez D, Bounameaux H, Huisman M, King CS, Morris TA, Sood N et al (2016) Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest 149(2):315–352
Underhill J, Sherman MA, Howard R, Hage A, Obi A, Napolitano L, Coleman DM (2017) The natural history and outcomes of line-associated upper extremity deep venous thromboses in critically ill patients. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 5(5):630–637
Levy MM, Albuquerque F, Pfeifer JD (2012) Low incidence of pulmonary embolism associated with upper-extremity deep venous thrombosis. Ann Vasc Surg 26(7):964–972
Keiler J, Seidel R, Wree A (2019) The femoral vein diameter and its correlation with sex, age and body mass index—an anatomical parameter with clinical relevance. Phlebology 34(1):58–69
Vaidya GN, Ghafghazi S (2021) Correlation of internal jugular and subclavian vein diameter variation on bedside ultrasound with invasive right heart catheterization. Indian Heart J 73(2):231–235
Patel P, Braun C, Patel P, Bhatt M, Begum H, Wiercioch W, Varghese J, Wooldridge D, Alturkmani HJ, Thomas M et al (2020) Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis of the upper extremity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of test accuracy. Blood Adv 4(11):2516–2522
Tan M, Bornais C, Rodger M (2012) Interobserver reliability of compression ultrasound for residual thrombosis after first unprovoked deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 10(9):1775–1782
Sarolo L, Milan M, Turatti G, Bilora F, Prandoni P (2016) Inter-observer variability of compression ultrasound for the assessment of residual vein thrombosis. Thromb Res 145:1–2
Timsit JF, Baleine J, Bernard L, Calvino-Gunther S, Darmon M, Dellamonica J, Desruennes E, Leone M, Lepape A, Leroy O et al (2020) Expert consensus-based clinical practice guidelines management of intravascular catheters in the intensive care unit. Ann Intensive Care 10(1):118
Schmidt GA, Blaivas M, Conrad SA, Corradi F, Koenig S, Lamperti M, Saugel B, Schummer W, Slama M (2019) Ultrasound-guided vascular access in critical illness. Intensive Care Med 45(4):434–446
Scholten HJ, Ten Bloemendal E, Botter B, Korsten HHM, Bouwman RA (2019) Barriers to ultrasound guidance for central venous access: a survey among Dutch intensivists and anaesthesiologists. J Clin Monit Comput 33(6):1023–1031
Maizel J, Bastide MA, Richecoeur J, Frenoy E, Lemaire C, Sauneuf B, Dupont H, Tamion F, Nseir S, Du Cheyron D et al (2016) Practice of ultrasound-guided central venous catheter technique by the French intensivists: a survey from the BoReal study group. Ann Intensive Care 6(1):76
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the contribution of Qijiang Chen, Weili Hong, Zhiping huang, Luping Wang, Dengpan Lai, Ning Zhang, Lujiao Mo, Yunchao Shi, Wansheng Li, Qin Chen, Hong Liu, Jie Qin, Chen Zhu, Binbin Wu, Lifeng Wu, Weidong Tang, Qingyu Wang, Weiting Chen, Guojuan Ding, Tao Zhang, Bei Tang, Jian Bo, Laifa Kong, Qunjie Pan, Jinyan Fang, Junzhong Ke, Zhaohui Ji in the development and execution of this study.
Members of the Study Group of Central Venous Catheter-related Thrombosis: Chunshuang Wu, Mao Zhang, Wenjie Gu, Hong Liu, Qin Lu, Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine. Caimu Wang, Qijiang Chen, The First hospital of Ninghai. Weili Hong, Xudong Zheng, Ruian People’s Hospital. Junfeng Zhang, Zhiping huang, Beilun District People's Hospital. Xingwen Zhang, Luping Wang, Hunan People’s Hospital. Shijin Lv, Dengpan Lai, The Affilated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University. Xuwei He, Ning Zhang, Qingli Chen, Lishui People’s Hospital. Xiaoyuan Shen, Lujiao Mo, the First People’s Hospital of Xiaoshan District. Wenlong Wei, Yunchao Shi, Jiaxing First Hospital. Guotao Wang, Wansheng Li, Taizhou Municipal Hospital. Yingru Lu, Qin Chen, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University. Renfei Shan, Jie Qin, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province. Lingcong Wang, Chen Zhu, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. Feng Wu, Binbin Wu, Zhejiang Quhua Hospital. Ting Shen, Lifeng Wu, Yuyao People’s Hospital of Zhejiang Province. Xuebo Shao, Weidong Tang, the First People’s Hospital of Fuyang Hangzhou. Qingyu Wang, Shaoyi Xu, the Second Hospital of Jiaxing. Fuzheng Tao, Weiting Chen, Taizhou Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital. Haiying Cai, Guojuan Ding, Shaoxing People’s Hospital. Tao Zhang, Qunjie Pan, Lishui Municipal Central Hospital. Bei Tang, the First People’s Hospital of Jiande. Jianbo Gao, Fuyang District Maternity and Child Care Hospital. Laifa Kong, Jinhua Municipal Central Hospital Medical Group. Jinyan Fang, Hangzhou First People’s Hospital. Junzhong Ke, the First People’s Hospital of Wenling. Zhaohui Ji, the First People’s Hospital of Huzhou.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the 2015 Welfare Scientific Research Project from the Chinese Ministry of Health (2015SQ00050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
Patient recruitment: CW, CMW, XZ, JZ, SL, XH, XS, WW, GW, YL, QC, RS, LW, FW, TS, XS, JC, FT, HC, TZ, BT, JG, LK, QP, JF, JK, ZJ. Data collection: CW, WG, QL, CMW, XZ, JZ, XZ, SL, XH, XS, WW, GW, YL, QC, RS, LW, FW, TS, XS, JC, FT, HC, TZ, BT, JG, LK, QP, JF, JK, ZJ. Data interpretation and analysis: CW, WG, QL. Drafting of the manuscript: CW, MZ, QL. Study design: CW, MZ. All authors were involved in the editing and approval of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
The protocol was prospectively approved by Human Research Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University and the relevant ethics committees in all study sites.
Consent to participate
Consent to participate was provided prospectively from all participants or their next of kin. The authors all consent to publication of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The members of the Study Group of Central Venous Catheter-related Thrombosis are listed in the acknowledgement section.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Zhang, M., Gu, W. et al. Daily point-of-care ultrasound-assessment of central venous catheter-related thrombosis in critically ill patients: a prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med 49, 401–410 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-023-07006-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-023-07006-x