Abstract
Purpose
Type 1 angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonists have anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in patients. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether losartan (LOS), an AT1 receptor antagonist, reduces lung damage by inhibiting the induction of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein and cytokines by lipopolysaccharide (LPS; serotype: O127:B8) in a rat model.
Methods
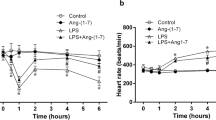
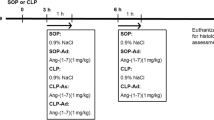
We used male Wistar rats. Control group rats received a 0.9% NaCl solution. The LOS + LPS group rats received LOS (50 mg kg−1) before LPS (7.5 mg kg−1) administration. LPS group rats received injection of LPS (7.5 mg kg−1).
Measurements and results
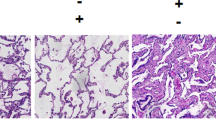
We performed immunohistochemistry, ELISA, and western blot analysis to examine the suppressive effects of LOS on LPS-induced cytokine induction. Plasma concentrations of cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) and HMGB1 (p < 0.05) were markedly reduced in the LOS + LPS group compared to the LPS group. LOS also inhibited the LPS-mediated decrease in angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) activity (p < 0.05). Immunohistochemical analysis revealed positive staining for ACE2 in lungs from both control and LOS + LPS groups. The intensity and degree of ACE2 labeling in lung tissue sections from the LPS group were markedly reduced compared to the control and LOS + LPS groups (p < 0.05). Additionally, RAW264.7 murine macrophages were stimulated with LPS, with or without simultaneous LOS treatment, resulting in inhibition of IκB phosphorylation.
Conclusions
Treatment with LOS improved lung injury in an endotoxin shock model system by an anti-inflammatory action that inhibits reduction of ACE2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heron M (2007) Deaths: leading causes for 2004. Natl Vital Stat Rep 56:1–95
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M (2003) The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348:1546–1554
Wyncoll LA, Evans TW (1999) Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet 354:497–501
Opal SM, Fisher CJ Jr, Dhainaut JF, Vincent JL, Brase R, Lowry SF, Sadoff JC, Slotman GJ, Levy H, Balk RA, Shelly MP, Pribble JP, LaBrecque JF, Lookabaugh J, Donovan H, Dubin H, Baughman R, Norman J, DeMaria E, Matzel K, Abraham E, Seneff M (1997) Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. The Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Sepsis Investigator Group. Crit Care Med 25:1115–1124
Abraham E, Wunderink R, Silverman H, Perl TM, Nasraway S, Levy H, Bone R, Wenzel RP, Balk R, Allred R (1995) Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with sepsis syndrome. A randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial. TNF-alpha MAb Sepsis Study Group. JAMA 273:934–941
Riedemann NC, Ward PA (2003) The enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest 112:460–467
Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ (2001) HMGB1 as a late mediator of lethal systemic inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1768–1773
Bustin M (1999) Regulation of DNA-dependent activities by the functional motifs of the high-mobility-group chromosomal proteins. Mol Cell Biol 19:5237–5246
Wang H, Yang H, Zhang M (1999) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Wang H, Vishnubhakat JM, Tracey KJ (1999) Proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1) stimulate release of high mobility group protein-1 by pituicytes. Surgery 126:389–392
Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Suzuki Y, Rupérez M, Egido J (2001) Proinflammatory actions of angiotensins. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:321–329
Krämer C, Sunkomat J, Witte J, Luchtefeld M, Walden M, Schmidt B, Tsikas D, Böger RH, Forssmann WG, Drexler H, Schieffer B (2002) Angiotensin II receptor-independent antiinflammatory and antiaggregatory properties of losartan: role of the active metabolite EXP3179. Circ Res 90:770–776
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S (2001) Effects of Losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 345:861–869 RENAAL Study Investigators
Granger CB, McMurray JJ, Yusuf S, Held P, Michelson EL, Olofsson B, Ostergren J, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K (2003) Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and reduced left-ventricular systolic function intolerant to angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibitors: the CHARM-Alternative trial. Lancet 362:772–776 CHARM Investigators, Committees
Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Beevers G, de Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Ibsen H, Kristiansson K, Lederballe-Pedersen O, Lindholm LH, Nieminen MS, Omvik P, Oparil S, Wedel H (2002) Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 359:995–1003 LIFE Study Group
Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, Huan Y, Guo F, Guan B, Yang P, Sarao R, Wada T, Leong-Poi H, Crackower MA, Fukamizu A, Hui CC, Hein L, Uhlig S, Slutsky AS, Jiang C, Penninger JM (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 436:112–116
Ferrario CM, Jessup J, Chappell MC, Averill DB, Brosnihan KB, Tallant EA, Diz DI, Gallagher PE (2005) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation 111:2605–2610
Murakami K, McGuire R, Cox RA (2002) Heparin nebulization attenuates acute lung injury in sepsis following smoke inhalation in sheep. Shock 18:236–241
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Matsumoto S, Noguchi T (2008) High dose antithrombin III inhibits HMGB1 and improves endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats. Intensive Care Med 34:361–367
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, Breitbart RE, Acton S (2000) A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res 87:E1–E9
Harmer D, Gilbert M, Borman R, Clark KL (2002) Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme. FEBS Lett 532:107–110
Danilczyk U, Penninger JM (2006) Angiotensin-converting enzyme II in the heart and the kidney. Circ Res 98:463–471
Parsons PE, Moore FA, Moore EE, Iklé DN, Henson PM, Worthen GS (1992) Studies on the role of tumor necrosis factor in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:694–700
Abraham E, Jesmok G, Tuder R, Allbee J, Chang YH (1995) Contribution of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to pulmonary cytokine expression and lung injury after hemorrhage and resuscitation. Crit Care Med 23:1319–1326
Parsey MV, Tuder RM, Abraham E (1998) Neutrophils are major contributors to intraparenchymal lung IL-1 beta expression after hemorrhage and endotoxemia. J Immunol 160:1007–1013
Remick DG, Bolgos GR, Siddiqui J, Shin J, Nemzek JA (2002) Six at six: interleukin-6 measured 6 h after the initiation of sepsis predicts mortality over 3 days. Shock 17:463–467
Ueno H, Matsuda T, Hashimoto S, Amaya F, Kitamura Y, Tanaka M, Kobayashi A, Maruyama I, Yamada S, Hasegawa N, Soejima J, Koh H, Ishizaka A (2004) Contributions of high mobility group box protein in experimental and clinical acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1310–1316
Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey KJ (2000) HMGB1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165:2950–2954
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Liu SF, Malik AB (2006) NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:622–645
Palumbo R, Galvez BG, Pusterla T, De Marchis F, Cossu G, Marcu KB, Bianchi ME (2007) Cells migrating to sites of tissue damage in response to the danger signal HMGB1 require NF-kappaB activation. J Cell Biol 179:33–40
Park WY, Goodman RB, Steinberg KP, Ruzinski JT, Radella F, Park DR, Pugin J, Skerrett SJ, Hudson LD, Martin TR (2001) Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1896–1903
Park JS, Arcaroli J, Yum HK, Yang H, Wang H, Yang KY, Choe KH, Strassheim D, Pitts TM, Tracey KJ, Abraham E (2003) Activation of gene expression in human neutrophils by high mobility group box 1 protein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284:C870–C879
Liu SF, Malik AB (2006) NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L622–L645
Guha M, Mackman N (2001) LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal 13:85–94
Kwak HJ, Song JS, Heo JY, Yang SD, Nam JY, Cheon HG (2005) Roflumilast inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:1188–1195
Schottelius AJ, Mayo MW, Sartor RB, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) Interleukin-10 signaling blocks inhibitor of kappaB kinase activity and nuclear factor kappaB DNA binding. J Biol Chem 274:31868–31874
Bonizzi G, Karin M (2005) The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25:280–288
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Tomohisa Uchida for providing helpful advice and for scoring lung injuries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagiwara, S., Iwasaka, H., Hidaka, S. et al. Antagonist of the Type-1 ANG II receptor prevents against LPS-induced septic shock in rats. Intensive Care Med 35, 1471–1478 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1545-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1545-x