Abstract
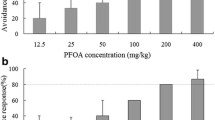
Contamination of soil with petroleum is common in oil-producing areas across the tropical regions of the world. There is limited knowledge on the sensitivity of endogeic tropical earthworms to the contamination of soil with total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) present in crude oil. Pontoscolex corethrurus is a dominant species in tropical agroecosystems around oil-processing facilities. The sensitivity of P. corethrurus to soil artificially contaminated with “Maya” Mexican heavy crude oil was investigated through avoidance and acute ecotoxicity tests, using the following measured concentrations: 0 (reference soil), 551, 969, 4845, 9991 and 14,869 mg/kg. The avoidance test showed that P. corethrurus displayed a significant avoidance behavior to heavy crude oil at a concentration of 9991 mg/kg or higher. In contrast, acute toxicity tests indicate that the median lethal concentration (LC50) was 3067.32 mg/kg; however, growth (weight loss) was more sensitive than mortality. Our study revealed that P. corethrurus is sensitive to TPH, thus highlighting the importance of P. corethrurus for petroleum ecotoxicological tests.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buch AC, Brown GG, Niva CC, Sautter KD, Lourençato LF (2011) Life cycle of Pontoscolex corethrurus (Muller, 1857) in tropical artificial soil. Pedobiologia 54S:S19–S25
Buch AC, Brown GG, Niva CC, Sautter KD, Sousa JP (2013) Toxicity of three pesticides commonly used in Brasil to Pontoscolex corethrurus (Müller, 1857) and Eisenia andrei (Bouché, 1972). Appl Soil Ecol 69:32–38
Buch AC, Schmelz RM, Niva CC, Fernandes CME, Silva-Filho EV (2017) Mercury critical concentrations to Enchytraeus crypticus (Annelida:Oligochaeta) under normal and extreme conditions of moisture in tropical soil- reproduction and survival. Environ Res 155:365–372
Ceccanti B, Masciandaro G, Garcia C, Macci C, Doni S (2006) Soil bioremediation: combination of erathworms and compost for ecological remediation of a hydrocarbon polluted soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 177:383–397
Cermak JH, Stephenson GL, Birkholz D, Wang Z, Dixon DG (2010) Toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon destillates to soil organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2685–2694
Da Silva PMCS, Van Gestel CAM (2009) Comparative sensitivity of Eisenia andrei and Perionyx excavatus in earthworm avoidance tests using soil types in the tropics. Chemosphere 77:1609–1613
Da Silva E, Nahmani J, Lapied E, Alphonse V, Garnier-Zarli E, Bousserrhine N (2016) Toxicity of mercury to the earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus in a tropical soil French Guiana. Appl Soil Ecol 104:79–84
Duarte AP, Melo VF, Brown GG, Pauletti V (2014) Earthworms (Pontoscolex corethrurus) survival and impacts on properties of soils from a lead mining site Southern Brazil. Biol Fertil Soils 50:851–860
Ekperusi OA, Aigbodion FI (2015) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons from crude oil-contaminated soil with the earthworm: Hyperiodrilus africanus. 3 Biotech 5:957–965
Fernández MD, Pro J, Alonso C, Aragonese P, Tarazona JV (2011) Terrestrial microcosms in a feasibility study on the remediation of diesel-contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:2133–2140
Fiedler S, Siebe C, Herre A, Roth B, Cram S, Stahr K (2009) Contribution of oil industry activities to environmental loads of heavy metal in the Tabasco lowlands, Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:35–47
García JA, Fragoso C (2003) Influence of different food substrates on growth and reproduction of two tropical earthworms species (Pontoscolex corethrurus and Amynthas corticis). Pedobiologia 47:754–763
García-Pérez JA, Alarcón-Gutiérrez E, Perroni Y, Barois I (2014) Earthworm communities and soil properties in shaded coffe plantations with and without application of glyphosate. Appl Soil Ecol 83:230–237
Geissen V, Gomez-Rivera P, Huerta E, Bello R, Trujillo A, Barba E (2008) Using earthworms to test the efficiency of remediation of oil-polluted soil in tropical Mexico. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 7:638–642
Gibbs MH, Wicker LF, Stewart AJ (1996) A method for assessing sublethal effects of contaminants in soils to the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:360–368
Gilman AP, Vardanis A (1974) Carbofuran: comparative toxicity and metabolism in the worms Lumbricus terrestris L. and Eiseni foetida S. J Agric Food Chem 22:625–628
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassay. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Hanna SHS, Weaver RW (2002) Earthworm survival in oil contaminated soil. Plant Soil 240:127–132
Hentati O, Lachhab R, Ayadi M, Ksibi M (2013) Toxicity assessment for petroleum-contaminated soil using terrestrial invertebrates and plant bioassays. Environ Monit Assess 185:2989–2998
Hernández-Castellanos B, Ortiz-Ceballos AI, Martínez-Hernández S, Noa-Carrazana JC, Luna-Guido M, Dendoveen L, Contreras-Ramos SM (2013) Removal of benzo(a)pyrene from using an endogeic earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Müller, 1857). Appl Soil Ecol 70:62–69
Hund-Rinke K, Wiechering H (2001) Earthworm avoidance test for soil assessments: An alternative for acute and reproduction test. J Soil Sedim 1:15–20
International Standard Organization (ISO) (2008) Soil quality-Avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour. ISO-17512-1:2008. Part 1: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei)
International Standard Organization (ISO) (2012) Soil quality-Effects of pollutants on earthworms. ISO-11268-1:2012 (2nd ed). Part 1: determination of acute toxicity to Eisenia fetida/ Eisenia Andrei
Jusselme MD, Poly F, Miambi E, Mora P, Blouin M, Pando A, Rouland-Lefèvre (2012) effect of earthworms on plant Lantana camara Pb-uptake and on bacterial communities in root-adhering soil. Sci Total Environ 416:200–207
Lavelle P, Barois I, Cruz I, Fragoso C, Hernández A, Pineda A, Rangel P (1987) Adaptive strategies of Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossscolecidae, Oligochaeta), a peregrine geophagous earthworm of the humid tropics. Biol Fertil Soils 5:188–194
Lowe CN, Butt KR (2007) Earthworm culture, maintenance and species selection in chronic ecotoxicological studies: a critical review. Eur J Soil Biol 43:S281–S288
Norton D (1996) Earthworm bioassay protocol for soil toxicity screening. Washington State Department of Ecology, Olympia. Publication No. 96–327
Oboh BO, Adeyinka Y, Awonuga A, Akinola MO (2007) Impact of soil types and petroleum effluents on the earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae. J Environ Biol 28:209–212
Ortiz-Ceballos AI, Pérez-Staples D, Pérez-Rodríguez P (2016) Nest site selection and nutritional provision through excreta: a form of parental care in a tropical endogeic earthworm. PeerJ 4:e2032. doi:10.7717/peerj.2032
Ortiz-Gamino D, Pérez-Rodríguez P, Ortiz-Ceballos AI (2016) Invasion of the tropical earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Rhinodrilidae, Oligochaeta) in temperate grasslands. PeerJ 4:e2572. doi:10.7717/peerj.2572
Patowary R, Patowary K, Devi A, Kalita MC, Deka S (2017) Uptake of total petroleum hydrocarbon (THP) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Oryza sativa L. grown in soil contaminated with crude oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:120–126
Pelosi C, Joimel S, Makowski D (2013) Searching for a more sensitive earthworm species to be used in pesticide homologation tests—A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 90:895–900
Pelosi C, Barot S, Capowiez, Hedde M, Vandenbulcke F (2014) Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:199–228
Plice MJ (1949) Some effects of crude petroleum on soil fertility. Soil Sci Soc Am J 13:413–416
Reinecke AJ, Maboeta MS, Vermeulen LA, Reinecke SA (2002) Assessment of lead nitrate and mancozeb toxicity in earthworms using the avoidance response. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:779–786
Schaefer M (2003) Behavioural endpoints in earthworm ecotoxicology. Evaluation of different test systems in soil toxicity assessment. J Soils Sedim 3:79–84
Schaefer M, Filser J (2007) The influence of earthworms and organic additives on the biodegradation of soil contaminated soil. Appl Soil Ecol 36:53–62
Schaefer M, Petersen SO, Filser J (2005) Effects of Lumbricus terrestris, Allolobophora chlorotica and Eisenia fetida on microbial community dynamics in oil-contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2065–2076
SEMARNAT (2006) Mexican Official Standard NMX-AA-134-SCFI-2006. Soils-Heavy fraction hydrocarbons by extraction and gravimetry. México
SEMARNAT (2013) Mexican Official Standard NOM-138-SEMANAT/SSA1-2012. Límites máximos permisibles de hidrocarburos en suelos y lineamientos para el muestreo en la caracterización y expecificaciones para la remediación. México
Tang J, Wang M, Wang F, Sun Q, Zhou Q (2011) Eco-toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. J Environ Sci 23:845–851
Trejo-Hernández MR, Ortiz A, Okoh AI, Morales D, Quintero (2007) Biodegradation of heavy crude oil Maya using spent compost and sugar cane bagasse wastes. Chemosphere 68:848–855
Vermeulen LA, Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA (2001) Evaluation of the fungicide manganese-zinc ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) (Mancozeb) for sublethal and acute toxicity to Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:183–189
Villalobos M, Avila-Forcada P, Gutierrez-Ruiz ME (2008) An improved gravimetric method to determine petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 194:151–161
Xie X, Qian Y, Wu Y, Yin J, Zhai J (2013) Effects decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) on avoidance response, survival, growth and reproduction of earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 90:21–27
Yasu T, Toyota F, Hiroaki KS (2005) Enhanced bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil by a combination of the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) and Tea extraction residue. Edaphologia 77:1–9
Yeardley RB, Lazorchak JM, Gast LC (1996) The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1532–1537
Zavala-Cruz J, Trujillo-Capistrán F, Ortiz-Ceballos G, Ortiz-Ceballos AI (2013) Tropical endogeic earthworm population in a pollution gradient with weathered crude oil. Res J Environ Sci 7:15–26
Zhang L, Liu X, You L, Zhou D, Wang Q, Li F et al (2011) Benzo(a)pyrene-induced metabolic responses in Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (H1 NMR) based metabolomics. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32:218–225
Acknowledgements
We thank Rafael Ramos Morales for helpful discussion and Alejandro Castro-Luna for support in the statistical analysis. This research work was provided by the PRODEP-SEP (CA-UVER-173 and CA-UVER-332) and Mexican CONACYT (CB-2007-01/83600). We also two anonymous reviewers for valuable comments and careful revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
del Carmen Cuevas-Díaz, M., Vázquez-Luna, D., Martínez-Hernández, S. et al. Sensitivity of the Endogeic Tropical Earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus to the Presence of Heavy Crude Oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 154–160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2126-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2126-2