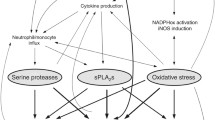
Abstract
Purpose
Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) is a life-threatening neonatal lung injury, whose pathophysiology has been mainly studied in animal models. In such models, pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2-IB) and proinflammatory cytokines present in meconium challenge the lungs, catabolising surfactant and harming the alveoli. Locally produced phospholipases might perpetuate the injury and influence clinical pictures and therapeutic approaches. Our aim is to verify whether pulmonary phospholipase A2 (sPLA2-IIA) is involved in the damage and to determine if phospholipases and their modulators are associated with MAS clinical pictures.
Methods
We studied distinct phospholipases A2 and their modulators in broncho-alveolar lavage (BAL) fluids and in meconium of five MAS neonates and in five control neonates ventilated for extrapulmonary reasons.
Results
MAS patients have higher amounts of pulmonary phospholipase (sPLA2-IIA; P = 0.016) and Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP; P = 0.032). The local production of such proteins by the lung is confirmed by their very low levels in meconium. sPLA2-IIA contributes to the higher total enzyme activity in MAS patients, as compared to controls (P = 0.008). Cytosolic phospholipase was not detected in meconium or alveolar fluid. sPLA2 activity and sPLA2-IIA concentrations are correlated with the TNFα and with the release of CCSP. sPLA2 total activity, sPLA2-IIA and TNFα concentrations in BAL fluids correlate with the oxygenation impairment and haemorrhagic lung oedema.
Conclusions
Pulmonary sPLA2 is locally produced and contributes to the total sPLA2 activity during MAS. CCSP is also produced in trying to lower the inflammation. Both sPLA2 activity and sPLA2-IIA are significantly correlated with oxygenation impairment and haemorrhagic lung oedema.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Yerland Y, de Beaufort AJ (2009) Why does meconium cause meconium aspiration syndrome? Current concepts of MAS pathophysiology. Early Hum Dev 85:617–620
Berdeli A, Akisu M, Dagci T, Akisu C, Yalaz M, Kultursay N (2004) Meconium enhances platelet-activating factor and tumor necrosis factor production by rat alveolar macrophages. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 71:227–232
de Beaufort AJ, Bakker AC, van Tol MJD, Poorthuis BJ, Schrama AJ, Berger HM (2003) Meconium is a source of pro-inflammatory substances and can induce cytokine production in cultured A549 epithelial cells. Pediatr Res 54:491–495
Zagariya A, Bhat R, Uhal B, Navale S, Freidine M, Vidyasagar D (2000) Cell death and lung cell histology in meconium aspirated newborn rabbit lungs. Eur J Pediatr 159:819–826
Hurley BP, McCormick BA (2008) Multiple roles of phospholipase A2 during lung infection and inflammation. Infect Immun 76:2259–2272
Granata F, Petraroli A, Boilard E, Bezzine S, Bollinger J, Del Vecchio L, Gelb MH, Lambeau G, Marone G, Triggiani M (2005) Activation of cytokine production by secreted phospholipase A2 in human lung macrophages expressing the M-type receptor. J Immunol 174:464–474
Niewoehner DE, Rice K, Duane P, Sinha AA, Gebhard R, Wangensteen D (1989) Induction of alveolar epithelial injury by phospholipase A2. J Appl Physiol 66:261–267
Sommers CD, Bovvitt JL, Bemis KG, Snyder DW (1992) Porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2-induced contractions of guinea pig lung pleural strips. Eur J Pharmacol 216:87–96
Duncan Hite R, Seeds MC, Safta AM, Jacinto RB, Gyves JL, Bass DA, Waite BM (2005) Lysophospholipid generation and phosphatidylglycerol depletion in phospholipase A2-mediated surfactant dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L618–L624
Kitsiouli E, Nakos G, Lekka ME (2009) Phospholipase A2 subclasses in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:941–953
De Luca D, Baroni S, Vento G, Piastra M, Pietrini D, Romitelli F, Capoluongo E, Romagnoli C, Conti G, Zecca E (2008) Secretory phospholipase A2 and neonatal respiratory distress: pilot study on broncho-alveolar lavage. Intensive Care Med 34:1858–1864
De Luca D, Minucci A, Cogo P, Capoluongo ED, Conti G, Pietrini D, Carnielli VP, Piastra M (2011) Secretory phospholipase A2 pathway during pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: a preliminary study. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:e20–e24
Kaapa P, Soukka A (2008) Phospholipase A2 in meconium-induced lung injury. J Perinatol 28:S120–S122
De Luca D, Minucci A, Zecca E, Piastra M, Pietrini D, Carnielli VP, Zuppi C, Tridente A, Conti G, Capoluongo ED (2009) Bile acids cause secretory phospholipase A2 activity enhancement, revertible by exogenous surfactant administration. Intensive Care Med 35:321–326
Magrioti V, Kokotos G (2010) Phospholipase A2 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Ther Patents 20:1–18
Pilon AL (2000) Rationale for the development of recombinant human CC10 as a therapeutic for inflammatory and fibrotic disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 923:280–299
Dargaville PA, Copnell B, Australian and New Zealand Neonatal Network (2006) The epidemiology of meconium aspiration syndrome: incidence, risk factors, therapies, and outcome. Pediatrics 117:1712–1721
American Heart Association, American Academy of Pediatrics (2006) 2005 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care of pediatric and neonatal patients: neonatal resuscitation guidelines. Pediatrics 117:1029–1038
European Respiratory Society Task Force on bronchoalveolar lavage in children (2000) Bronchoalveolar lavage in children. Eur Respir J 15:217–231
Dargaville PA, Sought M, McDougall PN (1999) Comparison of two methods of diagnostic lung lavage in ventilated infants with lung disease. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 160:771–777
Berdat P, Wehrle TJ, Küng A, Achermann F, Sutter M, Carrel TP, Nydegger UE (2003) Age-specific analysis of normal cytokine levels in healthy infants. Clin Chem Lab Med 4:1335–1339
Coppens JT, Van Winkle LS, Pinkerton KE, Plopper CG (2007) Distribution of Clara cell secretory protein expression in the tracheobronchial airways of rhesus monkeys. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:1155–1162
Reynolds LJ, Hughes LL, Dennis EA (1992) Analysis of human synovial fluid phospholipase A2 on short chain phosphatidylcholine-mixed micelles: development of a spectrophotometric assay suitable for a microtiter plate reader. Anal Biochem 204:190–197
Reynolds LJ, Hughes LL, Yu L, Dennis EA (1994) 1-Hexadecyl-2-arachidonoylthio-2-deoxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine as a substrate for the microtiterplate assay of human cytosolic phospholipase A2. Anal Biochem 217:25–32
Capoluongo E, Ameglio F, Lulli P, Minucci A, Santonocito C, Concolino P, Di Stasio E, Boccacci S, Vendettuoli V, Giuratrabocchetta G, De Cunto A, Tana M, Romagnoli C, Zuppi C, Vento G (2007) Epithelial lining fluid free IGF-I-to-PAPP-A ratio is associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E308–E313
Broeckaert F, Clippe A, Knoops B, Hermans C, Bernard A (2000) Clara cell secretory protein (CC16): features as a peripheral lung biomarker. Ann N Y Acad Sci 923:68–77
Angert RM, Pilon AL, Chester D, Davis JM (2007) CC10 reduces inflammation in meconium aspiration syndrome in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 62:684–688
Wu YZ, Medjane S, Chabot S, Kubrusly FS, Raw I, Chignard M, Touqui L (2003) Surfactant-protein A and phosphatidylglycerol suppress type IIA phospholipase A2 synthesis via nuclear factor-κB. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 168:692–699
Dargaville PA, South M, McDougall PN (2001) Surfactant and surfactant inhibitors in meconium aspiration syndrome. J Pediatr 138:113–115
Wright JR (2005) Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 5:58–68
Berger A, Havet N, Vial D, Arbibe L, Dumarey C, Watson ML, Touqui L (1999) Dioleylphosphatidylglycerol inhibits the expression of type II-phospholipase A2 in macrophages. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 159:613–618
de Beaufort AJ, Pelikan DMV, Elferink JGR, Berger HM (1998) Effect of interleukin 8 in meconium on in vitro neutrophil chemotaxis. Lancet 352:102–105
Bolognese B, McCord M, Marshall LA (1995) Differential regulation of elicited-peritoneal macrophage 14 kDa and 85 kDa phospholipase A2(s) by transforming growth factor-beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1256:201–209
Korhonen K, Soukka H, Halkola L, Peuravuori H, Aho H, Pulkki K, Kero P, Kaapa PO (2003) Meconium induces only localised inflammatory lung injury in piglets. Pediatr Res 54:192–197
Vidyasagar D, Bhat R, Uhal B, Navale S, Zagariya A (1999) TNFα, IL1β, IL6, IL8, IFNγ, PGE2 and IL10 expression in meconium aspirated newborn lungs. Pediatr Res 45:325A
Sippola T, Aho H, Peuravuori H, Lukkarinen H, Gunn J, Kaapa P (2006) Pancreatic phospholipase A2 contributes to lung injury in experimental meconium aspiration. Pediatr Res 59:641–645
Simpson CM, Smolich JJ, Shekerdemian LS, Penny DJ (2010) Urotensin-II contributes to pulmonary vasoconstriction in a perinatal model of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn secondary to meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatr Res 67:150–157
Nakos G, Kitsiouli E, Hatzidaki E, Koulouras V, Touqui L, Lekka ME (2005) Phospholipase A2 and platelet-activating-factor acetylhydrolase in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 33:772–779
Ivanov VA, Gewolb IH, Uhal BD (2010) A new look at the pathogenesis of the meconium aspiration syndrome: a role for fetal pancreatic proteolytic enzymes in epithelial cell detachment. Pediatr Res 68:221–224
Durham SK, Selig WM (1990) Phospholipase A2-induced pathophysiologic changes in the guinea pig lung. Am J Pathol 136:1283–1291
Okazaki K, Kondo M, Kato M, Kakinuma R, Nishida A, Noda M, Tanigushi K, Kimura H (2008) Serum cytokine and chemokine profiles in neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatrics 121:e748–e753
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Joaquim Trias (PhD) and Chiara Campana (MD) for the critical review of manuscript and English style. They also thank Michal Karpisek (PhD) for his collaboration in the cross-reactivity test and for kindly providing human recombinant sPLA2-IIA. This study was funded by QProgetti Ltd (Roma, Italy; grant 1-2/2010) and NeoSal Foundation (Ancona, Italy). These institutions financed the research as charity programs and had no role either in the project or in the development of the study and data management.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Luca, D., Minucci, A., Tripodi, D. et al. Role of distinct phospholipases A2 and their modulators in meconium aspiration syndrome in human neonates. Intensive Care Med 37, 1158–1165 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2243-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2243-z