Abstract
Objective. To study the haemodynamic effects of a hypertonic saline/dextran solution compared with a normal saline solution in patients with severe sepsis.
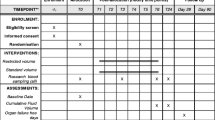
Design. Prospective double blind and control-randomised study.
Setting. Adult intensive care unit in a university hospital.
Patients. Twenty-nine patients with sepsis with a pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) lower than 12 mmHg.
Interventions. Patients were randomised to receive 250 ml of blinded solutions of either normal saline (SS group, n=16) or hypertonic saline (NaCl 7.5%)/dextran 70 8% (HSS group, n=13) solutions.
Measurements and results. Haemodynamic, blood gas, and sodium data were collected at the following time points: baseline, 30 min, 60 min, 120 min, and 180 min. PAOP was higher in the HSS group at 30 min (10.7±3.2 mmHg vs 6.8±3.2 mmHg) and 60 min (10.3±3 mmHg vs 7.4±2.9 mmHg); P<0.05. The cardiac index increased in the HSS group and it was greater than the SS group at 30 min (6.5±4.7 l min–1 m–2 vs 3.8±3.4 l min–1 m–2), 60 min (4.9±4.5 l min–1 m–2 vs 3.7±3.3 l min–1 m–2), and 120 min (5.0±4.3 l min–1 m–2 vs 4.1±3.4 l min–1 m–2); P<0.05. The stroke volume index followed a comparable course and it was higher at 30 min [53.6(39.2–62.8) ml m–2 vs 35.6(31.2–49.2) ml m–2] and 60 min [46.8(39.7–56.6) ml m–2 vs 33.9(32.2–47.7) ml m–2]; P<0.05. Systemic vascular resistance decreased in the HSS group and became significantly lower at 30 min (824±277 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2 vs 1139±245 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2), 60 min (921±256 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2 vs 1246±308 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2), and 120 min (925±226 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2 vs 1269±494 dyne s–1 cm–5 m–2). Sodium levels increased in the HSS group (P=0.056) and were higher than in the SS group at 30 min (145±3 mEq l–1 vs 137±7 mEq l–1), 60 min (143±4 mEq l–1 vs 136±7 mEq l–1), 120 (142±5 mEq l–1vs 136±7 mEq l–1), and 180 min (142±5 mEq l–1 vs 136±8 mEq l–1).
Conclusion. Hypertonic saline/dextran solution may improve cardiovascular performance in severe sepsis without significant side effects. The haemodynamic effect appears related mainly to a volume effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, .R., Weingartner, .R., Ribas, .E. et al. Acute haemodynamic effects of a hypertonic saline/dextran solution in stable patients with severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med 28, 1574–1581 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1509-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1509-x