Abstract
Objective
We previously showed that infusing rats with a solution of ethyl pyruvate ameliorates intestinal mucosal injury after mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion. Ethyl pyruvate also has been shown to inhibit the expression of various pro-inflammatory cytokines in several animal models of critical illness, but dose-response relationships have not been investigated.
Design
Anesthetized C57BL/6 mice were subjected to 60 min of mesenteric ischemia followed by 60 min of reperfusion. After 55 min of ischemia, groups of mice were treated with normal saline or graded bolus doses of ethyl pyruvate dissolved in a calcium-containing balanced salt solution. Some animals (i.e., those in the sham group) were subjected to the anesthetic, but not mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion. Gut mucosal permeability was assessed using an everted gut sac technique.
Setting
University research laboratory.
Measurements and Results
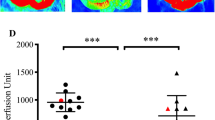
Mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion significantly increased ileal mucosal permeability to the hydrophilic macromolecule, fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran (molecular mass 4,000 Da). Whereas the lowest dose of ethyl pyruvate evaluated (17 mg/kg) had no effect on gut mucosal permeability, the two highest doses tested (50 and 150 mg/kg) significantly ameliorated the development of ischemia/reperfusion-induced mucosal hyperpermeability to about the same extent. The two highest doses of ethyl pyruvate also significantly ameliorated deficits in ileal serosal and mucosal and hepatic surface microvascular perfusion induced by mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion. Ethyl pyruvate inhibited post-ischemia/reperfusion hepatic NF-κB activation and TNF mRNA expression in a dose-dependent fashion.
Conclusion
Doses of ethyl pyruvate equal to or greater than 50 mg/kg ameliorate inflammation, microvascular hypoperfusion and gut mucosal damage induced by mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion in mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Donnell-Tormey J, Nathan CF, Lanks K, DeBois CJ, de la Harpe J (1987) Secretion of pyruvate. An antioxidant defense of mammalian cells. J Exp Med 165:500–514
Holleman MAF (1904) Notice sur l'action de l'eau oxygénée sur les acétoniques et sur le dicétones 1.2. Recl Trav Chim Pays-bas Belg 23:169–171
Adickes F, Andresen G (1943) Zur kenntnis der reihe der normalen aliphatischen b-oxysauren und der a-ketosauren. Ann Chem 50:41–57
Bunton CA (1949) Oxidation of a-diketones and a-keto-acids by hydrogen peroxide. Nature 163:144
Melzer E, Schmidt H (1988) Carbon isotope effects on the decarboxylation of carboxylic acids. Biochem J 252:913–915
Salahudeen AK, Clark EC, Nath KA (1991) Hydrogen peroxide-induced renal injury. A protective role for pyruvate in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 88:1886–1893
Bunger R, Mallet RT, Hartman DA (1989) Pyruvate-enhanced phosphorylation potential and inotropism in normoxic and postischemic isolated working heart. Near-complete prevention of reperfusion contractile failure. Eur J Biochem 180:221–233
Cicalese L, Lee K, Schraut W, Watkins S, Borle A, Stanko R (1999) Pyruvate prevents ischemia-reperfusion mucosal injury of rat small intestine. Am J Surg 171:97–100
Sileri P, Schena S, Morini S, Rastellini C, Pham S, Benedetti E, Cicalese L (2001) Pyruvate inhibits hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 72:27–30
Gupta SK, Mohanty I, Trivedi D, Tandon R, Srivastava S, Joshi S (2002) Pyruvate inhibits galactosemic changes in cultured cat lens epithelial cells. Ophthalmic Res 34:23–28
Zhao W, Devamanoharan PS, Henein M, Ali AH, Varma SD (2000) Diabetes-induced biochemical changes in rat lens: attenuation of cataractogenesis by pyruvate. Diabetes Obes Metab 2:165–174
Lee JY, Kim YH, Koh JY (2001) Protection by pyruvate against transient forebrain ischemia in rats. J Neurosci 21:1–6
Slovin PN, Huang CJ, Cade JR, Wood CE, Nasiroglu O, Privette M, Orbach P, Skimming JW (2001) Sodium pyruvate is better than sodium chloride as a resuscitation solution in a rodent model of profound hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation 50:109–115
Varma SD, Devamanoharan PS, Rutzen AR, Ali AH, Henein M (1999) Attenuation of galactose-induced cataract by pyruvate. Free Rad Res 30:253–263
Zhao W, Devamanoharan PS, Varma SD (2000) Fructose induced deactivation of antioxidant enzymes: preventive effect of pyruvate. Free Rad Res 33:23–30
Varma SD, Devamanoharan PS, Ali AH (1998) Prevention of intracellular oxidative stress to lens by pyruvate and its ester. Free Rad Res 28:131–135
Montgomery CM, Webb JL (1956) Metabolic studies on heart mitochondria. II. The inhibitory action of parapyruvate on the tricarboxylic acid cycle. J Biol Chem 221:359–368
Montgomery CM, Fairhurst AS, Webb JL (1956) Metabolic studies on heart mitochondria. III. The action of parapyruvate on a-ketoglutaric oxidase. J Biol Chem 221:369–376
Willems JL, de Kort AFM, Vree TB, Trijbels JMF, Veerkamp JH, Monnens LAH (1978) Non-enzymatic conversion of pyruvate in aqueous solution to 2,4-dihydroxy-2-methylglutaric acid. Febs Lett 86:42–44
Margolis SA, Coxon B (1986) Identification and quantitation of the impurities in sodium pyruvate. Anal Biochem 58:2504–2510
Sims CA, Wattanasirichaigoon S, Menconi MJ, Ajami AM, Fink MP (2001) Ringer's ethyl pyruvate solution ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal mucosal injury in rats. Crit Care Med 29:1513–1518
Yang R, Gallo DJ, Baust JJ, Uchiyama T, Watkins SK, Delude RL, Fink MP (2002) Ethyl pyruvate modulates inflammatory gene expression in mice subjected to hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283: G212-G22
Tawadrous ZS, Delude RL, Fink MP (2002) Resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock with Ringer's ethyl pyruvate solution improves survival and ameliorates intestinal mucosal hyperpermeability in rats. Shock 17:473–477
Venkataraman R, Kellum JA, Song M, Fink MP (2002) Resuscitation with Ringer's ethyl pyruvate solution prolongs survival and modulates plasma cytokine and nitrite/nitrate concentrations in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced shock. Shock 18: 507–512
Ulloa L, Ochani M, Yang H, Halperin D, Yang R, Czura CJ, Fink MP, Tracey KJ (2002) Ethyl pyruvate prevents lethality in mice with established lethal sepsis and systemic inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12351–12356
Wattanasirichaigoon S, Menconi MJ, Delude RL, Fink MP (1999) Effect of mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion or hemorrhagic shock on intestinal mucosal permeability and ATP content in rats. Shock 12:127–133
Sappington PL, Han X, Yang R, Delude RL, Fink MP (2003) Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in endotoxemic mice and immunostimulated Caco-2 enterocytic monolayers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:464–476
Mertz RJ, Worley JFI, Spencer B, Johnson JH, Dukes ID (1996) Activation of stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic b-cells by specific products of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem 271:4838–4845
Zawalich WS, Zawalich KC (1997) Influence of pyruvic acid methyl ester on rat pancreatic islets. Effects on insulin secretion, phosphoinositide hydrolysis, and sensitization of the beta cell. J Biol Chem 272:3527–3531
Lembert N, Joos HC, Idahl L-Å, Ammon HPT, Wahl MA (2001) Methyl pyruvate initiates membrane depolarization and insulin release by metabolic factors other than ATP. Biochem J 354:345–350
Fox ES, Cantrell CH, Leingang KA (2003) Inhibition of the Kupffer cell inflammatory response by acute ethanol: NF-kappa B activation and subsequent cytokine production. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 225:134–140
Jonsson AS, Palmblad JE (2001) Effects of ethanol on NF-kappaB activation, production of myeloid growth factors, and adhesive events in human endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 184:761–769
Roman J, Colell A, Blasco C, Caballeria J, Pares A, Rodes J, Fernandez-Checa JC (1999) Differential role of ethanol and acetaldehyde in the induction of oxidative stress in HEP G2 cells: effect on transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Hepatology 30:1473–1480
Boyd AJ, Sherman IA, Saibil FG (1994) Intestinal microcirculation and leukocyte behavior in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Microvasc Res 47:355–368
Han JY, Miura S, Akiba Y, Higuchi H, Kato S, Suzuki H, Yokoyama H, Ishii H (2001) Chronic ethanol consumption exacerbates microcirculatory damage in rat mesentery after reperfusion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280: G939-G948
Hu S, Sheng ZY (2002) The effects of anisodamine and dobutamine on gut mucosal blood flow during gut ischemia/ reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 8:555–557
Sato A, Kuwabara Y, Sugiura M, Seo Y, Fujii Y (1999) Intestinal energy metabolism during ischemia and reperfusion. J Surg Res 82:261–267
Almond NE, Wheatley AM (1992) Measurement of hepatic perfusion in rats by laser Doppler flowmetry. Am J Physiol 262: G203-G209
Yamagishi Y, Horie Y, Kato S, Kajihara M, Tamai H, Granger DN, Ishii H (2002) Ethanol modulates gut ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G640-G646
Rahat MA, Lahat N, Smollar J, Brod V, Kinarty A, Bitterman H (2001) Divergent effects of ischemia/reperfusion and nitric oxide donor on TNFalpha mRNA accumulation in rat organs. Shock 15:312–317
Mentzer RMJr, Van Wylen DG, Sodhi J, Weiss RJ, Lasley RD, Willis J, Bunger R, Flint LM (1989) Effect of pyruvate on regional ventricular function in normal and stunned myocardium. Ann Surg 209:629–633
Hermann HP, Zeitz O, Keweloh B, Hasenfuss G, Janssen PM (2000) Pyruvate potentiates inotropic effects of isoproterenol and Ca(2+) in rabbit cardiac muscle preparations. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279: H702-H708
Hermann HP, Pieske B, Schwarzmuller E, Keul J, Just H, Hasenfuss G (1999) Haemodynamic effects of intracoronary pyruvate in patients with congestive heart failure: an open study. Lancet 353:1321–1323
Acknowlegements
This study was made possible by a grant from DARPA (N65236-00-1-5434) and NIH grants GM58484 and GM37631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchiyama, T., Delude, R.L. & Fink, M.P. Dose-dependent effects of ethyl pyruvate in mice subjected to mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion. Intensive Care Med 29, 2050–2058 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1966-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1966-x