Abstract
Purpose
To investigate if femoral venous pressure (FVP) measurement can be used as a surrogate measure for intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) via the bladder.
Methods
This was a prospective, multicenter observational study. IAP and FVP were simultaneously measured in 149 patients. The effect of BMI on IAP was investigated.
Results
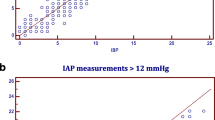
The incidences of intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) were 58 and 7% respectively. The mean APACHE II score was 22 ± 10, SAPS 2 score 42 ± 20, and SOFA score 9 ± 4. The mean IAP was 11.2 ± 4.5 mmHg versus 12.7 ± 4.7 mmHg for FVP. The bias and precision for all measurements were −1.5 and 3.6 mmHg respectively with the lower and upper limits of agreement being −8.6 and 5.7. When IAP was above 20 mmHg, the bias between IAP and FVP was 0.7 with a precision of 2.0 mmHg (lower and upper limits of agreement −3 and 4.6 respectively). Excluding those with ACS, according to the receiver operating curve analysis FVP = 11.5 mmHg predicted IAH with a sensitivity and specificity of 84.8 and 67.0% (AUC of 0.83 (95% CI 0.81–0.86) with P < 0.001). FVP = 14.5 mmHg predicted IAP above 20 mmHg with a sensitivity of 91.3% and specificity of 68.1% (AUC 0.85 (95% CI 0.79–0.91), P < 0.001). Finally, at study entry, the mean IAP in patients with a BMI less then 30 kg/m2 was 10.6 ± 4.0 mmHg versus 13.8 ± 3.8 mmHg in patients with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
FVP cannot be used as a surrogate measure of IAP unless IAP is above 20 mmHg.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malbrain ML, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Wilmer A, Brienza N, Malcangi V, Bihari D, Innes R, Cohen J, Singer P, Japiassu A, Kurtop E, De Keulenaer BL, Daelemans R, Del Turco M, Cosimini P, Ranieri M, Jacquet L, Laterre PF, Gattinoni L, Malbrain MLNG, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Wilmer A, Brienza N, Malcangi V, Bihari D, Innes R, Cohen J, Singer P, Japiassu A, Kurtop E, De Keulenaer BL, Daelemans R, Del Turco M, Ranieri M, Jacquet L, Laterre P-F, Gattinoni L (2004) Prevalence of intra-abdominal hypertension in critically ill patients: a multicentre epidemiological study. Intensive Care Med 30:822–829
Malbrain ML, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Bihari D, Innes R, Ranieri VM, Del Turco M, Wilmer A, Brienza N, Malcangi V, Cohen J, Japiassu A, De Keulenaer BL, Daelemans R, Jacquet L, Laterre PF, Frank G, de Souza P, Cesana B, Gattinoni L, Malbrain MLNG, Chiumello D, Pelosi P, Bihari D, Innes R, Ranieri VM, Del Turco M, Wilmer A, Brienza N, Malcangi V, Cohen J, Japiassu A, De Keulenaer BL, Daelemans R, Jacquet L, Laterre P-F, Frank G, de Souza P, Cesana B, Gattinoni L (2005) Incidence and prognosis of intraabdominal hypertension in a mixed population of critically ill patients: a multiple-center epidemiological study. Crit Care Med 33:315–322
Cheatham ML, Safcsak K, Cheatham ML, Safcsak K (2010) Is the evolving management of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome improving survival? Crit Care Med 38:402–407
Cheatham ML, Malbrain ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M, De Waele J, Balogh Z, Leppaniemi A, Olvera C, Ivatury R, D’Amours S, Wendon J, Hillman K, Wilmer A (2007) Results from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. II. recommendations. Intensive Care Med 33:951–962
Malbrain ML, Cheatham ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M, De Waele J, Balogh Z, Leppaniemi A, Olvera C, Ivatury R, D’Amours S, Wendon J, Hillman K, Johansson K, Kolkman K, Wilmer A, Malbrain MLNG, Cheatham ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M, De Waele J, Balogh Z, Leppaniemi A, Olvera C, Ivatury R, D’Amours S, Wendon J, Hillman K, Johansson K, Kolkman K, Wilmer A (2006) Results from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. I. definitions. Intensive Care Med 32:1722–1732
Malbrain ML (2004) Different techniques to measure intra-abdominal pressure (IAP): time for a critical re-appraisal. Intensive Care Med 30:357–371
Balogh Z, De Waele JJ, Malbrain ML, Malbrain MLNG (2007) Continuous intra-abdominal pressure monitoring. Acta Clin Belg 62(Suppl):26–32
De Waele JJ, De laet I, Malbrain ML, Malbrain MLNG (2007) Rational intraabdominal pressure monitoring: how to do it? Acta Clin Belg 62(Suppl):16–25
De Keulenaer BL, De Waele JJ, Powell B, Malbrain ML, Malbrain MLNG (2009) What is normal intra-abdominal pressure and how is it affected by positioning, body mass and positive end-expiratory pressure? Intensive Care Med 35:969–976
Balogh Z, Jones F, D’Amours S, Parr M, Sugrue M (2004) Continuous intra-abdominal pressure measurement technique. Am J Surg 188:679–684
Williams JF, Seneff MG, Friedman BC, McGrath BJ, Gregg R, Sunner J, Zimmerman JE (1991) Use of femoral venous catheters in critically ill adults: prospective study. Crit Care Med 19:550–553
Regli A, De Keulenaer BL, Hockings LE, Musk GC, Roberts B, van Heerden PV (2011) The role of femoral venous pressure and femoral venous oxygen saturation in the setting of intra-abdominal hypertension—a pig model. Shock 35:422–427
Arfvidsson B, Eklof B, Balfour J (2005) Iliofemoral venous pressure correlates with intraabdominal pressure in morbidly obese patients. Vasc Endovascular Surg 39:505–509
Lee S, Anderson J, Kraut E, Wisner D, Wolfe B (2002) A simplified approach to the diagnosis of elevated intra-abdominal pressure. J Trauma 52:1169–1172
Gudmundsson FF, Viste A, Gislason H, Svanes K (2002) Comparison of different methods for measuring intra-abdominal pressure. Intensive Care Med 28:509–514
Kron IL, Harman PK, Nolan SP (1984) The measurement of intra-abdominal pressure as a criterion for abdominal re-exploration. Ann Surg 199:28–30
Malbrain ML, De laet I, Viaene D, Schoonheydt K, Dits H, Malbrain MLNG, De laet I, Viaene D, Schoonheydt K, Dits H (2008) In vitro validation of a novel method for continuous intra-abdominal pressure monitoring. Intensive Care Med 34:740–745
Magder S, Magder S (2006) Central venous pressure monitoring. Curr Opin Crit Care 12:219–227
Ball C, Westhorpe RN (2009) Central venous pressure monitoring. Anaesth Intensive Care 37:689
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Guzder RN, Gatling W, Mullee MA, Mehta RL, Byrne CD (2005) Prognostic value of the Framingham cardiovascular risk equation and the UKPDS risk engine for coronary heart disease in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: results from a United Kingdom study. Diabet Med 22:554–562
Youden WJ (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3:32–35
Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD (2000) Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med 45:23–41
Markou N, Grigorakos L, Myrianthefs P, Boutzouka E, Rizos M, Evagelopoulou P, Apostolakos H, Baltopoulos G (2004) Venous pressure measurements in the superior and inferior vena cava: the influence of intra-abdominal pressure. Hepatogastroenterology 51:51–55
Barnes GE, Laine GA, Giam PY, Smith EE, Granger HJ (1985) Cardiovascular responses to elevation of intra-abdominal hydrostatic pressure. Am J Physiol 248:R208–R213
Harman PK, Kron IL, McLachlan HD, Freedlender AE, Nolan SP (1982) Elevated intra-abdominal pressure and renal function. Ann Surg 196:594–597
Lacey SR, Bruce J, Brooks SP, Griswald J, Ferguson W, Allen JE, Jewett TC Jr, Karp MP, Cooney DR (1987) The relative merits of various methods of indirect measurement of intraabdominal pressure as a guide to closure of abdominal wall defects. J Pediatr Surg 22:1207–1211
Gudmundsson FF, Viste A, Gislason H, Svanes K (2002) Comparison of different methods for measuring intra-abdominal pressure. Intensive Care Med 28:509–514
Bloomfield G, Saggi B, Blocher C, Sugerman H (1999) Physiologic effects of externally applied continuous negative abdominal pressure for intra-abdominal hypertension. J Trauma 46:1009–1014; discussion 1014–1006
Ishizaki Y, Bandai Y, Shimomura K, Abe H, Ohtomo Y, Idezuki Y (1993) Safe intraabdominal pressure of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum during laparoscopic surgery. Surgery 114:549–554
Jakob SMKR, Tenhunen JJ, Pradl R, Takala J (2010) Increasing abdominal pressure with and without PEEP: effects on intra-peritoneal, intra-organ and intra-vascular pressures. BMC Gastroenterol 10:70
De Waele JJ, Cheatham ML, Malbrain ML, Kirkpatrick AW, Sugrue M, Balogh Z, Ivatury R, De Keulenaer B, Kimball EJ, Malbrain MLNG (2009) Recommendations for research from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. Acta Clin Belg 64:203–209
Merrer J, De Jonghe B, Golliot F, Lefrant JY, Raffy B, Barre E, Rigaud JP, Casciani D, Misset B, Bosquet C, Outin H, Brun-Buisson C, Nitenberg G, French Catheter Study Group in Intensive Care (2001) Complications of femoral and subclavian venous catheterization in critically ill patients: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 286:700–707
Deshpande KS, Hatem C, Ulrich HL, Currie BP, Aldrich TK, Bryan-Brown CW, Kvetan V, Deshpande KS, Hatem C, Ulrich HL, Currie BP, Aldrich TK, Bryan-Brown CW, Kvetan V (2005) The incidence of infectious complications of central venous catheters at the subclavian, internal jugular, and femoral sites in an intensive care unit population. Crit Care Med 33:13–20; discussion 234–235
Lorente L, Henry C, Martin MM, Jimenez A, Mora ML, Lorente L, Henry C, Martin MM, Jimenez A, Mora ML (2005) Central venous catheter-related infection in a prospective and observational study of 2, 595 catheters. Crit Care 9:R631–R635
Durbec O, Viviand X, Potie F, Vialet R, Albanese J, Martin C (1997) A prospective evaluation of the use of femoral venous catheters in critically ill adults. Crit Care Med 25:1986–1989
Parienti JJ, Thirion M, Megarbane B, Souweine B, Ouchikhe A, Polito A, Forel JM, Marque S, Misset B, Airapetian N, Daurel C, Mira JP, Ramakers M, du Cheyron D, Le Coutour X, Daubin C, Charbonneau P, Members of the Cathedia Study G, Parienti J-J, Thirion M, Megarbane B, Souweine B, Ouchikhe A, Polito A, Forel J-M, Marque S, Misset B, Airapetian N, Daurel C, Mira J-P, Ramakers M, du Cheyron D, Le Coutour X, Daubin C, Charbonneau P (2008) Femoral vs jugular venous catheterization and risk of nosocomial events in adults requiring acute renal replacement therapy: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 299:2413–2422
Richardson JD, Trinkle JK (1976) Hemodynamic and respiratory alterations with increased intra-abdominal pressure. J Surg Res 20:401–404
Acknowledgments
To standardize the IAP measurement technique, Wolfe-Tory provided the AbViser bladder monitoring kits to study sites that did not currently use this device, free of charge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Keulenaer, B.L., Regli, A., Dabrowski, W. et al. Does femoral venous pressure measurement correlate well with intrabladder pressure measurement? A multicenter observational trial. Intensive Care Med 37, 1620–1627 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2298-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2298-x