Abstract
Objective
To assess the levels of expression of the antiapoptotic gene Bcl-2 and the proapoptotic gene Bax in circulating mononuclear cells (CMNC) harvested during the course of severe sepsis (SS) in formerly non-immunocompromised patients undergoing hospital-acquired infection, in parallel to cytokine levels.
Design
Prospective study.
Setting
Intensive care unit.
Participants
A total of 24 patients without immunodeficiency undergoing standard goal-directed therapy for nosocomial SS, 10 critically ill patients without sepsis, and 10 healthy controls.
Interventions
Blood was collected before infection and within 12 h, 1, 3 and 7 days after fever onset, to determine plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-10, TNF-alpha, C-reactive protein, whole blood cell counts, lymphocyte subsets, annexin V labelling for apoptosis, and Bax and Bcl-2 relative RNA expression by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results
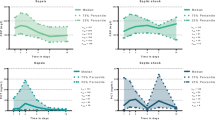
SS patients displayed increased cytokine concentrations, TNF-alpha being significantly increased at full-blown sepsis. Within 12 h after onset of infection, lymphocyte counts were lower in SS patients than in critically ill controls (p=0.001), and this phenomenon was marked in CD4+ and CD8+ subsets (p<0.001). This was associated with enhanced apoptosis in CMNC (15.7±8.7% vs 3.4±2.1%, p<0.001) and a significant down-expression of the Bcl-2 gene throughout the study (p<0.05). In contrast, the expression of Bax did not change significantly. Within 12 h of fever onset, non-survivors expressed a 10-fold down-expression of Bcl-2 when compared to survivors (p<0.001).
Conclusions
An early transient down-expression of the gene Bcl-2 occurred in CMNC harvested from SS patients who died despite intensive care. In contrast, the expression of the gene Bax did not change significantly.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munford RS, Pugin J (2001) Normal responses to injury prevent systemic inflammation and can be immunosuppressive. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:316–321
Bone RC, Grodzin CJ, Balk RA (1997) Sepsis: a new hypothesis for pathogenesis of the disease process. Chest 112:235–243
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD et al. (1999) Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 27:1230–1251
Docke WD, Randow F, Syrbe U et al. (1997) Monocyte deactivation in septic patient: restoration by IFNgamma treatment. Nat Med 3:678–681
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Cobb JP, Jacobson A, Buchman TH, Karl IE (1997) Apoptosis in lymphoid and parenchymal cells during sepsis: findings in normal and T and B cell-deficient mice. Crit Care Med 25:1298–1307
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE et al. (1999) Prevention of lymphocyte cell death in sepsis improves survival in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:14541–14546
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Knudson CM et al. (1999) Over expression of Bcl-2 in transgenic mice decreases apoptosis and improves survival in sepsis. J Immunol 162:4148–4156
Coopersmith CM, Stanley PE, Davis CG, Arniot DR, Buchman TG, Karl IE, Hochkin RS (2002) Inhibition of intestinal epithelial apoptosis and survival in a murine model of pneumonia-induced sepsis. JAMA 287:1716–1721
Kroemer G (1997) The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med 3:614–620
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl-2 family: regeneration of the cellular life or death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry DE, Oltuai ZN (1993) Bcl-2/Bax: a rheostat that regulates an anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Cancer Biol 4:327–330
American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference (1992) Definition for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest 101:1644–1655
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Haustad S et al. for the Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group (2001) Early goal-direct therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 345:1368–1377
Le Gall JR, Lermeshow S, Saunier F (1993) A new simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) based on European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 270:2957–2963
Le Gall JR, Klar J, Lemeshow S, Saunier F, Alberti C, Artigas A, Teres D for the ICU Scoring Group (1996) The logistic organ dysfunction system. A new way to assess organ dysfunction in the intensive care unit. JAMA 276:802–810
Vandesompece J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalisation of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:1–12
Cassinat B, Zassadowski F, Balitrand N et al. (2000) Quantitation of minimal residual disease in acute promyelotic leukemia patients with t(15;17) translocation using real-time RT-PCR. Leukemia 14:324–328
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Bone RC (1996) Immunologic dissonance: a continuing evolution in one understanding of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Ann Intern Med 125:680–687
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE et al. (2001) Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive profound depletion of B and CD4+ T lymphocytes in human. J Immunol 166:6952–6963
Pinsky OR, Vincent JL, Device J, Alegre M, Kahn RJ, Dupont E (1993) Serum cytokine levels in human septic shock. Relation to multiple system organ failure and mortality. Chest 103:565–575
Presterl E, Staudinger T, Pettermann M et al. (1997) Cytokine profile and correlation to the Apache III and MPM II scores in patients with sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:825–832
Van Dissel JT, Van Langevelde P, Westendorps RG, Kwappenberg K, Frolich M (1998) Anti-inflammatory cytokine profile and mortality in febrile patients. Lancet 351:950–953
Adrie C, Bachelet M, Vayssier-Taussat M et al. (2001) Mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptosis peripheral blood monocytes in severe human sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:389–395
Oberholtzer C, Oberholtzer A, Clare-Salzler M, Moldawer LL (2001) Apoptosis in sepsis: a new target for therapeutic exploration. FASEB J 15:879–892
Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Negiski I, Knida K, Santa H, Loh DY (1994) Targeted disruption of Bcl-2αβ in mice: occurrence of grey hair, polycystic kidney disease, and lymphocytopenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3700–3704
Menges T, Engel J, Welters J et al. (1999) Changes in blood lymphocyte count after multiple trauma: association with post-traumatic complications. Crit Care Med 27:733–740
Le Tulzo Y, Pangault C, Gacoin A et al. (2002) Early circulating lymphocyte apoptosis in human septic shock is associated with poor outcome. Shock 18:487–494
Knudson CM, Tung KSK, Tourtelotte WG, Bronn AJ, Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Bax-deficient mice with lymphoid hyperplasia and male germ cell death. Science 270:96–99
Cheng T, Liu D, Griffin JH, Fernandez JA et al. (2003) Activated protein C blocks p53-mediated apoptosis in ischemic human brain endothelium and is neuroprotective. Nat Med 9:338–342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Délégation à la Recherche Clinique des Hôpitaux Universitaires de Strasbourg (PHRC Régional 2001-Grant 2629).
Pascal Bilbault and Thomas Lavaux contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilbault, P., Lavaux, T., Lahlou, A. et al. Transient Bcl-2 gene down-expression in circulating mononuclear cells of severe sepsis patients who died despite appropriate intensive care. Intensive Care Med 30, 408–415 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-2118-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-2118-z