Abstract
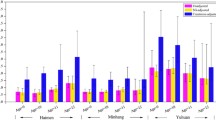
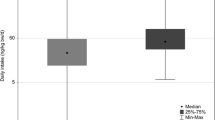
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disrupting environmental chemical. Urinary concentrations of BPA were measured in samples collected nationwide from Chinese young adults. The geometric mean urinary concentration of BPA in Chinese young adults was 2.23 ng/mL. The estimated daily exposure dose for BPA was 64.8 ng/kg bw/day. Contributions of various BPA sources to exposure in Chinese young adults were estimated. Dietary intake was the primary exposure pathway. The contribution of dietary intake, indoor dust, paper products and personal care products to BPA intake was 72.5 %, 0.74 %, 0.98 %, 0.22 % of the total exposure dose, respectively. This is the first study on the occurrence of BPA in young adults from most provinces and autonomous regions of China. The results can be used to establish a database for BPA exposure assessment for Chinese general population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battal D, Cok I, Unlusayin I, Aktas A, Tunctan B (2014) Determination of urinary levels of Bisphenol A in a Turkish population. Environ Monit Assess 186:8443–8452
Becker K, Güen T, Seiwert M, Conrad A, Pick-Fuß H, Müller J et al (2009) GerES IV: phthalate metabolites and bisphenol A in urine of German children. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:685–692
Biedermann S, Tschudin P, Grob K (2010) Transfer of bisphenol A from thermal printer paper to the skin. Anal Bioana Chem 398(1):571–576
Bushnik T, Haines D, Levallois P, Levesque J, Van Oostdam J, Viau C (2010) Lead and bisphenol A concentrations in the Canadian population. Health Rep 21(3):7–18
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong L-Y, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Exposure of the US population to Bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-Octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116(1):39–44
Cao XL, Perez-Locas C, Dufresne G, Clement G, Popovic S, Beraldin F et al (2011) Concentrations of bisphenol A in the composite food samples from the 2008 Canadian total diet study in Quebec City and dietary intake estimates. Food Addit Contam 28:791–798
Chen M, Zhu P, Xu B, Zhao R, Qiao S, Chen X et al (2012) Determination of nine environmental phenols in urine by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 36:608–615
Christensen K, Lorber M, Koslitz S, Brüning T, Koch H (2012) The contribution of diet to total bisphenol A body burden in humans: results of a 48 hour fasting study. Environ Int 50:7–14
EFSA (Europe Food Safety Authority) (2006) Opinion of the scientific panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane. EFSA 428:1–75
Fan R, Zeng B, Liu X, Chen C, Zhuang Q, Wang Y et al (2015) Levels of bisphenol-A in different paper products in Guangzhou, China, and assessment of human exposure via dermal contact. Environ Sci Process Impacts 17:667–673
Frederiksen H, Jensen TK, Jørgensen N, Kyhl HB, Husby S, Skakkebæk NE et al (2014) Human urinary excretion of non-persistent environmental chemicals: an overview of Danish data collected between 2006 and 2012. Reproduction 147:555–565
Galloway T, Cipelli R, Guralnik J, Ferrucci L, Bandinelli S, Corsi AM et al (2010) Daily bisphenol A excretion and associations with sex hormone concentrations: results from the InCHIANTI adult population study. Environ Health Perspect 118:1603–1608
Geens T, Apelbaum TZ, Goeyens L, Neels H, Covaci A (2010) Intake of bisphenol A from canned beverages and foods on the Belgian market. Food Addit Contam 27:1627–1637
Geens T, Goeyens L, Kannan K, Neels H, Covaci A (2012) Levels of bisphenol-A in thermal paper receipts from Belgium and estimation of human exposure. Sci Total Environ 435:30–33
Goldinger DM, Demierre AL, Zoller O, Rupp H, Reinhard H, Magnin R et al (2015) Endocrine activity of alternatives to BPA found in thermal paper in Switzerland. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 71(3):453–462
Guo Y, Alomirah H, Cho H-S, Minh TB, Mohd MA, Nakata H et al (2011) Occurrence of phthalate metabolites in human urine from several Asian countries. Environ Sci Technol 45:3138–3144
GVR (Grand View Research) (2014) Global bisphenol A (BPA) market by application (appliances, automotive, consumer, construction, electrical and electronics) expected to reach USD 20.03 billion by 2020. http://www.digitaljournal.com/pr/2009287
Hong Y-C, Park E-Y, Park M-S, Ko JA, Oh S-Y, Kim H et al (2009) Community level exposure to chemicals and oxidative stress in adult population. Toxicol Lett 184:139–144
Hormann AM, vom Saal FS, Nagel SC, Stahlhut RW, Moyer CL, Ellersieck MR et al (2014) Holding thermal receipt paper and eating food after using hand sanitizer results in high serum bioactive and urine total levels of bisphenol A (BPA). PLoS One 9:e110509
Koch HM, Aylward LL, Hays SM, Smolders R, Moos RK, Cocker J et al (2014) Inter-and intra-individual variation in urinary biomarker concentrations over a 6-day sampling period. Part 2: personal care product ingredients. Toxicol Lett 231:261–269
Lassen TH, Frederiksen H, Jensen TK, Petersen JH, Joensen UN, Main KM et al (2014) Urinary bisphenol A levels in young men: association with reproductive hormones and semen quality. Environ Health Perspect 122:478
Li X, Ying G-G, Zhao J-L, Chen Z-F, Lai H-J, Su H-C (2013) 4-Nonylphenol, bisphenol-A and triclosan levels in human urine of children and students in China, and the effects of drinking these bottled materials on the levels. Environ Int 52:81–86
Liao C, Kannan K (2011a) High levels of bisphenol A in paper currencies from several countries, and implications for dermal exposure. Environ Sci Technol 45:6761–6768
Liao C, Kannan K (2011b) Widespread occurrence of bisphenol A in paper and paper products: implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 45:9372–9379
Liao C, Kannan K (2013) Concentrations and profiles of bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues in foodstuffs from the United States and their implications for human exposure. J Agric Food chem 61:4655–4662
Liao C, Kannan K (2014a) A survey of alkylphenols, bisphenols, and triclosan in personal care products from China and the United States. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67:50–59
Liao C, Kannan K (2014b) A survey of bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues in foodstuffs from nine cities in China. Food Addit Contam 31:319–329
Liao C, Liu F, Guo Y, Moon H-B, Nakata H, Wu Q et al (2012) Occurrence of eight bisphenol analogues in indoor dust from the United States and several Asian countries: implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 46:9138–9145
Loganathan SN, Kannan K (2011) Occurrence of bisphenol A in indoor dust from two locations in the eastern United States and implications for human exposures. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61:68–73
Ma W-L, Wang L, Guo Y, Liu L-Y, Qi H, Zhu N-Z et al (2013) Urinary concentrations of parabens in Chinese young adults: implications for human exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:611–618
Ma W-L, Subedi B, Kannan K (2014) The occurrence of bisphenol A, phthalates, parabens and other environmental phenolic compounds in house dust: a review. Curr Org Chem 18:2182–2199
Mendum T, Stoler E, VanBenschoten H, Warner JC (2011) Concentration of bisphenol A in thermal paper. Green Chem Lett Rev 4:81–86
Mielke H, Partosch F, Gundert-Remy U (2011) The contribution of dermal exposure to the internal exposure of bisphenol A in man. Toxicol Lett 204(2–3):190–198
Munguia-Lopez E, Gerardo-Lugo S, Peralta E, Bolumen S, Soto-Valdez H (2005) Migration of bisphenol A (BPA) from can coatings into a fatty-food simulant and tuna fish. Food Addit Contam 22:892–898
Niu Y, Zhang J, Duan H, Wu Y, Shao B (2015) Bisphenol A and nonylphenol in foodstuffs: Chinese dietary exposure from the 2007 total diet study and infant health risk from formulas. Food Chem 167:320–325
Noonan GO, Ackerman LK, Begley TH (2011) Concentration of bisphenol A in highly consumed canned foods on the US market. J Agric Food Chem 59:7178–7185
Perucca J, Bouby N, Valeix P, Bankir L (2007) Sex difference in urine concentration across differing ages, sodium intake, and level of kidney disease. Am J Physiol Reg Integr Comp Physiol 292:R700–R705
Porras SP, Heinälä M, Santonen T (2014) Bisphenol A exposure via thermal paper receipts. Toxicol Lett 230(3):413–420
Rochester JR (2013) Bisphenol A and human health: a review of the literature. Reprod Toxicol 42:132–155
Samanidou V, Livadiotou D, Palaghias G, Papadoyannis I (2015) A simple and rapid HPLC method for the direct determination of residual monomers released from dental polymeric materials in blood serum and urine. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 38:201–207
Sioen I, Hond ED, Nelen V, Mieroop EV, Larebeke NV, Schoeters G (2012) Vlaams humaan biomonitoringsprogramma 2007–2011. CLB 3:1
Tsai W-T (2006) Human health risk on environmental exposure to bisphenol-A: a review. J Environ Sci Health Part C 24:225–255
U.S. EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2007) Bisphenol A, Integrated risk information system. http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0356.htm
Yang Y, Guan J, Yin J, Shao B, Li H (2014) Urinary levels of bisphenol analogues in residents living near a manufacturing plant in south China. Chemosphere 112:481–486
Zalko D, Jacques C, Duplan H, Bruel S, Perdu E (2011) Viable skin efficiently absorbs and metabolizes bisphenol A. Chemosphere 82(3):424–430
Zhang Z, Alomirah H, Cho H-S, Li Y-F, Liao C, Minh TB et al (2011) Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and their implications for human exposure in several Asian countries. Environ Sci Technol 45:7044–7050
Zhang T, Sun H, Kannan K (2013) Blood and urinary bisphenol A concentrations in children, adults, and pregnant women from china: partitioning between blood and urine and maternal and fetal cord blood. Environ Sci Technol 47:4686–4694
Acknowledgments
We thank all the volunteers for providing urine samples. This study was funded by a Grant (1U38EH000464-01) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, GA). Samples were analyzed at Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21277038). This study was partly supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. HIT. NSRIF. 2014095) and Independent Research from State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (No. 2013DX15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C., Liu, L., Ma, W. et al. Bisphenol A in Urine of Chinese Young Adults: Concentrations and Sources of Exposure. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 162–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1703-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1703-5