Abstract
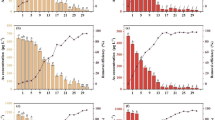
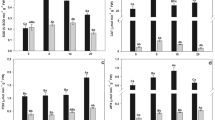
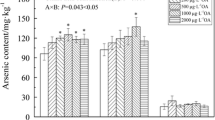
Influences of sulfur (S) on the accumulation and detoxification of arsenic (As) in Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara, an arsenic hyperaccumulating submerged aquatic plant, were investigated. At low sulfur levels (<20 mg/L), the thiols and As concentrations in the plant increased significantly with increasing sulfate nutrient supply. If sulfur levels were above 20 mg/L, the thiols and As concentrations in the plant did not increase further. There was a significant positive correlation between thiols and As in the plant. As(III) is the main form (>75%) present in the plant after exposure to As(V). Sulfur plays an important role in the arsenic translocation and detoxification, possibly through stimulating the synthesis of thiols and complexation of arsenite-phytochelatins. This suggests that addition of sulfur to the arsenic-contaminated water may provide a way to promote arsenic bioaccumulation in plants for phytoremediation of arsenic pollution.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleeker PM, Hakvoort HW, Bliek M, Souer E, Schat H (2006) Enhanced arsenate reduction by a CDC25-like tyrosine phosphatase explains increased phytochelatin accumulation in arsenate-tolerant Holcus lanatus. Plant J 45:917–929
Cai Y, Su J, Ma LQ (2004) Low molecular weight thiols in arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata upon exposure to arsenic and other trace elements. Environ Pollut 129:69–78
Chen G, Liu X, Brookes PC, Xu J (2015) Opportunities for phytoremediation and bioindication of arsenic contaminated water using a submerged aquatic plant: Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Int J Phytoremediation 17:249–255
Clemens S, Kim EJ, Neumann D, Schroeder JI (1999) Tolerance to toxic metals by a gene family of phytochelatin synthases from plants and yeast. Embo J 18:3325–3333
Delnomdedieu M, Basti MM, Otvos JD, Thomas DJ (1994) Reduction and binding of arsenate and dimethylarsinate by glutathione: a magnetic resonance study. Chem Biol Interact 90:139–155
Dhankher OP, Rosen BP, Mckinney EC, Meagher RB (2006) Hyperaccumulation of arsenic in the shoots of Arabidopsis silenced for arsenate reductase (ACR2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5413–5418
Dixit G, Singh AP, Kumar A, Singh PK, Kumar S, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Pandey V, Norton GJ, Dhankher OP, Tripathi RD (2015) Sulfur mediated reduction of arsenic toxicity involves efficient thiol metabolism and the antioxidant defense system in rice. J Hazard Mater 298:241–251
Favas PJC, Pratas J, Prasad MNV (2012) Accumulation of arsenic by aquatic plants in large-scale field conditions: opportunities for phytoremediation and bioindication. Sci Total Environ 433:390–397
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Vooijs RBW, Schat H (2001) Phytochelatins are involved in differential arsenate tolerance in Holcuslanatus. Plant Physiol 126:299–306
Hell R (1997) Molecular physiology of plant sulfur metabolism. Planta 202:138–148
Kärenlampi S, Schat H, Vangronsveld J, Verkleij JAC, Lelie DVD, Mergeay M, Tervahauta AI, Romantschuk M (2000) Genetic engineering in the improvement of plants for phytoremediation of metal polluted soils. Environ Pollut 107:225–231
Lafabrie C, Major KM, Major CS, Cebrian J (2011) Arsenic and mercury bioaccumulation in the aquatic plant, Vallisneria neotropicalis. Chemosphere 82:1393–1400
Liu WJ, Wood BA, Raab A, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Feldmann J (2010) Complexation of arsenite with phytochelatins reduces arsenite efflux and translocation from roots to shoots in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152:2211–2221
McMahon PJ, Anderson JW (1998) Preferential allocation of sulphur into y-glutamylcysteinyl peptides in wheat plants grown at low sulphur nutrition in the presence of cadmium. Physiol Plant 104:440–448
Mondal P, Majumder CB, Mohanty B (2006) Laboratory based approaches for arsenic remediation from contaminated water: recent developments. J Hazard Mater 137:464–479
Nordstrom DK (2002) Public health. Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 296:2143–2145
Oliveira LMD, Ma LQ, Santos JAG, Guilherme LRG, Lessl JT (2014) Effects of arsenate, chromate, and sulfate on arsenic and chromium uptake and translocation by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata (L.). Environ Pollut 184:187–192
Pickering IJ, Prince RC, George MJ, Smith RD, George GN, Salt DE (2000) Reduction and coordination of arsenic in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 122:1171–1177
Raab A, Schat H, Meharg AA, Feldmann J (2005) Uptake, translocation and transformation of arsenate and arsenite in sunflower (Helianthus annuus): formation of arsenic-phytochelatin complexes during exposure to high arsenic concentrations. New Phytol 168:551–558
Rama Devi S, Prasad MNV (1998) Copper toxicity in Ceratophyllum demersum L. (Coontail), a free floating macrophyte: response of antioxidant enzymes and antioxidants. Plant Sci 138:157–165
Saito K (2000) Regulation of sulfate transport and synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:188–195
Smith AH, Lopipero PA, Bates MN, Steinmaus CM (2002) Public health. Arsenic epidemiology and drinking water standards. Science 296:2145–2146
Srivastava S, Mishra S, Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Tandon PK (2007) Phytochelatins and Antioxidant systems respond differentially during arsenite and arsenate stress in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Technol 41:2930–2936
Wang J, Zhao FJ, Meharg AA, Raab A, Feldmann J, Mcgrath SP (2002) Mechanisms of arsenic hyperaccumulation in Pteris vittata. Uptake kinetics, interactions with phosphate, and arsenic speciation. Plant Physiol 130:1552–1561
Xia Y, Liu J (2004) An overview on chronic arsenism via drinking water in PR China. Toxicology 198:25–29
Xue P, Yan C (2011) Arsenic accumulation and translocation in the submerged macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Chemosphere 85:1176–1181
Yu Y, Guo Y, Zhang J, Xie J, Zhu Y, Yan J, Wang B, Li Z (2017) A perspective of chronic low exposure of arsenic on non-working women: risk of hypertension. Sci Total Environ 580:69–73
Zhang J, Zhao Q, Duan G, Huang Y (2011) Influence of sulphur on arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 72:34–40
Zhao FJ, Wang JR, Barker JHA, Schat H, Bleeker PM, Mcgrath SP (2003) The role of phytochelatins in arsenic tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. New Phytol 159:403–410
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41501343, 31671635, 31400374 and 51408214), Scientific Research Foundation of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Nos. 14B066 and 15C0534).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Feng, T., Li, Z. et al. Influence of Sulfur on the Arsenic Phytoremediation Using Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 411–414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2135-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2135-1